Overview
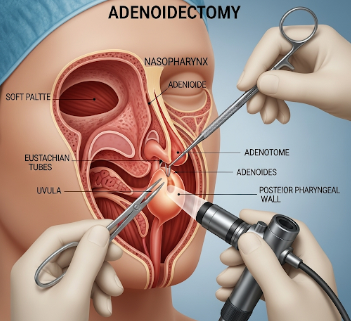
Adenoidectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the adenoids—small lymphatic tissue located at the back of the nasal passage, above the tonsils. The adenoids form part of the body’s immune system in childhood, helping fight infections by trapping harmful bacteria and viruses entering through the nose. However, in many children, the adenoids can become enlarged, chronically infected, or obstructive, leading to difficulty breathing, recurrent infections, and sleep disturbances.
While adenoids usually shrink by adolescence and often disappear in adulthood, their enlargement during childhood can cause significant health problems, necessitating removal. Adenoidectomy is one of the most common surgical procedures performed in children, though in some cases, adults may require the surgery if residual or regrown adenoid tissue causes complications.
In Korea, adenoidectomy is widely available in specialized ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) hospitals and pediatric centers. The procedure is performed using modern techniques such as endoscopic visualization, suction cautery, and coblation, ensuring minimal bleeding, fast recovery, and reduced pain. Korean hospitals are also popular among international patients seeking high-quality yet cost-effective surgical care.
Why It’s Done
Doctors may recommend adenoidectomy if the adenoids cause persistent or severe health issues.
Common reasons include:
- Chronic nasal obstruction: Difficulty breathing through the nose, leading to mouth breathing.
- Recurrent ear infections (otitis media): Enlarged adenoids can block the Eustachian tubes, leading to fluid buildup and infections.
- Sleep apnea or snoring: Blocked airways during sleep cause disrupted rest and potential long-term complications.
- Recurrent sinus infections: Frequent sinusitis not improving with medical treatment.
- Speech or swallowing problems: Enlarged adenoids affect speech resonance and swallowing.
- Chronic bad breath and nasal congestion: Due to trapped bacteria and mucus buildup.
Alternatives
Not every child or adult with enlarged adenoids requires surgery. Doctors often consider non-surgical treatments first:
- Antibiotics or nasal sprays to treat infections or inflammation.
- Allergy management (antihistamines, decongestants) for related nasal symptoms.
- Watchful waiting if the child is expected to outgrow enlarged adenoids naturally.
- Adenoid-sparing procedures such as laser reduction (used in select cases).
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): For patients with sleep apnea where surgery isn’t preferred.
If these measures fail to provide long-term relief, adenoidectomy becomes the recommended option.
Preparation
Preparation for adenoidectomy is straightforward but essential to ensure safety:
- ✅ Medical evaluation: ENT specialists assess symptoms, medical history, and often perform imaging or nasoendoscopy.
- ✅ Blood tests: To rule out clotting disorders or infections before surgery.
- ✅ Fasting instructions: No food or drinks 6–8 hours before surgery due to general anesthesia.
- ✅ Medication review: Stop blood-thinning medicines (if applicable) as per doctor’s instructions.
- ✅ Parental guidance: For children, parents are informed about anesthesia, risks, and recovery expectations.
How It’s Done
Adenoidectomy is usually an outpatient procedure, meaning patients can return home the same day.
Step-by-step process:
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia ensures the patient is asleep and pain-free.
- Access: The surgeon reaches the adenoids through the mouth, so there are no external incisions or scars.
- Removal methods:
- Curettage: Surgical scraping of adenoids.
- Electrocautery / Suction cautery: Heat-based removal with minimal bleeding.
- Coblation (radiofrequency energy): Precise removal with less tissue damage and faster recovery.
- Endoscopic-assisted adenoidectomy: Camera-guided removal for accuracy.
- Bleeding control: Cauterization or packing is used to stop bleeding.
- Completion: The procedure typically lasts 20–45 minutes.
In many cases, adenoidectomy is performed along with tonsillectomy (adenotonsillectomy) if both tissues are problematic.
Recovery
Recovery from adenoidectomy is generally smooth, especially in children.
Typical recovery timeline:
- ✔️ Hospital stay: Usually discharged the same day or after overnight observation.
- ✔️ Pain: Mild throat or nasal discomfort for 3–5 days, managed with painkillers.
- ✔️ Diet: Soft, cool foods (ice cream, yogurt, soup) recommended for the first week.
- ✔️ Activity: Rest for a few days; avoid strenuous activity for 1–2 weeks.
- ✔️ Healing: Most children return to normal activities within 7–10 days.
Benefits noticed after surgery:
- Better breathing through the nose.
- Improved sleep quality (reduced snoring and apnea).
- Fewer ear and sinus infections.
- Enhanced speech clarity and overall quality of life.
Possible Complications
While adenoidectomy is safe, as with any surgery, complications can occur:
- ⚠️ Bleeding: Rare but possible during or after surgery.
- ⚠️ Infection: Minor throat or nasal infections may occur.
- ⚠️ Nasal regrowth: In rare cases, adenoids can regrow, especially in young children.
- ⚠️ Velopharyngeal insufficiency (VPI): A rare condition where speech sounds nasal due to improper closure between the nose and mouth.
- ⚠️ Adverse reactions to anesthesia.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea is one of the leading countries for pediatric ENT surgeries, including adenoidectomy.
- 🏥 Advanced technology: Korean hospitals use endoscopic and coblation methods for precise, minimally invasive adenoid removal.
- 🏥 Skilled surgeons: ENT specialists in Korea undergo rigorous training and handle thousands of adenoid and tonsil surgeries each year.
- 🏥 Medical tourism infrastructure: International patients benefit from English-speaking coordinators, streamlined booking, and affordable package deals.
- 🏥 Child-friendly hospitals: Many pediatric centers provide comfort-focused care, reducing anxiety for both children and parents.
- 🏥 Integrated care: Adenoidectomy is often combined with allergy management, sinus treatments, or ear tube placement for comprehensive outcomes.