Overview
Colposcopy is a diagnostic procedure used to examine the cervix, vagina, and vulva for abnormal cells or tissue. It is typically performed when a Pap smear or HPV test shows abnormal results, enabling doctors to detect precancerous changes or early-stage cervical cancer.
Importance of colposcopy:
- Provides direct visualization of cervical and vaginal tissues.
- Allows early detection and treatment of precancerous lesions.
- Guides biopsies to confirm abnormal cell changes.
- Reduces the risk of progression to cervical cancer.
In South Korea, colposcopy is routinely performed in gynecology and women’s health clinics, using high-definition imaging and modern colposcopes, ensuring accuracy, patient comfort, and early intervention.
Why It’s Done
Colposcopy is indicated for diagnostic and monitoring purposes.
Common indications include:
- ➤ Abnormal Pap smear results (e.g., atypical squamous cells, high-grade lesions).
- ➤ Positive HPV test, especially for high-risk strains.
- ➤ Unexplained vaginal bleeding or postcoital bleeding.
- ➤ Suspicious cervical lesions or genital warts.
- ➤ Follow-up after previous abnormal Pap smear or cervical treatment.
Benefits for patients:
- ✔️ Detects precancerous changes before progression to cervical cancer.
- ✔️ Guides targeted biopsies for accurate diagnosis.
- ✔️ Reduces unnecessary treatments through precise assessment.
- ✔️ Supports long-term cervical health monitoring.
Alternatives
While colposcopy is the gold standard for cervical evaluation, alternatives may include:
- ➤ Pap smear: Screening test but does not allow direct visualization.
- ➤ HPV testing: Detects high-risk HPV strains but does not provide tissue assessment.
- ➤ Endocervical curettage: Sampling tissue from the cervical canal.
- ➤ Visual inspection with acetic acid (VIA): Limited, mostly in low-resource settings.
Key point: Colposcopy allows direct visualization and biopsy, making it superior for diagnosis and treatment planning.
Preparation
Preparation for colposcopy ensures accurate results and patient comfort.
Steps include:
- ✅ Schedule timing: Ideally performed when not menstruating.
- ✅ Avoid vaginal products: No douching, creams, or intercourse 24–48 hours before the procedure.
- ✅ Medical history review: Prior cervical procedures, infections, medications, or pregnancy status.
- ✅ Consent: Discuss procedure, biopsy, discomfort, and potential risks.
- ✅ Pain management planning: Usually minimal; topical anesthetic or local anesthesia may be used if biopsy is needed.
Important: Proper preparation improves visualization and reduces discomfort during colposcopy.
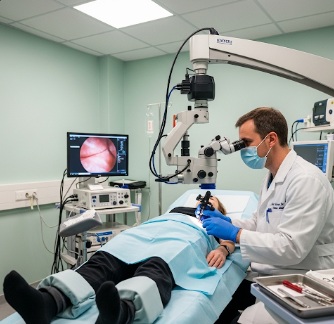
How It’s Done
Colposcopy is a minimally invasive outpatient procedure.
Procedure steps:
- Positioning: Patient lies on the examination table with feet in stirrups.
- Speculum insertion: Allows visualization of the cervix.
- Application of acetic acid or iodine: Highlights abnormal areas.
- Colposcope examination: High-powered magnifying instrument visualizes tissue.
- Targeted biopsy: Abnormal areas sampled for laboratory analysis.
- Hemostasis and dressing: Minor bleeding controlled, and biopsy site protected.
Duration: 10–30 minutes
Hospital stay: Outpatient; no overnight stay required.
Key point: Colposcopy is safe, quick, and allows both diagnosis and targeted biopsy during the same visit.
Recovery & Post-Procedure Care
Recovery from colposcopy is usually rapid and uncomplicated.
Immediate post-procedure:
- Mild cramping or spotting may occur.
- Monitor for excessive bleeding or severe pain, which requires medical attention.
Short-term care:
- Avoid intercourse, tampons, or douching for 24–48 hours.
- Use pads instead of tampons to manage light bleeding.
- Resume normal activities unless advised otherwise.
Long-term outcomes:
- Biopsy results guide treatment or monitoring.
- Early intervention prevents progression of precancerous lesions.
- Routine follow-up with Pap smear or colposcopy as recommended.
Important: Adhering to post-procedure instructions ensures healing and accurate follow-up results.
Possible Complications
Colposcopy is generally very safe, but minor risks may include:
- ⚠️ Mild cramping or discomfort during or after the procedure.
- ⚠️ Spotting or light bleeding from biopsy sites.
- ⚠️ Infection: Rare, usually preventable with standard sterile technique.
- ⚠️ Pain or discomfort during speculum insertion in sensitive individuals.
- ⚠️ Allergic reaction to acetic acid or iodine (extremely rare).
In South Korea, colposcopy is performed with modern colposcopes, trained gynecologists, and strict aseptic protocols, minimizing complications.
Treatment Options / Clinical Relevance in Korea
Colposcopy is a routine and essential procedure in women’s health care in South Korea.
Key features:
- 🏥 High-definition colposcopes for precise detection of abnormal tissue.
- 🏥 Outpatient procedure with minimal discomfort and rapid recovery.
- 🏥 Biopsy and treatment planning performed during the same visit if needed.
- 🏥 Integrated care with gynecology, oncology, and pathology teams for accurate diagnosis.
- 🏥 Screening programs support early detection of cervical cancer nationwide.
Hospitals and clinics performing colposcopy in Korea:
- Seoul National University Hospital – Gynecology and cervical health programs
- Asan Medical Center – High-definition colposcopy with biopsy and treatment
- Samsung Medical Center – Women’s health and cervical cancer prevention services
- Private gynecology clinics – Nationwide accessibility with experienced specialists
Highlights in Korea:
- ✔️ Early detection and management of cervical abnormalities improve long-term outcomes.
- ✔️ Safe, minimally invasive procedure with excellent patient comfort.
- ✔️ Combines diagnosis and targeted biopsy in one visit.
- ✔️ Nationwide accessibility in hospitals and specialized clinics.
Highlights
- ➤ Colposcopy examines the cervix, vagina, and vulva for abnormal cells or tissue.
- ➤ Indicated for abnormal Pap smear, positive HPV test, unexplained bleeding, or follow-up after previous lesions.
- ➤ Alternatives include Pap smear, HPV testing, endocervical curettage, or visual inspection with acetic acid.
- ➤ Preparation involves timing, avoiding vaginal products, medical review, consent, and pain management planning.
- ➤ Procedure is outpatient, 10–30 minutes, with acetic acid/iodine application and targeted biopsy.
- ➤ Recovery includes monitoring for mild bleeding, avoiding tampons/intercourse for 24–48 hours, and follow-up for biopsy results.
- ➤ South Korea offers advanced colposcopy with high-definition imaging, biopsy capabilities, and integrated women’s health care services.