Overview
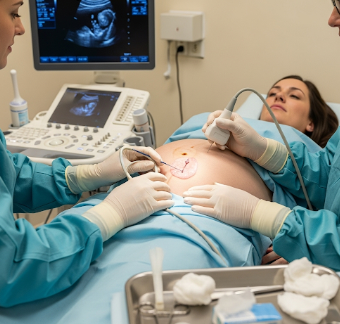
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is a prenatal diagnostic test used to detect chromosomal, genetic, and certain metabolic disorders in a developing fetus. The procedure involves taking a small sample of placental tissue (chorionic villi), which shares the baby’s genetic makeup.
Importance of CVS:
- Detects genetic disorders such as Down syndrome, cystic fibrosis, and Tay-Sachs disease early in pregnancy.
- Provides critical information for parents and healthcare providers to make informed decisions.
- Allows testing earlier than amniocentesis, usually between 10–13 weeks of gestation.
- Helps guide further prenatal care or interventions if abnormalities are detected.
In South Korea, CVS is performed in specialized obstetrics and prenatal diagnostic centers, with modern imaging guidance and laboratory support to ensure safety and accurate results.
Why It’s Done
CVS is done to identify chromosomal or genetic abnormalities early in pregnancy.
Common indications include:
- ➤ Advanced maternal age: Higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
- ➤ Abnormal first-trimester screening: Such as elevated nuchal translucency.
- ➤ Family history of genetic disorders: Known carrier status or inherited conditions.
- ➤ Previous pregnancy with a genetic condition.
- ➤ Parental anxiety or desire for early diagnosis.
Benefits for patients:
- ✔️ Provides early and reliable genetic information.
- ✔️ Allows for earlier decision-making regarding pregnancy management.
- ✔️ Reduces the need for later, potentially more invasive tests.
- ✔️ Offers peace of mind when results are normal.
Alternatives
While CVS is a highly informative test, alternatives exist depending on gestational age and risk profile:
- ➤ Amniocentesis: Usually performed after 15 weeks of gestation; analyzes amniotic fluid for chromosomal or genetic abnormalities.
- ➤ Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT): Blood test from the mother to screen for certain chromosomal abnormalities.
- ➤ Ultrasound screening: Detects structural anomalies but not all genetic disorders.
- ➤ Combined first-trimester screening: Blood test plus nuchal translucency measurement for risk assessment.
Key point: CVS provides early and definitive genetic information compared to non-invasive methods, which are primarily screening tools.
Preparation
Preparation for CVS involves medical evaluation, counseling, and logistical planning.
Steps include:
- ✅ Medical history review: Maternal health, prior pregnancies, and family history of genetic disorders.
- ✅ Counseling session: Discuss procedure, benefits, risks, and alternatives.
- ✅ Blood tests: Evaluate maternal blood type and screen for infections.
- ✅ Imaging: Ultrasound to determine fetal position, placenta location, and gestational age.
- ✅ Fasting and hydration: Usually not required, but follow specific clinic instructions.
- ✅ Consent: Obtain informed consent after discussing potential complications and results.
Important: Proper preparation ensures patient safety and optimal sampling.
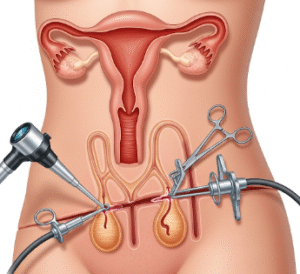
How It’s Done
CVS is performed under ultrasound guidance to ensure precision and safety.
Procedure options:
- Transcervical CVS:
- Patient lies in lithotomy position.
- Thin catheter inserted through the cervix to collect placental tissue.
- Ultrasound guidance ensures correct placement and sample collection.
- Transabdominal CVS:
- Patient lies on the back.
- Needle inserted through the abdominal wall into the placenta.
- Ultrasound guidance ensures correct placement and avoids fetal injury.
Duration: 15–30 minutes
Hospital stay: Usually outpatient; patient can return home the same day.
Sample handling: Tissue sent to a genetics lab for analysis; results typically available in 1–2 weeks.
Key point: CVS allows early detection of chromosomal and genetic abnormalities in a minimally invasive manner.
Recovery & Post-Procedure Care
Recovery from CVS is generally rapid, with some precautions:
Immediate post-procedure:
- Monitor for bleeding, cramping, or discomfort.
- Rest for several hours; avoid strenuous activity for 24–48 hours.
- Observe for fever or fluid leakage, which may indicate complications.
Short-term care:
- Avoid sexual intercourse, heavy lifting, or intense exercise for a few days.
- Mild cramping or spotting is common and usually resolves.
- Follow-up appointment for ultrasound check if recommended.
Long-term outcomes:
- Most women recover fully without complications.
- Results guide further pregnancy management and decision-making.
Important: Following post-procedure instructions minimizes the risk of complications.
Possible Complications
CVS is generally safe, but some risks exist:
- ⚠️ Miscarriage: Occurs in 0.5–1% of cases.
- ⚠️ Bleeding or spotting at the cervix or vagina.
- ⚠️ Cramping or abdominal pain for a few days.
- ⚠️ Infection: Rare but may require antibiotics.
- ⚠️ Rh sensitization: If mother is Rh-negative; managed with Rho(D) immune globulin.
- ⚠️ Limb defects or fetal injury: Extremely rare, mostly in very early gestation.
In South Korea, CVS is performed by experienced specialists with ultrasound guidance and sterile technique, minimizing risk and ensuring accurate results.
Treatment Options / Clinical Relevance in Korea
CVS is an essential early prenatal diagnostic tool in South Korea, offered in specialized obstetric and prenatal genetic centers.
Key features:
- 🏥 Early detection of chromosomal abnormalities for informed pregnancy management.
- 🏥 Expert prenatal counseling for families at risk of genetic disorders.
- 🏥 Integration with advanced ultrasound and genetic labs for accurate analysis.
- 🏥 Outpatient procedure with minimal recovery time.
- 🏥 Follow-up support for parents based on results and pregnancy decisions.
Hospitals and clinics performing CVS in Korea:
- Seoul National University Hospital – Prenatal genetic testing and counseling
- Asan Medical Center – Advanced prenatal diagnostics with ultrasound guidance
- Samsung Medical Center – Early pregnancy interventions and CVS procedures
- Specialized obstetrics clinics nationwide – Accessible CVS for high-risk pregnancies
Highlights in Korea:
- ✔️ CVS provides early and reliable detection of genetic conditions.
- ✔️ Procedures performed by experienced obstetricians and genetic specialists.
- ✔️ Ultrasound guidance ensures safe and precise tissue sampling.
- ✔️ Early results allow timely decisions regarding pregnancy management.
Highlights
- ➤ Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) detects chromosomal and genetic disorders early in pregnancy.
- ➤ Indicated for advanced maternal age, abnormal screening, family history, or prior affected pregnancy.
- ➤ Alternatives include amniocentesis, NIPT, ultrasound screening, or first-trimester combined tests.
- ➤ Preparation involves counseling, medical review, imaging, and informed consent.
- ➤ Procedure is minimally invasive, 15–30 minutes, and outpatient.
- ➤ Recovery includes rest, avoidance of strenuous activity, and monitoring for bleeding or cramping.
- ➤ South Korea provides advanced CVS services with experienced specialists, ultrasound guidance, and lab support for accurate prenatal genetic testing.