Overview
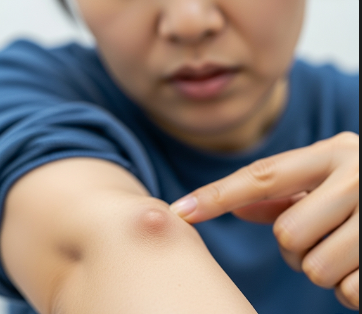
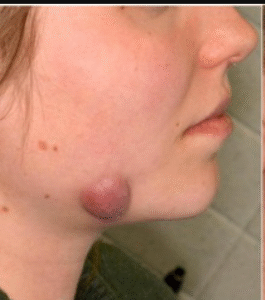
Rheumatoid nodules are firm, round, non-painful lumps that develop under the skin, most often near pressure points such as the elbows, fingers, or heels. They are strongly associated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation in the joints.
In Korea, rheumatology specialists frequently encounter rheumatoid nodules as part of RA management. While they are generally harmless, their presence often indicates more severe or long-standing disease activity, and in some cases, they may cause discomfort or complications if they press on nerves or tissues.
➤ Usually seen in advanced rheumatoid arthritis
➤ Appear as firm, rubbery lumps under the skin
➤ Not usually painful, but may interfere with movement
➤ Treated mainly by controlling underlying RA
Key Facts
➤ Found in up to 20–30% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
➤ More common in patients with positive rheumatoid factor (RF) or anti-CCP antibodies
➤ Size can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters
➤ Rarely appear in people without rheumatoid arthritis
What are Rheumatoid Nodules?
Rheumatoid nodules are subcutaneous lumps of inflamed tissue caused by chronic immune activity in RA. They develop due to:
- Inflammatory cell accumulation
- Fibrosis (scar tissue formation)
- Necrosis (tissue breakdown) in the center of the nodule
They are usually firm, movable under the skin, and often located in areas exposed to pressure or trauma.
What Symptoms Are Related To
Most patients with rheumatoid nodules do not feel pain from the nodules themselves. However, symptoms may include:
➤ Firm lumps under the skin, usually near elbows, fingers, or forearms
➤ Multiple nodules may appear in clusters
➤ Occasional tenderness if irritated or infected
➤ Restriction of movement if nodules form near tendons or joints
➤ Internal nodules (rare) – may occur in lungs, heart, or other organs in severe RA
What Causes / Possible Causes
The exact cause is not fully understood, but rheumatoid nodules are linked to:
➤ Active Rheumatoid Arthritis – uncontrolled inflammation
➤ High levels of Rheumatoid Factor (RF) and anti-CCP antibodies
➤ Genetic predisposition (certain HLA types increase risk)
➤ Smoking – increases severity of RA and risk of nodules
➤ Methotrexate treatment (rarely) – paradoxically associated with accelerated nodulosis in some patients
When Should I See My Doctor
Consult a doctor if you notice:
➤ New or enlarging nodules under the skin
➤ Painful or infected nodules (red, swollen, warm)
➤ Nodules interfering with daily activities such as gripping or walking
➤ Breathing problems (possible lung nodules in severe RA)
➤ Rapid increase in number or size of nodules despite RA treatment
Care and Treatment
Most rheumatoid nodules do not require direct treatment unless they are painful or functionally limiting. Management focuses on controlling underlying rheumatoid arthritis.
➤ Medical Management
➤ Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs – methotrexate, leflunomide, sulfasalazine)
➤ Biologic therapies (anti-TNF, rituximab, tocilizumab) to reduce disease activity
➤ Corticosteroid injections into nodules (for temporary relief)
➤ Surgical Options
➤ Nodule removal if they become painful, infected, or restrict movement
➤ Surgery is rarely needed since nodules often recur if RA is uncontrolled
➤ Lifestyle and Supportive Care
➤ Avoid repetitive trauma/pressure on affected areas
➤ Smoking cessation (reduces RA severity and nodule risk)
➤ Regular monitoring by a rheumatologist
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers advanced rheumatology care with access to the latest biologic and targeted synthetic DMARDs for RA.
➤ Advanced Diagnostics
➤ Blood tests (RF, anti-CCP, ESR, CRP)
➤ Ultrasound or MRI to evaluate nodules and joint inflammation
➤ Biopsy if diagnosis is uncertain
➤ Treatment Approaches
➤ Customized DMARD and biologic therapy plans at major hospitals
➤ Image-guided steroid injections for symptomatic nodules
➤ Minimally invasive surgery in cases of functional impairment
➤ Top Hospitals in Korea for RA & Rheumatoid Nodules
➤ Seoul National University Hospital – Specialized Rheumatology Department
➤ Asan Medical Center – Advanced immunotherapy for RA
➤ Samsung Medical Center – Expertise in biologics and clinical trials
➤ Severance Hospital (Yonsei University) – Comprehensive arthritis care center
Final Thoughts
Rheumatoid nodules are a sign of advanced or severe rheumatoid arthritis. While not usually painful, they may indicate uncontrolled disease and can sometimes cause functional or cosmetic concerns.
In Korea, patients benefit from world-class rheumatology care, cutting-edge biologic therapies, and minimally invasive procedures when needed.
If you have rheumatoid arthritis and notice new lumps or nodules, consult a rheumatologist promptly for evaluation and treatment adjustments.