Overview
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of blood vessels due to contraction of the smooth muscle in the vessel walls, which decreases blood flow and increases blood pressure. It is a natural physiological response essential for regulating body temperature, blood pressure, and tissue perfusion.
➤ Vasoconstriction occurs in response to cold temperatures, stress, hormonal signals, and certain medications.
➤ While essential for survival, prolonged or excessive vasoconstriction can contribute to conditions like hypertension, heart disease, or tissue ischemia.
➤ In Korea, cardiovascular clinics provide diagnostic evaluation, medical management, and advanced therapies for conditions related to abnormal vasoconstriction.
Key Facts
► Definition: The narrowing of blood vessels caused by contraction of smooth muscle in the vessel walls.
► Prevalence: A normal physiological response; excessive vasoconstriction is common in cardiovascular diseases.
► Associated symptoms: Cold extremities, pale or bluish skin, high blood pressure, headaches, or tissue ischemia.
► Risk factors: Stress, smoking, diabetes, hypertension, certain medications, and autoimmune disorders.
► Treatment in Korea: Focuses on lifestyle modification, medications, and management of underlying cardiovascular or metabolic disorders.
What Is Vasoconstriction?
Vasoconstriction is a process in which blood vessels, particularly arteries and arterioles, reduce their diameter.
➔ This response is controlled by the autonomic nervous system, hormones (like norepinephrine and angiotensin II), and local chemical signals.
➔ Vasoconstriction helps redirect blood flow to vital organs, conserve heat, and maintain systemic blood pressure.
➔ Excessive or prolonged vasoconstriction can reduce oxygen supply to tissues, contributing to ischemia and organ damage.
What Symptoms Are Related to Vasoconstriction?
Symptoms vary depending on severity, location, and underlying cause:
→ Cold hands and feet due to reduced peripheral blood flow.
→ Pale or bluish skin (cyanosis) in affected areas.
→ High blood pressure (hypertension) from increased vascular resistance.
→ Headaches or migraines, often linked to cerebral vasoconstriction.
→ Chest pain or angina if coronary arteries are affected.
→ Muscle cramps or pain in severe peripheral vasoconstriction.
→ Delayed wound healing due to reduced tissue perfusion.
Causes / Possible Causes of Vasoconstriction
Physiological Causes
➤ Cold exposure: Vasoconstriction preserves core body temperature.
➤ Stress response: Release of catecholamines (adrenaline, norepinephrine) triggers vessel constriction.
➤ Exercise regulation: Redirects blood flow to muscles during activity.
Pathological Causes
➔ Hypertension: Chronic vasoconstriction contributes to high blood pressure.
➔ Raynaud’s phenomenon: Exaggerated vasoconstriction in fingers and toes causing pain and color changes.
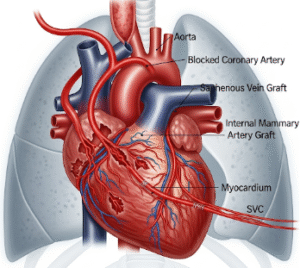
➔ Atherosclerosis: Narrowed arteries increase the risk of tissue ischemia.
Medications and Substances
→ Decongestants (pseudoephedrine), stimulants, nicotine, and certain chemotherapy drugs can cause vasoconstriction.
→ Caffeine and cocaine may trigger acute vessel narrowing.
Endocrine and Metabolic Causes
► Diabetes mellitus and hyperthyroidism may contribute to abnormal vascular tone.
► Hormonal imbalances affecting angiotensin or endothelin pathways.
When Should I See My Doctor?
Medical consultation is recommended if vasoconstriction:
➤ Causes persistent cold extremities, pain, or color changes.
➤ Is associated with high blood pressure, chest pain, or headaches.
➤ Occurs frequently or severely in fingers and toes (possible Raynaud’s phenomenon).
➤ Persists despite avoiding triggers like cold exposure or stress.
➤ Early evaluation helps prevent complications like tissue damage, cardiovascular events, or organ ischemia.
Care and Treatment
Lifestyle and Self-Care Measures
► Maintain warmth in cold environments (gloves, warm clothing).
► Avoid smoking, caffeine excess, and stimulant use.
► Practice stress management techniques like meditation or yoga.
► Regular physical activity to improve vascular health and circulation.
► Maintain a healthy diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants to support vessel function.
Medical Treatments
➔ Vasodilator medications to counteract excessive vasoconstriction (e.g., calcium channel blockers, nitrates).
➔ Alpha-blockers or beta-blockers for conditions like hypertension or Raynaud’s phenomenon.
➔ Topical or systemic therapy for localized vasoconstriction-related issues.
➔ Treatment of underlying conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or autoimmune disorders.
Surgical and Advanced Interventions
→ Rarely, angioplasty or bypass procedures may be required for severe arterial narrowing.
→ Advanced therapies in Korea include endovascular interventions and minimally invasive vascular procedures for patients with critical ischemia.
→ Multidisciplinary approach for cardiovascular, neurological, and endocrine contributors.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean cardiovascular and medical centers provide comprehensive care for vasoconstriction-related conditions:
Diagnosis in Korea
➤ Blood pressure monitoring and vascular imaging (Doppler ultrasound, CT angiography).
➤ Blood tests for lipid profile, glucose, and hormone levels.
➤ Evaluation of autonomic function and peripheral circulation.
Non-Surgical Care
► Lifestyle counseling, stress reduction, and dietary modification.
► Prescription medications to control blood pressure and improve vascular tone.
► Physical therapy for peripheral circulation and extremity warming.
Advanced and Surgical Care
➔ Angioplasty or stenting for narrowed arteries causing ischemia.
➔ Laser or endovascular treatments for localized vascular constriction.
➔ Multidisciplinary approach combining cardiology, endocrinology, and vascular surgery.
Rehabilitation and Lifestyle Support
→ Ongoing monitoring for blood pressure and circulation.
→ Guidance on exercise, diet, and avoiding vasoconstrictive triggers.
→ Long-term follow-up for patients with chronic hypertension, diabetes, or vascular disease.
Korean hospitals combine expert cardiologists, advanced diagnostic tools, and patient-centered care, ensuring effective management of vasoconstriction and its associated complications.