What is an Electroencephalogram (EEG)?
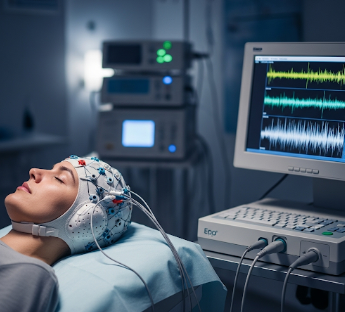
An Electroencephalogram (EEG) is a non-invasive test that measures electrical activity in the brain. It uses small metal electrodes attached to the scalp to detect and record brain wave patterns, providing crucial information about neurological function, seizures, and brain disorders.
EEG is widely used for:
✔️ Diagnosing epilepsy and seizure disorders
✔️ Monitoring brain activity during sleep or anesthesia
✔️ Evaluating unexplained neurological symptoms such as fainting, confusion, or memory problems
✔️ Assessing brain function in patients with head injury, stroke, or coma
Types of EEG:
🔹 Routine EEG – Standard recording lasting 20–40 minutes
🔹 Ambulatory EEG – Long-term monitoring over 24–72 hours
🔹 Video EEG – Combines EEG recording with video to correlate brain activity with observed events
🔹 Sleep EEG – Monitors brain activity during sleep cycles
In Korea, EEG is performed in neurology departments, specialized epilepsy centers, and advanced diagnostic clinics. Korean hospitals provide modern EEG machines, video EEG monitoring, and highly trained neurologists, making it a preferred choice for accurate diagnosis and management of neurological conditions.
➡️ Detects abnormal brain activity
➡️ Assists in diagnosing seizures and epilepsy
➡️ Monitors treatment effectiveness and brain health
Why It’s Done
EEG is performed to diagnose, monitor, and manage neurological conditions.
✔️ Diagnose epilepsy – Determine the type and focus of seizures
✔️ Monitor neurological disorders – Brain injury, stroke, encephalopathy, or tumors
✔️ Investigate unexplained symptoms – Fainting, dizziness, memory lapses, or sleep disturbances
✔️ Assess brain function – During coma, anesthesia, or critical illness
✔️ Guide treatment decisions – Medication adjustments, surgical planning, or therapy evaluation
Benefits of EEG:
➡️ Non-invasive and painless → No exposure to radiation or contrast agents
➡️ Real-time brain activity monitoring → Detects abnormalities even when symptoms are not occurring
➡️ Early diagnosis → Allows timely treatment and seizure prevention
➡️ Treatment monitoring → Evaluates response to antiepileptic medications
In Korea, EEG is a key diagnostic tool in epilepsy centers, neurology clinics, and comprehensive health check-ups for patients with neurological symptoms.
Alternatives
While EEG is the standard for evaluating electrical activity in the brain, other diagnostic methods exist:
⭐ MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) – Provides detailed structural images of the brain
⭐ CT Scan – Detects structural abnormalities, bleeding, or tumors
⭐ PET Scan – Assesses metabolic activity in the brain
⭐ MEG (Magnetoencephalography) – Measures magnetic fields generated by brain activity, often used in surgical planning
⭐ Blood Tests – Rule out metabolic or infectious causes of neurological symptoms
👉 EEG remains the first-line, non-invasive, and cost-effective method for assessing electrical activity and diagnosing epilepsy.
