Overview
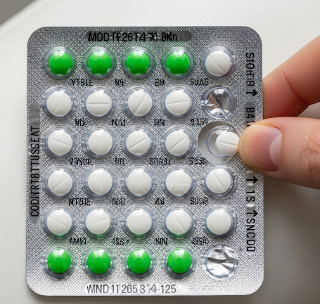
The Combined Pill, often called the oral contraceptive pill (OCP), is a medication taken by mouth containing two hormones – estrogen and progestin – to prevent pregnancy. Beyond contraception, it can also regulate menstrual cycles, reduce acne, manage endometriosis, and lower the risk of certain cancers.
Importance of the Combined Pill:
- Highly effective contraceptive method when taken correctly.
- Regulates menstrual cycles for women with irregular periods.
- Reduces menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea) and heavy bleeding (menorrhagia).
- Helps manage acne and hormonal imbalances.
- Provides long-term protection against endometrial and ovarian cancer.
In South Korea, the Combined Pill is widely available in gynecology clinics and family planning centers, with options for prescription guidance, monitoring, and education on safe use.
Why It’s Done
The Combined Pill is primarily prescribed for contraception, but also for medical and lifestyle benefits.
Common indications include:
- ➤ Contraception: Prevents ovulation and pregnancy.
- ➤ Menstrual regulation: For irregular, heavy, or painful periods.
- ➤ Acne treatment: Reduces androgen-related skin issues.
- ➤ Endometriosis or ovarian cyst management: Hormonal regulation reduces symptoms.
- ➤ Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) relief: Improves mood and physical symptoms.
- ➤ Protection against certain cancers: Reduces risk of endometrial and ovarian cancer.
Benefits for patients:
- ✔️ Highly effective birth control with typical-use failure rate <9% and perfect-use failure <1%.
- ✔️ Improves quality of life by managing pain, acne, or menstrual irregularities.
- ✔️ Can be temporarily discontinued when pregnancy is desired.
- ✔️ Offers long-term reproductive health benefits beyond contraception.
Alternatives
If the Combined Pill is not suitable, several alternatives are available:
- ➤ Progestin-only pill (mini-pill): Suitable for women who cannot take estrogen.
- ➤ Intrauterine device (IUD): Hormonal or copper device providing long-term contraception.
- ➤ Contraceptive patch or vaginal ring: Hormonal delivery similar to the combined pill.
- ➤ Barrier methods: Condoms, diaphragms, cervical caps.
- ➤ Natural family planning: Fertility awareness or abstinence during fertile periods.
- ➤ Emergency contraception: For occasional contraception after unprotected intercourse.
Key point: The Combined Pill is highly convenient and reversible, but alternatives may suit individual health, lifestyle, or preference considerations.
Preparation
Before starting the Combined Pill, medical evaluation and counseling are essential.
Steps include:
- ✅ Medical history assessment: Heart disease, migraines, hypertension, liver disease, or clotting disorders.
- ✅ Blood pressure measurement and baseline health check.
- ✅ Discussion of smoking and age-related risks: Especially in women over 35.
- ✅ Consent and counseling: Explain benefits, side effects, and correct usage.
- ✅ Pregnancy test: Ensure patient is not pregnant before initiation.
- ✅ Medication review: Check for drugs that may interact with hormonal contraceptives.
Important: Proper assessment reduces health risks and ensures safe use of the pill.
How It’s Done
The Combined Pill is a daily oral medication, taken ideally at the same time each day.
Administration steps:
- Start timing: Either on the first day of menstruation or Sunday after period starts, depending on doctor’s advice.
- Daily intake: One pill per day for 21 consecutive days, followed by a 7-day hormone-free interval or placebo pills.
- Missed pill protocol: Instructions provided for missed doses to maintain contraceptive effectiveness.
- Monitoring: Follow-up appointments may assess blood pressure, side effects, and overall health.
Duration: Can be used short-term or long-term depending on contraceptive or therapeutic goals.
Hospital stay: Not required; outpatient prescription and monitoring only.
Key point: The Combined Pill is safe, non-invasive, reversible, and highly effective when taken consistently.
Recovery & Post-Pill Care
While the Combined Pill does not involve surgery, monitoring and adjustment are part of ongoing care.
Immediate adaptation:
- Mild nausea, breast tenderness, or spotting may occur in the first few cycles.
- Adjustment period: 1–3 months for hormones to stabilize.
Ongoing care:
- Regular gynecological check-ups every 6–12 months.
- Monitor blood pressure, weight, and mood changes.
- Switch brands or formulations if side effects persist.
- Maintain backup contraception during initial cycles for maximum effectiveness.
Long-term outcomes:
- Continuous use reduces menstrual irregularities, acne, and risk of ovarian/endometrial cancer.
- Fertility typically returns rapidly after discontinuation.
- Supports overall reproductive health and menstrual management.
Important: Compliance and monitoring ensure effectiveness and reduce risks.
Possible Complications
While generally safe, the Combined Pill can have side effects and rare complications:
- ⚠️ Common minor side effects: Nausea, breast tenderness, spotting, mood changes, headaches.
- ⚠️ Increased risk of blood clots: Especially in women who smoke, are over 35, or have clotting disorders.
- ⚠️ Elevated blood pressure in some users.
- ⚠️ Hormonal interactions: Some medications (e.g., certain antibiotics or anticonvulsants) may reduce effectiveness.
- ⚠️ Rare complications: Stroke or heart attack in high-risk populations.
In South Korea, prescriptions are provided with comprehensive counseling, risk assessment, and follow-up to minimize complications.
Treatment Options / Clinical Relevance in Korea
The Combined Pill is a widely used contraceptive and therapeutic option in South Korea.
Key features:
- 🏥 Available in gynecology clinics, hospitals, and family planning centers nationwide.
- 🏥 Prescription-based with professional guidance on selection, dosage, and monitoring.
- 🏥 Used for contraception, menstrual regulation, acne management, and endometriosis therapy.
- 🏥 Patient education covers compliance, side effects, missed pill protocol, and alternative contraception.
- 🏥 Integrated care supports long-term reproductive and hormonal health.
Highlights in Korea:
- ✔️ Accessible and safe with medical supervision and regulatory approval.
- ✔️ Provides both contraceptive and non-contraceptive health benefits.
- ✔️ Easily discontinued to restore fertility when desired.
- ✔️ Supported by national health guidelines and family planning programs.
Highlights
- ➤ The Combined Pill is an oral contraceptive containing estrogen and progestin.
- ➤ Indicated for contraception, menstrual regulation, acne, endometriosis, and cancer prevention.
- ➤ Alternatives include mini-pill, IUD, patch, vaginal ring, barrier methods, or natural family planning.
- ➤ Preparation involves medical history review, blood pressure check, pregnancy test, and counseling.
- ➤ Taken daily for 21 days with a 7-day break or placebo; adherence is key for effectiveness.
- ➤ Recovery/adaptation includes mild initial side effects and routine follow-up for monitoring.
- ➤ South Korea offers safe, widely available combined pill options with professional guidance and reproductive health support.