Overview
Contraceptive injections are a long-acting hormonal method for preventing pregnancy. They contain progestin, a synthetic hormone that suppresses ovulation, thickens cervical mucus, and alters the uterine lining to prevent fertilization and implantation.
Importance of contraceptive injections:
- Highly effective with ~94–99% efficacy when administered on schedule.
- Provides long-term protection for 1–3 months per injection depending on the type.
- Non-daily method, ideal for women who prefer minimal routine attention.
- Suitable for women who cannot use estrogen-containing contraception.
In South Korea, contraceptive injections are offered in gynecology clinics, family planning centers, and hospitals, with medical supervision ensuring safe administration and follow-up.
Why It’s Done
Contraceptive injections are used for reliable, long-term pregnancy prevention and, in some cases, to manage menstrual disorders.
Common indications include:
- ➤ Long-term contraception without daily or weekly intervention.
- ➤ Women with difficulty adhering to daily pills.
- ➤ Medical contraindications to estrogen (smokers over 35, hypertension, migraines with aura).
- ➤ Management of heavy or irregular menstrual bleeding.
- ➤ Temporary spacing of pregnancies for health, education, or lifestyle reasons.
Benefits for users:
- ✔️ High efficacy when injections are on schedule.
- ✔️ Reversible; fertility returns within months after stopping.
- ✔️ Reduces risk of unintended pregnancy, improving reproductive autonomy.
- ✔️ Convenient and discreet, with minimal daily attention required.
- ✔️ Can help regulate menstrual cycles for some users.
Alternatives
Contraceptive injections are one option among many long-acting or short-term contraceptives:
- ➤ Hormonal pills: Combined or progestin-only oral contraceptives.
- ➤ Contraceptive implants: Long-term rod under the arm releasing hormones.
- ➤ Intrauterine devices (IUDs): Hormonal or copper options.
- ➤ Barrier methods: Condoms, diaphragms, or cervical caps.
- ➤ Permanent sterilization: Tubal ligation or vasectomy.
- ➤ Fertility awareness methods: Tracking ovulation to avoid intercourse during fertile periods.
Key point: Injections are ideal for users seeking medium-term, low-maintenance contraception without daily pills or invasive devices.
Preparation
Proper preparation ensures safe administration, patient understanding, and effective protection.
Steps include:
- ✅ Medical assessment: Review health history, allergies, previous contraceptive use, and menstrual patterns.
- ✅ Method selection: Choose injection type (e.g., Depo-Provera or 3-month progestin injections).
- ✅ Patient counseling: Discuss schedule, side effects, expected menstrual changes, and backup contraception if needed.
- ✅ Consent: Obtain informed agreement from the patient.
- ✅ Site preparation: Clean injection site (usually upper arm, thigh, or buttock) with antiseptic.
Important: Preparation ensures safe use, adherence, and patient satisfaction.
How It’s Done
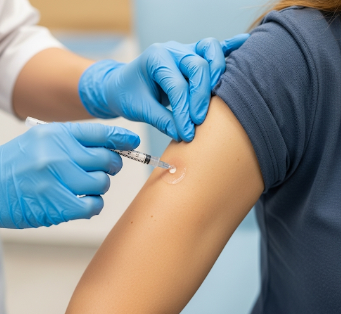
Contraceptive injections are administered by trained healthcare providers and do not require hospitalization.
Procedure steps:
- Assess injection site: Upper arm, thigh, or buttock.
- Apply antiseptic and local prep: Clean the site to prevent infection.
- Injection: Administer hormone via intramuscular (IM) or subcutaneous (SC) injection, depending on product.
- Post-injection care: Apply gentle pressure or bandage; advise patient to avoid strenuous activity for a short period.
Schedule:
- Typical injections are every 1–3 months depending on the formulation.
- Timely follow-up is critical for maintaining contraceptive effectiveness.
Key point: Injections are quick, outpatient procedures that provide medium-term contraception with minimal daily management.
Recovery & Post-Use Care
Recovery is generally immediate, with minor monitoring for side effects.
Immediate post-injection:
- Monitor for mild pain, swelling, or bruising at the injection site.
- Watch for allergic reactions (rare).
Short-term care:
- Track menstrual changes, including irregular bleeding or amenorrhea.
- Use backup contraception if injection is delayed.
Long-term outcomes:
- Highly effective contraception for 1–3 months per dose.
- Fertility generally returns within 3–12 months after discontinuation.
- Provides reliable family planning and reproductive autonomy.
Important: Regular follow-up ensures timely injections, side effect management, and sustained protection.
Possible Complications / Risks
Contraceptive injections are safe, but potential risks include:
- ⚠️ Injection site reactions: Pain, swelling, redness, or bruising.
- ⚠️ Menstrual irregularities: Spotting, prolonged bleeding, or absence of periods.
- ⚠️ Hormonal side effects: Headaches, weight gain, mood changes, or breast tenderness.
- ⚠️ Bone density reduction: Rare with long-term use (particularly with Depo-Provera), reversible after discontinuation.
- ⚠️ Delayed return to fertility: Fertility may take a few months to resume after stopping injections.
In South Korea, contraceptive injections are administered under medical supervision, with counseling and monitoring to reduce risks and manage side effects effectively.
Treatment Options / Clinical Relevance in Korea
Contraceptive injections are an important medium-term contraceptive option in South Korea, especially for women seeking non-daily, hormone-based contraception.
Key features:
- 🏥 Available in gynecology clinics, hospitals, and family planning centers.
- 🏥 Administered by trained healthcare professionals with safe injection protocols.
- 🏥 Effective for women who cannot use estrogen-containing contraceptives.
- 🏥 Integrated into reproductive health programs and family planning counseling.
- 🏥 Used alongside other contraceptive methods if required for backup or dual protection.
Highlights in Korea:
- ✔️ Provides medium-term, highly effective pregnancy prevention.
- ✔️ Discreet and convenient for working women or students.
- ✔️ Minor side effects monitored by healthcare professionals.
- ✔️ Supports planned pregnancies and reproductive autonomy.
- ✔️ Fertility returns after discontinuation, allowing flexible family planning.
Highlights
- ➤ Contraceptive injections are hormone-based shots providing medium-term pregnancy prevention.
- ➤ Indicated for women seeking 1–3 months of effective, low-maintenance contraception or who cannot use estrogen-based methods.
- ➤ Alternatives include pills, implants, IUDs, barrier methods, sterilization, or fertility awareness.
- ➤ Preparation involves medical assessment, counseling, informed consent, and site preparation.
- ➤ Administration is an outpatient procedure via IM or SC injection at regular intervals.
- ➤ Recovery is immediate, with minor site care and monitoring for hormonal side effects.
- ➤ South Korea provides regulated, professional administration with counseling and follow-up for safe and effective use.