Preparation
Preparation for an EEG is straightforward but important to ensure accurate results:
🔹 Wash hair thoroughly – Avoid hair products such as gels, oils, or sprays
🔹 Avoid caffeine or stimulant medications – Can alter brain wave activity
🔹 Get adequate sleep – Sleep deprivation may be required for certain EEGs
🔹 Bring a list of medications – Certain medications may affect brain activity
🔹 Inform the technician – Of pregnancy, recent illness, or neurological events
⭐ No fasting is required
⭐ Comfortable clothing recommended for long monitoring sessions
How It’s Done
The EEG procedure varies depending on the type of recording:
- Electrode Placement
✔️ Small metal electrodes placed on the scalp using conductive paste
✔️ Electrodes connected to the EEG machine to record electrical activity - Recording Brain Activity
🔹 Routine EEG – Patient rests quietly while brain waves are recorded for 20–40 minutes
🔹 Sleep EEG – Patient sleeps during recording, or sleep is induced
🔹 Video EEG – Simultaneous video recording to correlate physical events with EEG signals
🔹 Ambulatory EEG – Patient wears a portable recorder for 24–72 hours while going about daily activities - Data Analysis
➡️ Neurologist reviews wave patterns for abnormalities such as spikes, slow waves, or seizure activity
➡️ Identifies areas of the brain generating abnormal electrical activity
Highlights:
✔️ Non-invasive and painless
✔️ Real-time monitoring of brain function
✔️ Can be repeated for ongoing assessment
Recovery
EEG is generally safe and requires no recovery:
✔️ Immediate resumption of normal activities
✔️ Minor scalp irritation – Rarely occurs at electrode sites
✔️ Sleep EEG or long-term EEG – Mild fatigue may occur, especially after sleep deprivation
✔️ Resume medications as advised
⭐ Patients may be advised to avoid driving or operating heavy machinery if sedatives or sleep deprivation were involved
Complications
EEG is extremely safe, with minimal risks:
⚠️ Skin irritation or redness – From electrode paste
⚠️ Discomfort – Slight tightness from electrode cap
⚠️ Seizure induction – Rarely, flashing lights or hyperventilation may provoke a seizure (used intentionally during testing)
⚠️ Allergic reactions – Rarely, to conductive paste
➡️ In Korea, trained EEG technicians and neurologists ensure safety and immediate intervention if any adverse events occur.
Treatment Options in Korea
If EEG identifies abnormalities, Korea offers comprehensive neurological care:
🏥 Medication Therapy – Antiepileptic drugs for seizure control, anti-inflammatory or neuroprotective agents
🏥 Surgical Interventions – Epilepsy surgery, resective procedures, or neurostimulation devices
🏥 Neuromodulation Therapy – Vagus nerve stimulation, responsive neurostimulation
🏥 Lifestyle & Rehabilitation Programs – Cognitive therapy, sleep management, and physical therapy
🏥 Follow-up EEG Monitoring – Ensures effective seizure control and ongoing assessment
Why Korea is a Preferred Destination:
✔️ Modern EEG equipment – High-resolution, digital, and video-integrated systems
✔️ Expert neurologists and epileptologists – Experienced in complex seizure management
✔️ Affordable and accessible care – Lower cost than many Western countries with high-quality services
✔️ Medical tourism support – Translation services, travel assistance, and hospital coordination
Approximate Costs in Korea:
🔹 Routine EEG → $80 – $150
🔹 Video EEG Monitoring → $200 – $400
🔹 Ambulatory EEG (24–72 hours) → $250 – $500
🔹 Sleep EEG → $150 – $300
Conclusion
An Electroencephalogram (EEG) is a critical diagnostic tool for assessing brain electrical activity, diagnosing epilepsy, and monitoring neurological function.
It helps:
✔️ Detect abnormal brain activity early
✔️ Guide medication and treatment decisions
✔️ Evaluate neurological symptoms such as seizures, fainting, or confusion
✔️ Monitor treatment efficacy and disease progression
In Korea, patients benefit from:
✔️ Advanced EEG machines and video monitoring
✔️ Highly trained neurologists and epilepsy specialists
✔️ Affordable and accessible diagnostic services
✔️ Comprehensive follow-up care and support programs
👉 EEG is a safe, non-invasive, and invaluable tool for maintaining neurological health and managing seizures or other brain disorders.
Key Message: Electroencephalography provides real-time insight into brain function, enabling accurate diagnosis and effective neurological care.