➤ Overview
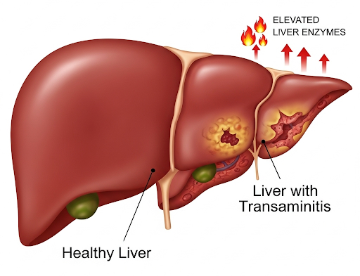
Transaminitis refers to an elevation of liver enzymes, specifically alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), which indicates liver inflammation or injury. It is not a disease itself but a biochemical marker suggesting possible underlying liver conditions. Transaminitis can be mild, moderate, or severe, and may result from hepatitis, fatty liver disease, medications, or metabolic disorders.
In South Korea, transaminitis is routinely evaluated in primary care and hepatology clinics using blood tests, imaging, and liver function panels. Timely assessment is critical to identify reversible causes, prevent progression, and reduce complications such as cirrhosis or liver failure.
➤ Key Facts
→ Transaminitis is defined as elevated ALT and AST above the upper normal limits.
→ Mild elevations are often asymptomatic and discovered incidentally on routine blood tests.
→ Common causes include viral hepatitis, fatty liver disease, alcohol use, and medications.
→ Persistent or severe elevations require immediate evaluation.
→ In Korea, transaminitis management combines modern hepatology, lifestyle interventions, and follow-up monitoring.
→ It can be temporary or chronic, depending on the underlying cause.
→ Early intervention can prevent liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and other complications.
➤ What is Transaminitis?
Transaminitis refers to abnormally high levels of liver enzymes in the blood:
→ Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) – Primarily found in the liver; a sensitive marker of hepatocellular injury.
→ Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) – Found in liver, heart, and muscles; elevations indicate liver or muscle involvement.
→ Mild, moderate, or severe – Classified based on multiples of the upper normal limit.
→ Acute vs. chronic – Sudden elevations may indicate infection or drug-induced injury; chronic elevations may signal fatty liver or autoimmune hepatitis.
→ Asymptomatic vs. symptomatic – Many patients have no symptoms, while some experience fatigue, abdominal discomfort, or jaundice.
→ Marker, not disease – Transaminitis indicates liver stress or damage but requires evaluation to identify the cause.
➤ What Symptoms are Related to Transaminitis?
Transaminitis itself may not cause symptoms, but associated liver conditions can produce:
→ Fatigue or malaise → Common in mild or chronic liver injury.
→ Abdominal discomfort → Especially in the right upper quadrant.
→ Jaundice → Yellowing of skin or eyes in significant liver damage.
→ Nausea or vomiting → Can accompany hepatitis or drug-induced liver injury.
→ Dark urine and pale stools → Indicate impaired bile excretion.
→ Loss of appetite → Often seen in chronic liver disease.
→ Itching (pruritus) → May occur with cholestasis.
→ Weight loss or muscle wasting → In prolonged liver disease.
➤ What Causes / Possible Causes?
Transaminitis can arise from numerous hepatic and systemic conditions:
→ Viral hepatitis – Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E infections.
→ Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) – Often linked to obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
→ Alcohol-related liver disease – Chronic alcohol consumption causing hepatocellular injury.
→ Medications and toxins – Acetaminophen overdose, statins, antibiotics, and herbal supplements.
→ Autoimmune hepatitis – Immune system attacks liver cells, leading to inflammation.
→ Genetic/metabolic disorders – Hemochromatosis, Wilson’s disease, or alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
→ Cardiac or muscle injury – AST elevations can be from myocardial infarction or muscle trauma.
→ Biliary obstruction – Gallstones or strictures causing liver stress.
→ Ischemic hepatitis – Reduced blood flow to the liver due to shock or heart failure.
➤ When Should I See My Doctor?
Prompt evaluation is necessary if transaminitis is:
→ Detected incidentally with elevated ALT/AST on routine labs.
→ Accompanied by jaundice, severe fatigue, or abdominal pain.
→ Persistent for more than a few weeks despite lifestyle modifications.
→ Associated with risk factors – Alcohol use, obesity, diabetes, or viral hepatitis exposure.
→ Linked to medications known to cause liver injury.
→ In Korea, hepatology and internal medicine specialists provide comprehensive evaluation, blood work, and imaging to identify the cause and plan treatment.
➤ Care and Treatment
Management focuses on identifying the cause and preventing liver damage:
→ Lifestyle modifications – Weight loss, diet control, and alcohol abstinence.
→ Medication review – Discontinue or adjust drugs causing liver injury.
→ Antiviral therapy – For hepatitis B or C infections.
→ Management of metabolic syndrome – Controlling diabetes, hypertension, and cholesterol.
→ Monitoring liver enzymes – Regular blood tests to assess improvement or progression.
→ Supportive care – Hydration, adequate nutrition, and avoidance of hepatotoxic substances.
→ Treatment of underlying disease – Autoimmune hepatitis, gallstones, or genetic disorders.
→ Patient education – Understanding liver health and risk factors.
➤ Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides advanced hepatology care for patients with transaminitis:
Diagnosis in Korea
→ Comprehensive blood tests – Liver function panels, viral hepatitis markers, autoimmune tests.
→ Ultrasound and imaging – Detect fatty liver, fibrosis, or structural abnormalities.
→ Elastography – Measures liver stiffness to assess fibrosis progression.
→ Genetic testing – For hereditary liver diseases if indicated.
→ Specialist evaluation – Hepatologists and internal medicine physicians collaborate on diagnosis.
Medical Treatments in Korea
→ Antiviral medications – For viral hepatitis B or C.
→ Lifestyle intervention programs – Supervised diet, exercise, and alcohol cessation programs.
→ Drug adjustment – For medications contributing to liver enzyme elevation.
→ Management of comorbidities – Diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia control.
Advanced Therapies in Korea
→ Interventional procedures – For biliary obstruction or liver lesions if detected.
→ Multidisciplinary care – Hepatology, gastroenterology, nutrition, and primary care coordination.
→ Patient education and follow-up – Ensures sustained liver health and monitoring for progression.
Rehabilitation & Support in Korea
→ Guidance on diet, exercise, and lifestyle modifications to maintain liver function.
→ Regular monitoring of liver enzymes and imaging for early detection of complications.
→ Support for chronic liver disease management and prevention of cirrhosis or liver failure.