Overview
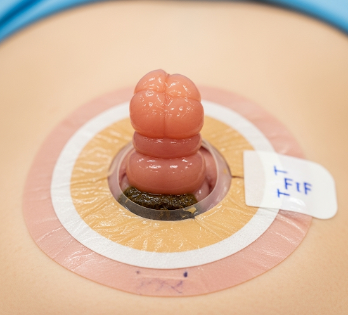
A colostomy is a surgical procedure that creates an opening (stoma) in the abdominal wall to divert the colon (large intestine) to the outside of the body. This allows fecal matter to bypass a damaged or diseased section of the colon, aiding in digestion, waste elimination, and patient health.
Importance of colostomy:
- Provides relief in bowel obstruction or injury.
- Allows management of colorectal cancer or inflammatory bowel disease.
- Facilitates healing after surgical resection of the colon.
- Improves quality of life in patients with irreversible bowel dysfunction.
In South Korea, colostomy is performed in specialized colorectal surgery centers and hospitals, with emphasis on preoperative planning, stoma care education, and postoperative support.
Why It’s Done
Colostomy is indicated for temporary or permanent diversion of the colon due to disease, trauma, or obstruction.
Common indications include:
- ➤ Colorectal cancer requiring bowel resection.
- ➤ Diverticulitis or perforated colon leading to infection.
- ➤ Traumatic bowel injury or severe abdominal trauma.
- ➤ Congenital anomalies such as anorectal malformations in children.
- ➤ Inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis) causing obstruction or fistulas.
- ➤ Bowel obstruction that cannot be managed conservatively.
Benefits for patients:
- ✔️ Allows bypassing damaged or diseased bowel to prevent complications.
- ✔️ Promotes healing of surgical or diseased segments of the colon.
- ✔️ Improves nutritional status and bowel management.
- ✔️ Provides temporary or permanent solution for patients with severe colon dysfunction.
Alternatives
Depending on the condition, alternatives to colostomy may include:
- ➤ Primary bowel resection and anastomosis: Directly reconnecting the colon without a stoma.
- ➤ Ileostomy: Diversion of the small intestine instead of the colon.
- ➤ Endoscopic interventions: For partial obstructions or polyps.
- ➤ Medication management: For mild inflammatory bowel disease or obstruction.
Key point: Colostomy is usually the preferred solution when the colon cannot function normally or requires protection during healing.
Preparation
Preparation for colostomy involves medical, nutritional, and psychological assessment.
Steps include:
- ✅ Medical evaluation: Review comorbidities, medications, and surgical risk.
- ✅ Imaging studies: Colonoscopy, CT scan, or X-ray to assess colon condition.
- ✅ Bowel preparation: In some cases, bowel cleansing may be required preoperatively.
- ✅ Nutritional assessment: Ensure adequate protein and calorie intake for healing.
- ✅ Stoma site marking: Performed by a stoma nurse to ensure optimal location.
- ✅ Consent and counseling: Discuss procedure, temporary vs permanent stoma, and post-op care.
Important: Adequate preparation reduces complications and supports postoperative recovery and adaptation.
How It’s Done
Colostomy is performed under general anesthesia by a colorectal surgeon.
Procedure steps:
- Anesthesia and sterile preparation: Patient under general anesthesia, abdomen cleaned and draped.
- Colon mobilization: Surgeon isolates the affected segment of the colon.
- Stoma creation: The colon is brought through the abdominal wall to create an opening (stoma).
- Colostomy type:
- End colostomy: Permanent or temporary; distal colon removed or bypassed.
- Loop colostomy: Temporary; a loop of colon is brought out and opened.
- Double-barrel colostomy: Two openings; one for stool, one for mucus drainage.
- Stoma maturation: Edges sutured to skin; appliance fitted.
- Closure and observation: Wound closed around stoma, patient monitored postoperatively.
Duration: 1–2 hours (depending on complexity)
Hospital stay: Typically 5–10 days; longer if complications arise.
Key point: Colostomy provides a controlled and safe route for fecal diversion, allowing healing and preventing complications.
Recovery & Postoperative Care
Recovery from colostomy is gradual and includes wound care, stoma management, and lifestyle adjustment.
Immediate post-procedure:
- Monitor vital signs, stoma function, and surgical site.
- Pain management with analgesics and antispasmodics.
- Early mobilization to prevent complications like deep vein thrombosis.
Short-term care:
- Stoma care education: Changing appliances, cleaning, and monitoring output.
- Dietary adjustments: Initially soft, low-fiber diet; gradually resume normal diet.
- Wound monitoring: Check for infection, bleeding, or skin irritation.
Long-term care:
- Regular follow-up with colorectal surgeon or stoma nurse.
- Adaptation to appliances, clothing, and daily activities.
- Nutritional support and counseling for optimal health.
Important: Proper postoperative care ensures stoma function, reduces complications, and improves quality of life.
Possible Complications
Colostomy is generally safe, but potential risks include:
- ⚠️ Stoma complications: Prolapse, retraction, or stenosis.
- ⚠️ Skin irritation or infection around the stoma site.
- ⚠️ Bleeding or abscess formation at the surgical site.
- ⚠️ Bowel obstruction or hernia around the stoma (parastomal hernia).
- ⚠️ Psychological adjustment issues: Stress, anxiety, or depression related to stoma.
- ⚠️ Anesthesia-related risks – rare but possible.
In South Korea, colostomy is performed with experienced colorectal surgeons, specialized stoma nurses, and modern appliances to minimize complications.
Treatment Options / Clinical Relevance in Korea
Colostomy in South Korea is a well-established procedure offered in tertiary hospitals and specialized surgical centers.
Key features:
- 🏥 Advanced surgical techniques for end, loop, or double-barrel colostomies.
- 🏥 Postoperative stoma care education with dedicated stoma nurses.
- 🏥 Modern appliances for comfort, hygiene, and convenience.
- 🏥 Integration with oncology, gastroenterology, and surgery teams for comprehensive care.
- 🏥 Temporary or permanent colostomy options depending on disease and patient needs.
Hospitals and clinics performing colostomy in Korea:
- Seoul National University Hospital – Colorectal surgery and stoma care programs
- Asan Medical Center – Oncology-related colostomy and postoperative rehabilitation
- Samsung Medical Center – Advanced stoma creation and education
- Private surgical centers – Nationwide availability for elective or emergency colostomies
Highlights in Korea:
- ✔️ Safe, standardized procedures with high surgical success rates.
- ✔️ Dedicated stoma care and education programs to improve adaptation.
- ✔️ Integrated care ensures long-term management and quality of life.
- ✔️ Offers both temporary and permanent colostomy options for diverse clinical needs.
Highlights
- ➤ Colostomy diverts fecal flow through a stoma to bypass diseased or damaged colon.
- ➤ Indicated for colorectal cancer, bowel obstruction, inflammatory bowel disease, trauma, or congenital anomalies.
- ➤ Alternatives include primary anastomosis, ileostomy, endoscopic interventions, or medication management.
- ➤ Preparation involves medical evaluation, imaging, bowel prep, stoma marking, and counseling.
- ➤ Procedure is 1–2 hours, performed under general anesthesia, and can be temporary or permanent.
- ➤ Recovery includes stoma care, wound monitoring, dietary adjustments, and psychological support.
- ➤ South Korea provides safe, advanced colostomy with stoma education, modern appliances, and multidisciplinary care.