What it is
An oophorectomy is a surgical procedure to remove one or both ovaries, the organs responsible for releasing eggs and producing female hormones like estrogen and progesterone. It may be performed as a standalone surgery or alongside other gynecological procedures such as hysterectomy or salpingectomy.
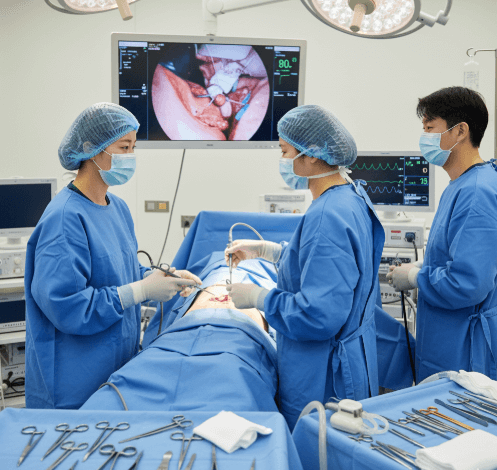
In Korea, oophorectomy is performed with advanced laparoscopic and robotic-assisted techniques, ensuring precision, reduced pain, and faster recovery. The procedure may be unilateral (one ovary removed) or bilateral (both ovaries removed).
➡️ Key points about oophorectomy:
- Unilateral oophorectomy: One ovary removed, preserving fertility and hormonal function from the remaining ovary
- Bilateral oophorectomy: Both ovaries removed, causing immediate menopause and infertility
- Can be done for medical, preventive, or emergency reasons
Why it’s done
Doctors recommend oophorectomy for several medical and preventive reasons.
✔️ Medical reasons include:
- Ovarian cancer or suspicion of malignancy
- Large or persistent ovarian cysts causing pain or risk of rupture
- Endometriosis involving the ovaries
- Ovarian torsion (twisting of the ovary, cutting off blood supply)
- Severe pelvic infections not responding to treatment
✔️ Preventive reasons include:
- Women with BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations to reduce risk of ovarian and breast cancer
- Family history of ovarian cancer
✔️ Benefits of oophorectomy:
- Eliminates cancerous or high-risk ovarian tissue
- Relieves pain and complications from cysts or torsion
- Prevents life-threatening conditions linked to ovarian disease
Alternatives
Oophorectomy is a major decision, especially for younger women. Alternatives may be explored depending on the condition.
🔹 Cystectomy:
- Removing only the cyst while preserving the ovary
- Preferred for women who wish to maintain fertility
🔹 Hormonal therapy:
- Used to control endometriosis or ovarian cyst growth
- Not suitable for cancer or severe conditions
🔹 Surveillance:
- Regular ultrasounds and blood tests for small, benign cysts or non-urgent cases
🔹 Hysterectomy with ovarian preservation:
- Uterus removed but ovaries left intact to maintain hormonal function
Preparation
Proper preparation helps ensure safe surgery and better recovery.
➡️ Medical preparation:
- Ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans to assess ovary size and condition
- Blood tests including tumor markers (like CA-125) for cancer risk evaluation
- General health screening before anesthesia
- Fertility counseling if only one ovary is to be preserved
➡️ Personal preparation:
- Fasting before surgery if general anesthesia is planned
- Packing hospital essentials for a short stay (1–3 days typical)
- Arranging support at home during initial recovery period
➡️ Mental preparation:
- Understanding effects of unilateral vs. bilateral removal
- Counseling on immediate menopause symptoms if both ovaries are removed
- Preparing emotionally for fertility changes and hormonal impact
How it’s done
In Korea, oophorectomy is usually performed using laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery for safety and precision.
✔️ Surgical approaches:
➡️ Laparoscopic oophorectomy
- Small incisions in the abdomen for camera and instruments
- Ovary carefully removed with minimal tissue damage
- Faster recovery and minimal scarring
➡️ Robotic-assisted oophorectomy
- Surgeon controls robotic arms for enhanced precision
- Ideal for complex cases, especially with cancer risk
- Reduces pain, scarring, and hospital stay
➡️ Open (abdominal) oophorectomy
- Larger incision used in emergencies or very large tumors
- Longer recovery but sometimes necessary
✔️ Step-by-step procedure:
- Anesthesia (general) administered
- Small abdominal incisions made for laparoscope or robotic instruments
- Ovary detached from surrounding ligaments and blood supply
- Ovary removed and sent for pathology testing
- Surrounding organs checked for abnormalities
- Incisions closed with sutures or surgical glue
✔️ Duration:
- Surgery typically lasts 1–2 hours
- Hospital stay: same-day or 1–3 days for minimally invasive methods, longer for open surgery
Recovery
Recovery depends on whether the procedure was unilateral or bilateral, and the surgical method used.
➡️ Immediate recovery:
- Mild abdominal pain, bloating, or fatigue from anesthesia
- Encouraged to walk within hours to prevent blood clots
- Hospital monitoring for infection, bleeding, or complications
➡️ Physical recovery:
- Return to light activities in 1–2 weeks for laparoscopic/robotic procedures
- 4–6 weeks for open abdominal surgery
- Hormonal replacement therapy (HRT) may be prescribed if both ovaries are removed
➡️ Emotional recovery:
- Relief from pain and risks of ovarian disease
- Emotional adjustment needed if fertility or hormonal function is affected
- Counseling and support groups available in Korean hospitals
➡️ Key recommendations:
- Adequate rest and proper wound care
- Balanced nutrition to support healing and hormone balance
- Regular follow-up with gynecologist
- Hormonal therapy discussions if menopause symptoms appear
Treatment option in Korea
Korea is globally recognized for its advanced gynecologic surgery and fertility-preserving care, making it an excellent destination for oophorectomy.
✔️ Hospital facilities:
- Equipped with cutting-edge laparoscopic and robotic surgical systems
- Specialized women’s hospitals with oncology and fertility programs
- Comprehensive pre- and post-operative monitoring systems
✔️ Medical expertise:
- Skilled surgeons with high success rates in minimally invasive oophorectomy
- Personalized surgical planning based on patient’s age, fertility goals, and cancer risk
- Integration of Western medical protocols with Korean recovery practices
✔️ Postoperative care:
- Hormone replacement therapy programs for women entering surgical menopause
- Fertility counseling for women retaining one ovary
- Holistic recovery support, including nutrition and stress management
✔️ Cultural aspect:
- Korean healthcare strongly emphasizes fertility preservation and quality of life
- Families often provide strong support during recovery
- Access to Sanhujoriwon-style recovery centers ensures rest, nutrition, and holistic healing
➡️ Highlight: Oophorectomy in Korea provides world-class surgical precision, fertility-conscious approaches, and holistic recovery programs, making it one of the safest and most supportive options for women facing ovarian conditions.