➤ Overview
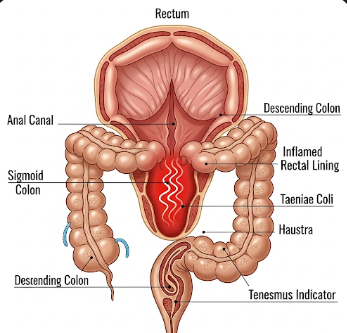
Tenesmus is a medical symptom characterized by a persistent feeling of incomplete bowel evacuation, often accompanied by straining, discomfort, or the urge to defecate without producing stool. It is not a disease itself but a sign of underlying gastrointestinal issues.
In South Korea, tenesmus is evaluated by gastroenterologists and colorectal specialists using advanced diagnostics to identify the underlying cause, which may range from infections to inflammatory or structural bowel disorders. Early recognition and treatment help relieve discomfort and prevent complications such as chronic constipation or rectal irritation.
➤ Key Facts
→ Tenesmus can affect all age groups, though causes may vary by age.
→ It is often associated with rectal pain, cramping, or urgency.
→ The symptom may be acute or chronic, depending on underlying conditions.
→ Common causes include infections, inflammatory bowel disease, colorectal tumors, or anal disorders.
→ In Korea, evaluation often includes physical examination, colonoscopy, imaging, and lab tests.
→ Untreated tenesmus may lead to anal fissures, hemorrhoids, or chronic discomfort.
→ Management focuses on treating the underlying condition and relieving symptoms.
➤ What is Tenesmus?
Tenesmus refers to the sensation of needing to pass stool even after a bowel movement, often associated with discomfort or straining:
→ Rectal tenesmus – Feeling of incomplete evacuation originating from the rectum.
→ Colonic tenesmus – Urge related to inflammation in the colon, such as ulcerative colitis.
→ Functional tenesmus – Occurring without structural abnormalities, sometimes linked to irritable bowel syndrome.
→ Painful tenesmus – Often caused by infection, inflammation, or tumor in the rectal area.
→ Chronic tenesmus – Persistent sensation lasting weeks or months, requiring medical evaluation.
In Korea, gastroenterologists differentiate tenesmus types based on history, clinical examination, and diagnostic testing.
➤ What Symptoms are Related to Tenesmus?
Tenesmus may occur with a variety of bowel, abdominal, and systemic symptoms:
→ Urgent need to defecate → Often with little or no stool passage.
→ Rectal pain or discomfort → Burning or cramping sensation.
→ Straining during bowel movements → Feeling of incomplete evacuation.
→ Mucus or blood in stool → May indicate infection or inflammation.
→ Frequent bowel movements → Especially in inflammatory bowel disease or infection.
→ Abdominal cramping or bloating → Often accompanies urgency.
→ Tenesmus at night → Could indicate more severe underlying conditions.
→ Nausea or fatigue → In chronic or severe cases.
→ Changes in stool consistency – Diarrhea or constipation may accompany tenesmus.
→ Fever – May occur if an infection is present.
➤ What Causes / Possible Causes?
Tenesmus can arise from infectious, inflammatory, structural, or functional causes:
→ Infections – Bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections of the rectum or colon.
→ Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) – Ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease causing rectal irritation.
→ Colorectal tumors – Benign or malignant growths leading to obstruction or irritation.
→ Hemorrhoids – Swollen veins in the rectal area causing discomfort and incomplete evacuation.
→ Anal fissures – Tears in the lining of the anus leading to pain during defecation.
→ Rectal prolapse or intussusception – Structural abnormalities affecting bowel movements.
→ Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) – Functional disorder causing urgency and incomplete evacuation.
→ Radiation proctitis – Inflammation following radiation therapy for pelvic cancers.
→ Post-surgical changes – After colorectal or anal surgery leading to altered rectal sensation.
➤ When Should I See My Doctor?
Medical evaluation is recommended if tenesmus is persistent, severe, or accompanied by warning signs:
→ Tenesmus lasting more than a few days or weeks.
→ Rectal bleeding, mucus, or pus in the stool.
→ Severe or worsening pain during bowel movements.
→ Unexplained weight loss or fatigue.
→ Fever or systemic symptoms suggesting infection.
→ Changes in bowel habits – Chronic diarrhea or constipation.
→ Tenesmus associated with a family history of colorectal cancer or inflammatory bowel disease.
→ Failure of symptom improvement with over-the-counter treatments or lifestyle changes.
Early consultation in Korea allows timely diagnosis, tailored therapy, and prevention of complications.
➤ Care and Treatment
Management of tenesmus focuses on relieving discomfort and treating the underlying cause:
→ Medications – Antibiotics for infections, anti-inflammatory drugs for IBD, or stool softeners.
→ Dietary modifications – High-fiber diet, adequate hydration, and avoidance of irritant foods.
→ Topical treatments – Suppositories or creams for hemorrhoids or anal fissures.
→ Behavioral interventions – Bowel training and scheduled defecation to reduce urgency.
→ Pain management – Analgesics or sitz baths to relieve rectal discomfort.
→ Surgical interventions – Removal of polyps, hemorrhoidectomy, or correction of prolapse if structural causes exist.
→ Monitoring and follow-up – Regular evaluation to track response to therapy.
→ Lifestyle adjustments – Stress management and regular physical activity to improve bowel function.
➤ Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides advanced diagnostic and therapeutic care for tenesmus:
Diagnosis in Korea
→ Physical examination – Rectal exam to assess anal and rectal health.
→ Colonoscopy – Detect inflammation, polyps, tumors, or structural abnormalities.
→ Imaging studies – CT, MRI, or ultrasound for bowel assessment.
→ Laboratory tests – Stool analysis, blood tests, and infection screening.
→ Functional assessment – Evaluating bowel movement patterns and rectal sensation.
Medical Treatments in Korea
→ Pharmacological therapy – Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, antispasmodics, or stool softeners.
→ Topical therapy – Suppositories, creams, or ointments for hemorrhoids or fissures.
→ Dietary counseling – High-fiber diet, hydration, and avoidance of irritants.
Advanced Therapies in Korea
→ Minimally invasive surgery – For hemorrhoids, polyps, or rectal prolapse.
→ Endoscopic procedures – Polyp removal or biopsy for diagnosis.
→ Integrated IBD management programs – Combining medication, nutrition, and lifestyle coaching.
Rehabilitation & Support in Korea
→ Education on bowel habits, dietary strategies, and symptom monitoring.
→ Regular follow-up to monitor treatment efficacy, prevent recurrence, and manage chronic conditions.
→ Collaboration with gastroenterology, colorectal surgery, and nutrition specialists for comprehensive care.