Overview
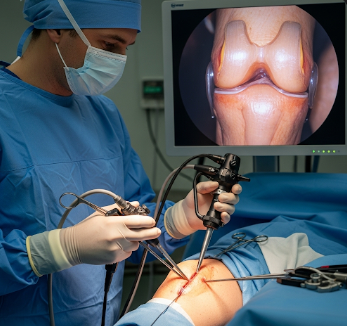
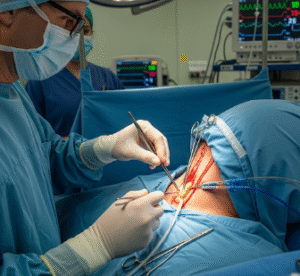
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to examine, diagnose, and treat problems inside a joint. It involves inserting a small camera called an arthroscope into the joint through a tiny incision, allowing the surgeon to visualize cartilage, ligaments, and other structures on a screen.
Commonly treated joints include:
- ➤ Knee
- ➤ Shoulder
- ➤ Hip
- ➤ Wrist
- ➤ Ankle
- ➤ Elbow
Benefits of arthroscopy:
- Minimally invasive: smaller incisions than open surgery.
- Reduced pain and scarring.
- Faster recovery and rehabilitation.
- Precise diagnosis of joint problems.
In South Korea, arthroscopy is widely performed in top orthopedic and sports medicine centers, with state-of-the-art equipment and expert surgeons skilled in advanced arthroscopic techniques. Korean hospitals also offer post-operative rehabilitation programs, making recovery faster and safer.
Why It’s Done
Arthroscopy is both diagnostic and therapeutic, meaning it can identify joint problems and, in many cases, treat them during the same procedure.
Common indications include:
- ➤ Meniscus tears – torn cartilage in the knee causing pain and locking.
- ➤ Ligament injuries – including ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) or PCL injuries.
- ➤ Cartilage damage – osteoarthritis or cartilage defects.
- ➤ Shoulder injuries – rotator cuff tears, labral tears, or impingement.
- ➤ Joint inflammation – synovitis or arthritis evaluation.
- ➤ Loose bodies – fragments of bone or cartilage floating in the joint.
- ➤ Joint infections – arthroscopy can help with diagnosis and cleaning.
Benefits for patients:
- ✔️ Less invasive than traditional open surgery.
- ✔️ Enables quicker return to daily activities and sports.
- ✔️ Allows targeted treatment with minimal joint trauma.
Alternatives
Alternative or complementary methods depend on the severity of the joint problem:
- ➤ Conservative management:
- Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE).
- Physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- ➤ Injections:
- Corticosteroids for inflammation.
- Hyaluronic acid for osteoarthritis.
- ➤ Open surgery:
- For severe joint damage that cannot be addressed arthroscopically.
- ➤ Imaging and monitoring:
- MRI or CT scan to assess internal joint structures before deciding on surgery.
Key difference: Arthroscopy is minimally invasive, diagnostic, and therapeutic, making it a preferred choice when conservative treatment fails or rapid intervention is needed.
Preparation
Proper preparation is critical for safety and effectiveness.
Typical steps include:
- ✅ Medical evaluation: Blood tests, imaging studies (X-ray, MRI), and medical history review.
- ✅ Medication adjustments: Blood thinners may need to be paused.
- ✅ Fasting: Usually no food or drink for 6–8 hours prior to surgery if general anesthesia is planned.
- ✅ Consent and explanation: Risks, benefits, and recovery expectations explained.
- ✅ Pre-operative rehabilitation advice: Guidance on exercises to support recovery.
- ✅ Hospital admission: Usually outpatient or short stay depending on joint and procedure.
How It’s Done
Arthroscopy is performed under general or regional anesthesia.
Step-by-step process:
- Joint preparation: The joint area is sterilized and draped.
- Small incision: A 0.5–1 cm incision is made to insert the arthroscope.
- Visualization: Saline may be injected to expand the joint and improve visibility.
- Diagnosis: Surgeon inspects cartilage, ligaments, and joint surfaces via camera.
- Treatment (if needed):
- Meniscus trimming or repair
- Ligament reconstruction
- Cartilage debridement or microfracture
- Removal of loose bodies
- Closure: Small incisions are stitched or taped.
- Dressing and compression: Applied to reduce swelling.
Duration: 30 minutes to 2 hours depending on joint and procedure.
Hospital stay: Usually outpatient; some patients may stay 1–2 days for monitoring.
Pain level:
- Mild to moderate post-operative pain, managed with medication.
- Swelling and stiffness are common initially.
Recovery
Recovery varies depending on the joint and extent of surgery, but arthroscopy generally allows faster rehabilitation than open surgery.
Immediate recovery:
- Joint elevation, ice, and compression to reduce swelling.
- Early gentle range-of-motion exercises encouraged.
- Pain management with prescribed medications.
Short-term recovery (1–6 weeks):
- Gradual increase in weight-bearing and mobility.
- Physical therapy for strengthening and flexibility.
- Monitoring for signs of infection or complications.
Long-term recovery (6–12 weeks):
- Return to work and light activities typically within a few weeks.
- Return to sports or heavy activities may take 2–3 months.
- Full joint recovery may take 3–6 months depending on complexity.
Possible Complications
Arthroscopy is generally safe but carries small risks:
- ⚠️ Infection – rare due to small incisions.
- ⚠️ Bleeding – minor bleeding in the joint.
- ⚠️ Blood clots – deep vein thrombosis (DVT) risk.
- ⚠️ Nerve or tissue injury – rare but possible.
- ⚠️ Joint stiffness or swelling – usually temporary.
- ⚠️ Incomplete repair – sometimes additional surgery may be required.
Korean orthopedic centers have high success rates and low complication incidence due to advanced techniques and strict infection control.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea is recognized for high-quality orthopedic care, offering arthroscopy with modern equipment and expert surgeons.
Why Korea for arthroscopy:
- 🏥 State-of-the-art operating rooms with high-definition arthroscopes.
- 🏥 Experienced orthopedic and sports medicine specialists.
- 🏥 Customized rehabilitation programs for faster recovery.
- 🏥 Minimally invasive techniques reducing hospital stay and scarring.
- 🏥 Affordable and internationally competitive care.
Hospitals and centers:
- Samsung Medical Center, Seoul – knee, shoulder, hip arthroscopy
- Asan Medical Center, Seoul – complex joint reconstructions
- Severance Hospital, Seoul – sports injury and ligament repair
- CHA Bundang Medical Center – comprehensive rehabilitation programs
Highlights
- ➤ Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure for joint diagnosis and treatment.
- ➤ Commonly used for knee, shoulder, hip, wrist, and ankle problems.
- ➤ Treats ligament tears, meniscus injuries, cartilage damage, inflammation, and loose bodies.
- ➤ Recovery is faster than open surgery, with most patients returning to daily activity within weeks.
- ➤ Risks are low but include infection, bleeding, DVT, stiffness, or incomplete repair.
- ➤ South Korea provides advanced arthroscopy, skilled surgeons, and rehabilitation programs, making it a top destination for joint care.