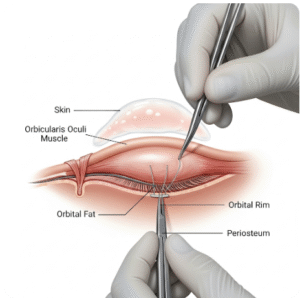
What it is
Diagnostic laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to examine the organs inside the abdomen and pelvis. A thin tube with a camera (laparoscope) is inserted through a small incision, allowing doctors to see conditions that may not appear clearly on imaging tests like ultrasound, CT, or MRI.
In Korea, diagnostic laparoscopy is widely used in gynecology and general medicine. It offers highly accurate visualization of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and other pelvic organs, helping doctors diagnose causes of pelvic pain, infertility, or unexplained symptoms.
➡️ Key points about diagnostic laparoscopy:
- Provides direct visualization of pelvic and abdominal organs
- Minimally invasive with small incisions and quick recovery
- Can transition from diagnosis to treatment during the same procedure if needed
Why it’s done
Diagnostic laparoscopy is performed when noninvasive tests cannot provide clear answers.
✔️ Gynecologic reasons include:
- Unexplained infertility (checking fallopian tube patency, endometriosis, adhesions)
- Chronic pelvic pain without clear cause on imaging
- Suspected endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory disease
- Evaluation of ovarian cysts, fibroids, or pelvic masses
✔️ General medical reasons include:
- Unexplained abdominal pain
- Suspected appendicitis, liver disease, or abdominal tumors
- Checking for cancer spread (staging procedure)
✔️ Benefits:
- Provides accurate diagnosis that imaging may miss
- Minimally invasive, reducing recovery time compared to open surgery
- Can immediately treat findings (e.g., remove adhesions or cysts) during the same procedure
Alternatives
While diagnostic laparoscopy is highly accurate, alternatives may be considered first.
🔹 Imaging tests:
- Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI for noninvasive assessment
- Useful for larger abnormalities but may miss small lesions or adhesions
🔹 Hysterosalpingography (HSG):
- X-ray test using contrast dye to check fallopian tube blockage
- Less invasive but provides limited information
🔹 Blood tests and clinical evaluation:
- Can suggest infections, cancer, or hormonal imbalances
- Do not provide direct visualization
🔹 Exploratory laparotomy (open surgery):
- Rarely done today, replaced by minimally invasive laparoscopy
Preparation
Preparation ensures accurate results and patient safety.
➡️ Medical preparation:
- Preoperative imaging and blood tests
- Pregnancy test in reproductive-age women
- Consultation about medical history and anesthesia risks
➡️ Personal preparation:
- Fasting for 6–8 hours before surgery if general anesthesia will be used
- Packing essentials for a short hospital stay (often same-day discharge)
- Arranging transportation after procedure due to anesthesia effects
➡️ Mental preparation:
- Understanding that this is both a diagnostic and potentially therapeutic procedure
- Preparing emotionally for possible discovery of unexpected conditions
- Reassurance about minimal scarring and quick recovery
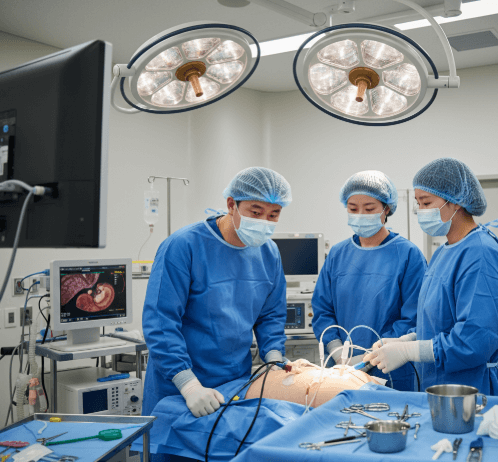
How it’s done
Diagnostic laparoscopy in Korea is performed with cutting-edge technology and skilled surgical teams.
✔️ Step 1 – Anesthesia
- General anesthesia is commonly used for patient comfort
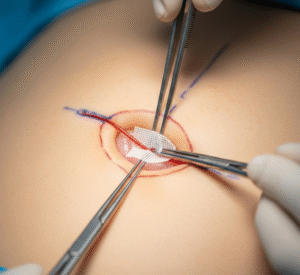
✔️ Step 2 – Creating access
- A small incision (about 1 cm) made near the navel
- Carbon dioxide gas introduced to inflate the abdomen for better visibility
✔️ Step 3 – Inserting the laparoscope
- A laparoscope (camera-equipped tube) inserted through the incision
- Images projected on a monitor for detailed examination
✔️ Step 4 – Examination
- Organs like the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, appendix, liver, and intestines are checked
- If abnormalities are found, small instruments may be inserted through additional incisions for biopsy or minor treatment
✔️ Step 5 – Completion
- Instruments removed, gas released, and incision closed with sutures or glue
✔️ Duration:
- Procedure typically lasts 30–90 minutes depending on findings
- Many patients discharged the same day
Recovery
Recovery is generally quick, especially with Korea’s minimally invasive techniques.
➡️ Immediate recovery:
- Mild abdominal discomfort, bloating, or shoulder pain (from CO₂ gas)
- Drowsiness or fatigue from anesthesia
- Monitoring in hospital for a few hours
➡️ Physical recovery:
- Return to normal activities in 1–2 weeks
- Avoiding strenuous exercise and heavy lifting for at least 1 week
- Follow-up appointment to discuss results and next steps
➡️ Emotional recovery:
- Relief from finally having a clear diagnosis
- Anxiety may occur if unexpected conditions are discovered, but Korean hospitals provide counseling and supportive care
➡️ Key recommendations:
- Adequate rest and hydration after surgery
- Pain management with simple medications if needed
- Attending follow-up visits to review biopsy results or treatment plans
Treatment option in Korea
Korea offers some of the best diagnostic laparoscopy services in the world, combining medical expertise, advanced technology, and patient-centered care.
✔️ Hospital facilities:
- Equipped with high-definition laparoscopic and robotic systems
- Specialized women’s hospitals for gynecologic laparoscopy
- On-site pathology labs for rapid biopsy results
✔️ Medical expertise:
- Highly experienced surgeons trained in both diagnostic and therapeutic laparoscopy
- Ability to switch from diagnostic to treatment (e.g., removing cysts or adhesions) in one session
- High success rates with low complication risks
✔️ Postoperative care:
- Comprehensive follow-up to discuss results and treatment options
- Fertility counseling for women diagnosed with tubal or endometriosis issues
- Holistic recovery care including nutrition and stress management
✔️ Cultural aspect:
- Korea places strong emphasis on fertility preservation, accurate diagnosis, and long-term health
- Families and hospital systems support women through both physical and emotional aspects of care
➡️ Highlight: Diagnostic laparoscopy in Korea provides precise diagnosis, fertility-focused care, and world-class medical expertise, making it an excellent choice for women seeking answers to complex pelvic or abdominal conditions.