Overview
Chronic wounds are wounds that fail to heal within the expected timeframe of 4–12 weeks despite appropriate care. They are a major healthcare concern worldwide due to their risk of infection, prolonged pain, and impaired quality of life.
➤ Chronic wounds are often associated with underlying medical conditions, including diabetes mellitus, vascular disease, and immune dysfunction.
➤ They may occur on the lower limbs, pressure points, or surgical sites, and require specialized treatment.
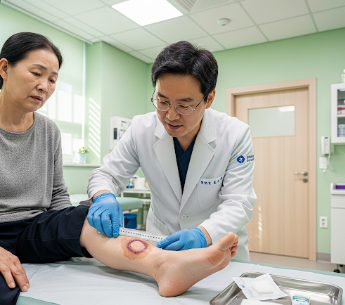
➤ In Korea, wound care centers provide advanced diagnostics, dressings, infection control, and surgical options for chronic wounds.
Key Facts
► Definition: Wounds that do not heal normally or remain open beyond 4–12 weeks.
► Prevalence: Common in elderly patients, diabetics, and immobile individuals.
► Associated symptoms: Persistent pain, redness, swelling, foul odor, and discharge.
► Risk factors: Diabetes, vascular disease, poor nutrition, smoking, infection, and immobility.
► Treatment in Korea: Includes advanced wound dressings, debridement, infection management, and surgical interventions.
What Are Chronic Wounds?
Chronic wounds differ from acute wounds due to their inability to progress through the normal healing stages: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling.
➔ They may persist due to poor blood supply, repeated trauma, infection, or systemic disease.
➔ Common types include diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, arterial ulcers, pressure sores (decubitus ulcers), and post-surgical non-healing wounds.
➔ Chronic wounds significantly increase the risk of complications, including severe infection and, in extreme cases, amputation.
What Symptoms Are Related to Chronic Wounds?
Symptoms may include:
→ Open sores or ulcers that fail to heal.
→ Persistent pain, burning, or tenderness around the wound.
→ Redness, warmth, or swelling indicating inflammation or infection.
→ Foul odor or purulent discharge in infected wounds.
→ Thickened or discolored surrounding skin, sometimes with necrosis.
→ Slow healing despite basic wound care.
→ Functional impairment if wounds affect limbs or joints.
Causes / Possible Causes of Chronic Wounds
Vascular Causes
➤ Peripheral artery disease (PAD) – Reduced blood flow impairs healing.
➤ Chronic venous insufficiency – Causes venous leg ulcers due to poor venous return.
Metabolic and Systemic Causes
➔ Diabetes mellitus – Hyperglycemia damages small vessels and nerves, leading to diabetic foot ulcers.
➔ Malnutrition – Protein, vitamin, or mineral deficiencies slow healing.
➔ Immune disorders – Impaired immunity can delay wound repair.
Mechanical and Pressure-Related Causes
→ Pressure ulcers (decubitus ulcers) – Result from prolonged pressure on bony prominences in immobile patients.
→ Repeated trauma or friction – Prevents normal healing.
→ Surgical wounds – Poor closure or infection may result in chronic wounds.
Infectious Causes
➤ Bacterial colonization or infection – Impedes normal healing and may worsen tissue damage.
➤ Fungal infections – Rare, but can contribute to delayed healing in immunocompromised patients.
Other Contributing Factors
➔ Smoking – Reduces blood flow and oxygen delivery to tissues.
➔ Medications – Steroids, chemotherapy, or immunosuppressants may impair healing.
➔ Chronic edema – Delays wound closure.
When Should I See My Doctor?
Immediate evaluation is necessary if:
➤ Wound does not heal within 4–12 weeks.
➤ Signs of infection: pus, redness, warmth, swelling, or foul odor.
➤ Wound causes severe pain or functional limitation.
➤ You have diabetes or vascular disease with a chronic wound.
➤ Early intervention helps prevent serious complications such as sepsis or amputation.
Care and Treatment
Lifestyle and Self-Care Measures
► Keep the wound clean and covered with sterile dressings.
► Avoid smoking and alcohol, which impede healing.
► Maintain adequate nutrition, including protein, vitamins C and A, and zinc.
► Offload pressure from affected areas, especially in foot or pressure ulcers.
► Monitor wounds daily for signs of infection or changes.
Medical Treatments
➔ Debridement – Removal of dead tissue to promote healing.
➔ Infection management – Topical or systemic antibiotics for bacterial infections.
➔ Advanced wound dressings – Hydrocolloid, foam, or antimicrobial dressings.
➔ Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) – Vacuum-assisted closure to stimulate tissue growth.
Procedural and Advanced Interventions
→ Skin grafting or flap surgery – For large, non-healing wounds.
→ Revascularization – Surgery for arterial insufficiency to improve blood flow.
→ Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) – Enhances tissue oxygenation in refractory wounds.
→ Laser or growth factor therapy – Stimulates wound healing in selected cases.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis in Korea
➤ Comprehensive assessment by wound care specialists or dermatologists.
➤ Laboratory tests to check for infection, diabetes control, and nutritional status.
➤ Imaging studies (ultrasound, angiography) to evaluate blood flow or tissue damage.
Non-Surgical Care
► Professional wound cleaning and dressing changes.
► Infection control with topical or systemic antibiotics.
► Education on offloading pressure, hygiene, and nutrition.
► Physical therapy to improve circulation and mobility.
Advanced Care
➔ Surgical interventions such as skin grafts, flaps, or revascularization.
➔ Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and novel growth factor or stem cell treatments for non-healing wounds.
➔ Multidisciplinary care for complex cases involving endocrinology, vascular surgery, and rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation and Lifestyle Support
→ Guidance on preventing recurrence and protecting affected areas.
→ Education on diabetes management, vascular health, and lifestyle modifications.
→ Regular follow-up to monitor healing, prevent infection, and maintain mobility.
Korean clinics provide advanced wound care services combining modern dressings, surgical options, and multidisciplinary management to ensure effective healing and prevention of complications in chronic wounds.