Overview
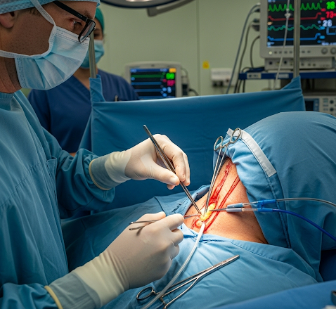
Carotid endarterectomy (CEA) is a surgical procedure performed to remove plaque buildup from the carotid arteries, which supply blood to the brain. The procedure aims to prevent stroke in patients with significant carotid artery narrowing (stenosis).
Importance of CEA:
- Reduces risk of ischemic stroke in patients with carotid artery disease.
- Improves blood flow to the brain.
- Prevents neurological complications such as transient ischemic attacks (TIAs).
- Enhances overall cerebrovascular health.
In South Korea, carotid endarterectomy is performed in specialized vascular and neurosurgery centers, with advanced imaging, intraoperative monitoring, and post-operative care to ensure high safety and effectiveness.
Why It’s Done
CEA is performed in patients with significant carotid artery stenosis to prevent stroke or TIA.
Common indications include:
- ➤ Severe carotid stenosis (≥70%) with or without symptoms.
- ➤ Moderate stenosis (50–69%) with symptoms such as TIA or minor stroke.
- ➤ Recurrent TIAs despite medical management.
- ➤ High-risk patients with atherosclerotic plaque prone to embolization.
- ➤ Preventive intervention in patients at risk of cerebrovascular events.
Benefits for patients:
- ✔️ Reduces risk of major stroke.
- ✔️ Improves blood flow to the brain, enhancing neurological function.
- ✔️ Prevents future transient ischemic attacks.
- ✔️ Supports long-term cerebrovascular health.
Alternatives
Several alternatives may be considered depending on patient health and stenosis severity:
- ➤ Medical management: Anti-platelet therapy, cholesterol-lowering medications, blood pressure control, and lifestyle modifications.
- ➤ Carotid artery stenting (CAS): Minimally invasive alternative using a stent to open the narrowed artery.
- ➤ Lifestyle changes: Smoking cessation, healthy diet, and regular exercise to reduce plaque progression.
Key point: CEA is generally preferred for symptomatic, high-grade stenosis, while stenting may be suitable for patients unsuitable for open surgery.
Preparation
Preparation for carotid endarterectomy is critical to reduce surgical risk.
Steps include:
- ✅ Comprehensive vascular evaluation: Doppler ultrasound, CT angiography, or MR angiography.
- ✅ Cardiac assessment: ECG, echocardiography, and assessment of anesthesia risk.
- ✅ Blood tests: CBC, kidney and liver function, coagulation profile.
- ✅ Medication review: Adjust anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents as advised.
- ✅ Consent and counseling: Explain procedure, risks, recovery expectations, and lifestyle changes.
- ✅ Fasting: Usually required 6–8 hours before surgery.
Important: Proper preoperative evaluation ensures patient safety and optimal surgical outcomes.
How It’s Done
Carotid endarterectomy is a surgical procedure performed under general or regional anesthesia.
Step-by-step process:
- Anesthesia administration: General anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation.
- Incision: Small incision along the side of the neck over the carotid artery.
- Artery exposure: The carotid artery is carefully isolated.
- Plaque removal: The surgeon removes the atherosclerotic plaque from the inner lining of the artery.
- Closure: The artery is repaired using sutures or a patch; blood flow is restored.
- Wound closure: Incision is closed; drains may be placed temporarily.
- Monitoring: Neurological function is closely observed during and after surgery.
Duration: 1–3 hours depending on complexity.
Hospital stay: Typically 1–3 days.
Key point: Intraoperative monitoring ensures neurological safety and blood flow integrity.
Recovery
Recovery after carotid endarterectomy involves close monitoring and gradual resumption of activities.
Immediate post-op:
- Monitoring of vital signs and neurological function in a high-dependency unit.
- Pain management and infection prevention.
- Early mobilization encouraged.
Short-term recovery:
- Mild neck pain or swelling may occur.
- Avoid strenuous activities for 2–4 weeks.
- Follow-up ultrasound to assess carotid artery patency.
Long-term recovery:
- Resume normal activities gradually.
- Continue medications as prescribed.
- Lifestyle modifications to prevent plaque recurrence.
- Regular follow-up with vascular specialist recommended.
Important: Compliance with medications and lifestyle recommendations ensures long-term success.
Possible Complications
CEA is generally safe but carries risks associated with surgery:
- ⚠️ Stroke – rare but serious complication.
- ⚠️ Heart attack – risk in patients with coronary artery disease.
- ⚠️ Nerve injury – causing temporary or permanent hoarseness, swallowing difficulties, or facial weakness.
- ⚠️ Bleeding or hematoma – may require intervention.
- ⚠️ Infection – incision or deeper tissue infection.
- ⚠️ Restenosis – recurrence of artery narrowing over time.
- ⚠️ Allergic reaction or anesthesia complications – rare but possible.
In South Korea, advanced surgical techniques, intraoperative monitoring, and post-operative care significantly reduce complication rates.
Treatment Options / Clinical Relevance in Korea
Carotid endarterectomy is performed in highly specialized vascular surgery centers in South Korea.
Key features:
- 🏥 Comprehensive vascular evaluation using Doppler ultrasound, CTA, and MRA.
- 🏥 Experienced vascular surgeons trained in advanced CEA and stenting techniques.
- 🏥 State-of-the-art operating theaters with intraoperative neuromonitoring.
- 🏥 Postoperative care including ICU monitoring, rehabilitation, and follow-up imaging.
- 🏥 Emergency and elective CEA available for symptomatic or high-risk patients.
Hospitals offering CEA in Korea:
- Asan Medical Center – High-volume vascular surgery center
- Samsung Medical Center – Advanced cerebrovascular surgery and monitoring
- Seoul National University Hospital – Comprehensive vascular and stroke program
- National Medical Center – Emergency and elective CEA services
Highlights in Korea:
- ✔️ Advanced surgical protocols ensure high success and low complication rates.
- ✔️ Integration of imaging, monitoring, and rehabilitation optimizes patient outcomes.
- ✔️ Both elective and urgent CEA are accessible across major hospitals.
- ✔️ Multidisciplinary approach with neurology, cardiology, and vascular surgery ensures comprehensive care.
Highlights
- ➤ Carotid endarterectomy removes plaque from carotid arteries to prevent stroke.
- ➤ Indicated for high-grade stenosis, symptomatic patients, or recurrent TIA.
- ➤ Alternatives include stenting, medical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
- ➤ Preparation involves vascular assessment, cardiac evaluation, blood tests, and fasting.
- ➤ Procedure duration: 1–3 hours under general or regional anesthesia.
- ➤ Recovery requires monitoring, gradual mobilization, and follow-up imaging.
- ➤ South Korea offers advanced CEA services with specialized surgical teams, modern operating theaters, and comprehensive post-operative care.