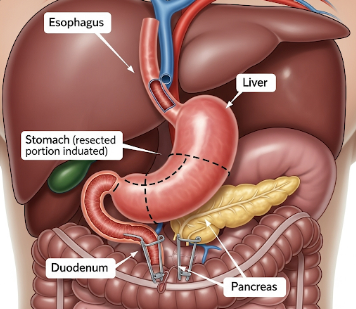
What is a Gastrectomy?
A gastrectomy is a surgical procedure to remove part or all of the stomach. It is performed to treat stomach cancer, severe ulcers, benign tumors, or other gastric disorders.
💡 Types of Gastrectomy:
✔️ Partial Gastrectomy – Only the diseased portion of the stomach is removed; remaining stomach is reconnected to the digestive tract
✔️ Total Gastrectomy – Entire stomach is removed; esophagus is connected directly to the small intestine
✔️ Sleeve Gastrectomy – Often used for weight-loss surgery; reduces stomach size while maintaining continuity
✔️ Distal or Proximal Gastrectomy – Based on which part of the stomach is affected
Purpose:
➡️ Remove diseased or cancerous tissue
➡️ Relieve symptoms such as bleeding, obstruction, or pain
➡️ Restore digestive function with surgical reconstruction
In Korea, gastrectomy is performed in tertiary hospitals and specialized cancer centers, with laparoscopic and robotic approaches increasingly used for minimally invasive surgery.
Why It’s Done
Gastrectomy is indicated for conditions that threaten health or cause severe symptoms.
✔️ Stomach cancer – Most common indication for gastrectomy
✔️ Severe peptic ulcer disease – Complicated ulcers not responding to medical therapy
✔️ Benign tumors or polyps – Prevent growth or bleeding
✔️ Obstruction or perforation – Due to tumor, ulcer, or trauma
✔️ Weight-loss surgery (bariatric indication) – Sleeve gastrectomy or subtotal gastrectomy
Clinical Benefits:
➡️ Removes malignant or diseased tissue → Life-saving for cancer patients
➡️ Alleviates symptoms → Pain, nausea, vomiting, bleeding
➡️ Improves quality of life → Reduces risk of complications from ulcers or tumors
➡️ Potential weight loss → For obese patients undergoing sleeve gastrectomy
In Korea, patients undergo diagnostic imaging, endoscopy, and biopsy prior to surgery to determine the exact need and extent of gastrectomy.
Alternatives
Depending on the condition, alternatives may be considered:
⭐ Endoscopic resection – Removal of small tumors or polyps without full surgery
⭐ Medications – Proton pump inhibitors, antibiotics for H. pylori, or chemotherapy for early-stage cancers
⭐ Lifestyle modifications – Dietary adjustments to reduce ulcer symptoms
⭐ Palliative care – For inoperable cancer to relieve symptoms
👉 Key Point: Gastrectomy is the definitive treatment for severe gastric disease, while alternatives may be suitable for early-stage conditions or palliative purposes.
