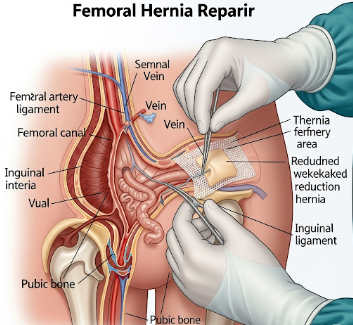
What is a Femoral Hernia Repair?
A femoral hernia occurs when tissue, usually intestine or fat, pushes through a weak spot in the femoral canal—located just below the groin crease. This type of hernia is less common than inguinal hernia, but it has a higher risk of complications like strangulation or obstruction, making repair important.
Femoral hernia repair is a surgical procedure to reposition herniated tissue and strengthen the weakened area to prevent recurrence.
💡 Types of Femoral Hernia Repair:
✔️ Open Surgical Repair – Incision made in the groin; hernia reduced, and the femoral canal is reinforced with sutures or mesh.
✔️ Laparoscopic Repair – Minimally invasive, uses small abdominal incisions, mesh placement, and laparoscope guidance.
✔️ Mesh Repair vs. Suture Repair – Mesh is often preferred for lower recurrence risk; suture repair may be used in selected cases.
In Korea, femoral hernia repair is performed in specialized general surgery departments, using state-of-the-art laparoscopic techniques for faster recovery and reduced complications.
Why It’s Done
Femoral hernia repair is indicated to prevent serious complications and restore normal anatomy.
✔️ Prevent incarceration – When hernia tissue becomes trapped, causing pain and obstruction
✔️ Prevent strangulation – Blood supply to herniated tissue may be compromised, leading to tissue death
✔️ Relieve discomfort – Groin swelling, pain, and heaviness
✔️ Reduce recurrence – Surgical reinforcement prevents future hernia formation
Clinical Benefits:
➡️ Safe and definitive treatment → Eliminates hernia and reduces emergency surgery risk
➡️ Symptom relief → Pain, swelling, and discomfort improve
➡️ Low recurrence rates → Especially with mesh repair
➡️ Improved quality of life → Patients resume normal activities safely
In Korea, early surgical intervention is recommended, particularly for women and elderly patients, as femoral hernias are more likely to incarcerate.
Alternatives
While surgery is the standard of care, alternatives or temporary measures include:
⭐ Watchful waiting – Only for small, asymptomatic hernias with close monitoring
⭐ Truss or supportive garments – External support to reduce hernia protrusion; not definitive
⭐ Lifestyle modifications – Avoid heavy lifting, maintain healthy weight, and manage constipation
⭐ Pain management – Analgesics for symptomatic relief until surgery
👉 Key Point: Non-surgical measures do not eliminate the hernia or prevent complications; definitive repair is generally recommended.
Preparation
Proper preparation ensures safe surgery and optimal outcomes:
🔹 Medical evaluation – History, physical examination, and assessment of comorbidities
🔹 Preoperative tests – Blood tests, ECG, chest X-ray, and imaging if needed
🔹 Medication review – Adjust anticoagulants, antiplatelets, or chronic medications
🔹 Fasting – Usually 6–8 hours before anesthesia
🔹 Informed consent – Discussion of procedure, risks, benefits, and alternatives
⭐ Arrange transportation – Patients may not drive after laparoscopic or open surgery
⭐ Clothing – Comfortable, loose-fitting attire for post-operative recovery
How It’s Done
Femoral hernia repair can be performed via open or laparoscopic techniques:
- Open Femoral Hernia Repair
✔️ Incision in the groin over femoral canal
✔️ Hernia sac identified, reduced, and contents repositioned
✔️ Canal reinforced using sutures or synthetic mesh
✔️ Incision closed in layers; dressing applied - Laparoscopic Repair
🔹 Small incisions in the abdomen
🔹 Camera and instruments inserted to visualize hernia
🔹 Mesh placed over defect and fixed in position
🔹 Minimally invasive approach reduces post-operative pain and recovery time - Mesh vs. Non-Mesh Repair
➡️ Mesh repair preferred for lower recurrence rates
➡️ Suture repair considered in select cases (e.g., contamination risk or patient preference)
Highlights:
✔️ Surgery duration – Typically 30–90 minutes depending on complexity
✔️ Anesthesia – General or regional anesthesia commonly used
✔️ Hospital stay – Outpatient for laparoscopic, 1–2 days for open repair
Recovery / Follow-up
Recovery from femoral hernia repair depends on technique and patient health:
✔️ Immediate post-op care – Monitor vitals, incision site, and urinary function
✔️ Pain management – Analgesics for mild to moderate pain
✔️ Activity – Light activity encouraged; avoid heavy lifting for 4–6 weeks
✔️ Follow-up visit – Usually 1–2 weeks after surgery for wound check and suture removal if needed
✔️ Return to work – Often 1–2 weeks for laparoscopic repair; 4–6 weeks for open repair
⭐ Long-term follow-up – Assess recurrence, chronic pain, and mesh-related complications
Complications / Risks
Femoral hernia repair is generally safe, but potential risks include:
⚠️ Surgical site infection – Usually minor and treated with antibiotics
⚠️ Bleeding or hematoma – Rare but may require drainage
⚠️ Recurrence – Less common with mesh repair
⚠️ Nerve injury – May cause numbness or tingling in thigh or groin
⚠️ Chronic pain – Occasional, usually resolves with conservative management
⚠️ Anesthesia-related risks – Allergic reaction, cardiovascular events, or respiratory issues
➡️ In Korea, experienced surgeons, sterile techniques, and modern monitoring minimize complications.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean hospitals provide state-of-the-art femoral hernia repair services, including:
🏥 Laparoscopic Femoral Hernia Repair – Minimally invasive, faster recovery, less pain
🏥 Open Hernia Repair – For complex or recurrent hernias
🏥 Mesh or Suture Repair Options – Tailored to patient needs
🏥 Pre- and Post-Operative Counseling – Ensures informed decisions and smooth recovery
🏥 Follow-up Care – Wound monitoring, pain management, and recurrence surveillance
Why Korea is a Preferred Destination:
✔️ Highly skilled general surgeons – Extensive experience with laparoscopic and open techniques
✔️ Advanced minimally invasive equipment – Reduces hospital stay and recovery time
✔️ Patient-centered care – Counseling, comfort, and privacy prioritized
✔️ Affordable and efficient – Short hospital stays and cost-effective treatment
✔️ Comprehensive post-op support – Pain management, physiotherapy, and long-term monitoring
Approximate Costs in Korea:
🔹 Laparoscopic Femoral Hernia Repair → $2,000 – $5,000
🔹 Open Femoral Hernia Repair → $1,500 – $4,000
🔹 Hospital stay (1–2 days) → $150 – $400 per day
🔹 Pre- and post-op consultation → $50 – $100
Conclusion
Femoral hernia repair is a safe, effective, and definitive treatment for preventing complications and restoring normal function.
It helps patients:
✔️ Avoid emergency complications such as strangulation or obstruction
✔️ Relieve pain, swelling, and discomfort
✔️ Prevent recurrence with durable repair
✔️ Resume normal daily activities safely
In Korea, patients benefit from:
✔️ Advanced laparoscopic and open surgical techniques
✔️ Experienced surgeons and multidisciplinary support
✔️ Comprehensive pre- and post-op care
✔️ Safe, cost-effective, and patient-focused treatment
👉 Key Message: Femoral hernia repair in Korea provides efficient, safe, and long-lasting relief, combining modern surgical techniques with expert care and rapid recovery.