Overview
Unexplained weight gain refers to a noticeable increase in body weight that occurs without obvious changes in diet, lifestyle, or physical activity. Unlike gradual weight gain due to aging, overeating, or lack of exercise, this type of weight gain often points to hidden medical, hormonal, or metabolic conditions.
It is important to recognize that this symptom is not always related to lifestyle. Instead, it can signal issues such as thyroid dysfunction, fluid retention, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), medication side effects, or cardiovascular disease.
➤ Many people first notice this problem when their clothes no longer fit, or when they feel swollen without dietary changes.
➤ Left untreated, unexplained weight gain may increase risks for diabetes, obesity, heart disease, and reduced quality of life.
➤ In South Korea, hospitals use advanced diagnostic testing and personalized treatment programs to help identify root causes and restore metabolic balance.
What is Unexplained Weight Gain?
Unexplained weight gain is not a disease but a symptom that indicates an underlying imbalance or condition. The body either retains excess fat, water, or both, leading to sudden or progressive weight increases.
➔ For some individuals, weight may increase rapidly over days or weeks.
➔ For others, it may build gradually despite stable eating habits and exercise routines.
Because the causes are diverse—from endocrine disorders to medication effects—diagnosis usually requires a comprehensive medical evaluation.
Symptoms Associated with Unexplained Weight Gain
Unexplained weight gain is often accompanied by other symptoms that provide clues to the underlying condition:
► Swelling or puffiness in the face, hands, legs, or ankles (possible fluid retention).
► Fatigue and low energy, commonly seen in hypothyroidism.
► Menstrual irregularities in women, especially with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
► Depression, anxiety, or mood swings, often linked to hormonal imbalances.
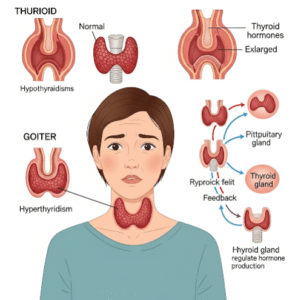
► Hair loss, dry skin, or brittle nails, common in thyroid-related disorders.
► Shortness of breath or chest discomfort, suggesting heart or kidney issues.
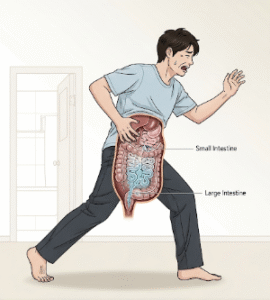
► Bloating or abdominal distension, which may indicate liver disease or digestive problems.
Causes of Unexplained Weight Gain
Hormonal and Endocrine Causes
➤ Hypothyroidism: An underactive thyroid slows metabolism, reducing calorie burning.
➤ Cushing’s syndrome: Excess cortisol production promotes fat accumulation in the abdomen, back, and face.
➤ PCOS: Affects reproductive-age women, causing weight gain, infertility, and irregular cycles.
➤ Menopause: Hormonal changes slow metabolism and shift fat storage patterns.
Metabolic and Organ-Related Causes
➔ Congestive heart failure: Causes fluid buildup in tissues, leading to sudden weight increases.
➔ Kidney disease: Reduced filtration leads to water retention and swelling.
➔ Liver cirrhosis: Triggers ascites, or fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity.
Medication-Induced Causes
→ Antidepressants (SSRIs, tricyclics) can increase appetite and alter metabolism.
→ Corticosteroids contribute to fat storage and water retention.
→ Diabetes medications (insulin, sulfonylureas) may increase body fat.
→ Beta-blockers slow metabolism and reduce activity levels.
Lifestyle and Psychological Causes
► Chronic stress raises cortisol, promoting abdominal fat storage.
► Poor sleep disrupts ghrelin and leptin, hormones that regulate appetite.
► Emotional eating due to depression or anxiety.
Other Factors
➤ Genetic predisposition to slow metabolism.
➤ Rare tumors affecting hormonal production.
➤ Systemic illnesses or hidden infections.
Risk Factors
Individuals more prone to unexplained weight gain include:
➔ Middle-aged adults experiencing natural metabolic slowdown.
➔ Women with PCOS, pregnancy-related hormonal shifts, or menopause.
➔ Patients on long-term medications such as antidepressants or steroids.
➔ People with a family history of thyroid or endocrine disorders.
When to See a Doctor
While minor fluctuations in weight are normal, medical attention is necessary when:
→ Weight gain exceeds 2–3 kg within a week without changes in diet or exercise.
→ Accompanied by persistent swelling, bloating, or fatigue.
→ Irregular periods, hair loss, or mood swings develop.
→ Weight increases despite normal or reduced food intake.
→ Symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or abdominal swelling appear.
Ignoring these warning signs may delay treatment for serious conditions like heart failure or thyroid disease.
Complications
If left untreated, unexplained weight gain can lead to:
➤ Obesity and increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
➤ Hypertension and cardiovascular disease.
➤ Joint pain and reduced mobility from added weight.
➤ Emotional distress due to appearance-related concerns.
➤ Chronic fatigue and reduced quality of life.
Care and Treatment
Self-Care and Lifestyle Adjustments
► Adopt a balanced, nutrient-rich diet while avoiding excessive calories.
► Engage in regular physical activity, including cardio and strength training.
► Limit sodium intake to reduce water retention.
► Prioritize quality sleep and stress management.
► Track weight weekly to detect sudden changes.
Medical Treatments
➔ Hormone replacement therapy for thyroid or adrenal conditions.
➔ Diuretics for fluid retention caused by heart or kidney problems.
➔ Adjustments in medications if weight gain is drug-induced.
➔ Prescription weight-loss medications for resistant cases.
Advanced Interventions
→ Bariatric surgery (gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy) for obesity resistant to lifestyle changes.
→ Endoscopic weight-loss procedures with minimal downtime.
→ Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for stress-related or emotional overeating.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea is a leading hub for endocrinology, weight management, and metabolic health care. Hospitals offer comprehensive diagnostic services and advanced treatments.
Diagnosis in Korea
➤ Hormonal and thyroid function testing.
➤ Complete metabolic and nutritional analysis.
➤ High-resolution imaging (MRI, ultrasound) for organ function.
➤ Genetic screening for rare metabolic disorders.
Non-Surgical Treatments
► Personalized diet and fitness programs tailored to individual metabolism.
► Medication optimization with close monitoring.
► Lifestyle counseling and stress reduction programs.
Surgical & Advanced Options
➔ Bariatric and metabolic surgery using minimally invasive techniques.
➔ Endoscopic procedures with faster recovery times.
➔ Specialized hormone therapy under endocrinologist supervision.
Rehabilitation and Long-Term Support
→ Ongoing health monitoring through mobile apps and digital platforms.
→ Integrative rehabilitation combining nutrition, exercise, and counseling.
→ Preventive care programs designed for sustainable weight management.
Korea’s healthcare system combines cutting-edge medical technology, highly trained specialists, and patient-centered care, making it one of the best destinations for managing unexplained weight gain.