Preparation
Preparation is critical for surgical success and recovery:
🔹 Comprehensive medical assessment – Blood tests, liver and kidney function, ECG, chest X-ray, and imaging studies
🔹 Endoscopy and biopsy – Confirm diagnosis and tumor extent
🔹 Medication review – Adjust anticoagulants, diabetes medications, or other chronic drugs
🔹 Nutritional optimization – Correct anemia, vitamin deficiencies, and protein levels
🔹 Fasting instructions – Usually 8–12 hours before surgery
🔹 Informed consent – Discuss procedure, risks, alternatives, and long-term dietary changes
⭐ Arrange support at home – Assistance with meals and daily activities post-surgery
⭐ Psychological preparation – Counseling to cope with lifestyle and dietary changes
How It’s Done
Gastrectomy can be performed via open surgery, laparoscopic, or robotic-assisted techniques:
- Open Gastrectomy
✔️ Large abdominal incision made for access
✔️ Diseased stomach portion removed
✔️ Reconstruction connects esophagus to remaining stomach or small intestine - Laparoscopic Gastrectomy
🔹 Small abdominal incisions used
🔹 Camera and instruments guide tissue removal
🔹 Reconstructive anastomosis performed with minimal invasiveness - Robotic-Assisted Gastrectomy
➡️ Surgeon controls robotic instruments with precision
➡️ Enhanced visualization, dexterity, and minimally invasive approach
Highlights:
✔️ Surgery duration – 2–5 hours depending on type
✔️ Anesthesia – General anesthesia
✔️ Hospital stay – Laparoscopic: 5–10 days; Open: 10–14 days
Recovery / Follow-up
Recovery from gastrectomy requires careful monitoring and gradual dietary adjustments:
✔️ Immediate post-op care – ICU or high-dependency monitoring in complex cases
✔️ Pain management – Analgesics and regional blocks
✔️ Dietary progression – Start with liquids, progress to soft foods, then normal diet
✔️ Physical activity – Light movement encouraged; avoid heavy lifting for 6–8 weeks
✔️ Follow-up appointments – Monitor wound healing, weight, digestion, and nutritional status
✔️ Vitamin and mineral supplementation – Especially after total gastrectomy
⭐ Long-term monitoring includes screening for recurrence in cancer patients and management of digestive adaptation
Complications / Risks
Gastrectomy carries potential risks, which vary with surgical type and patient condition:
⚠️ Surgical site infection – Mild to severe
⚠️ Bleeding – May require transfusion
⚠️ Anastomotic leak – Rare but serious complication at reconnection site
⚠️ Digestive issues – Dumping syndrome, diarrhea, or malabsorption
⚠️ Nutritional deficiencies – Vitamin B12, iron, calcium
⚠️ Delayed gastric emptying – Temporary or persistent
⚠️ Anesthesia-related complications – Allergic reactions, cardiovascular events, or respiratory issues
➡️ In Korea, high-volume surgical centers, laparoscopic and robotic technology, and multidisciplinary care significantly reduce complications.
Treatment Options / Gastrectomy in Korea
Korea offers advanced gastrectomy services, especially for cancer care and bariatric surgery:
🏥 Laparoscopic Gastrectomy – Minimally invasive, faster recovery, less pain
🏥 Open Gastrectomy – For complex tumors or prior surgeries
🏥 Robotic Gastrectomy – Enhanced precision and reduced complications
🏥 Pre- and Post-operative Counseling – Nutritional guidance, psychological support, and lifestyle advice
🏥 Follow-up Programs – Cancer recurrence monitoring, dietary adaptation, and rehabilitation
Why Korea is a Preferred Destination:
✔️ Expert surgeons – Highly trained in gastrectomy and minimally invasive techniques
✔️ Advanced equipment – Laparoscopic and robotic systems for precision
✔️ Comprehensive hospital care – Pre-op evaluation, surgery, and post-op recovery support
✔️ High success rates – Excellent patient outcomes with low complications
✔️ Accessible and affordable – Efficient care with short hospital stay
Approximate Costs in Korea:
🔹 Laparoscopic Gastrectomy → $6,000 – $12,000
🔹 Open Gastrectomy → $8,000 – $15,000
🔹 Robotic Gastrectomy → $10,000 – $18,000
🔹 Hospital stay (per day) → $200 – $500
🔹 Consultation and follow-up → $50 – $150
Conclusion
Gastrectomy is a life-saving and definitive procedure for severe stomach diseases, including cancer and complicated ulcers.
It helps patients:
✔️ Remove diseased or cancerous tissue
✔️ Alleviate pain, bleeding, and obstruction
✔️ Restore digestive function and improve quality of life
✔️ Prevent severe complications and recurrence
In Korea, patients benefit from:
✔️ Advanced laparoscopic and robotic techniques for minimally invasive surgery
✔️ Expert multidisciplinary surgical teams
✔️ Comprehensive pre- and post-operative care
✔️ Short hospital stay and fast recovery
👉 Key Message: Gastrectomy in Korea provides modern, safe, and effective care, allowing patients to recover quickly while ensuring optimal surgical outcomes and long-term health.