Overview
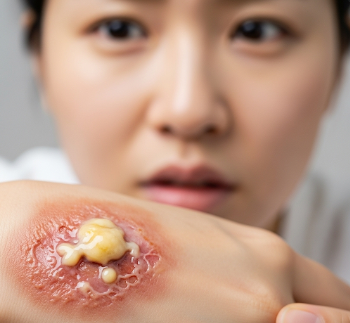
Pus is a thick, creamy, or yellowish fluid produced by the body during infection or inflammation. It is primarily composed of dead white blood cells, bacteria, tissue debris, and serum. The presence of pus indicates that the body’s immune system is actively fighting infection.
Pus can form in skin wounds, abscesses, surgical sites, or internal organs, and its characteristics—such as color, consistency, and odor—can provide clues about the type of infection or causative microorganism.
In Korea, hospitals offer advanced diagnostics, infection control, and surgical care, making them highly capable of managing conditions associated with pus formation. Proper evaluation is essential to prevent severe complications, including sepsis and organ damage.
➤ Thick, often yellow or green fluid indicating infection
➤ Composed of dead cells, bacteria, and tissue debris
➤ Sign of the body’s immune response to bacterial invasion
Key Facts
➤ Pus is a hallmark of bacterial infection, but can occasionally result from fungal or parasitic infections.
➤ It may appear in skin abscesses, boils, infected wounds, or internal infections such as appendicitis.
➤ Characteristics of pus (color, odor, volume) can indicate the type and severity of infection.
➤ Persistent or widespread pus may indicate chronic infection or immune dysfunction.
➤ Korean hospitals utilize advanced imaging, culture tests, and minimally invasive drainage for treatment.
What is Pus?
Pus is an accumulation of inflammatory cells and tissue debris produced during an immune response to infection. White blood cells (especially neutrophils) attack pathogens, and their breakdown contributes to pus formation.
Types of pus include:
➤ Seropurulent: Thin, yellowish fluid, often seen in early infections.
➤ Purulent: Thick, opaque, and often green or yellow; indicates active bacterial infection.
➤ Hemopurulent: Contains blood; may occur in severe or deep infections.
Pus can develop in superficial wounds or deep tissues such as the liver, lungs, or brain, requiring prompt medical attention.
What Symptoms Are Related To
Pus is usually associated with signs of infection and inflammation, including:
➤ Thick yellow, green, or brown discharge from a wound or abscess.
➤ Foul odor (indicating bacterial activity).
➤ Redness, warmth, or swelling around the infected site.
➤ Pain or tenderness at the location of pus accumulation.
➤ Fever, chills, or malaise (systemic infection).
➤ Slow healing or reopening of wounds.
➤ Fatigue or weakness in chronic infections.
What Causes / Possible Causes
Pus forms as a result of infection or inflammation. The main causes include:
➤ Bacterial Infections
➤ Staphylococcus aureus – common in skin infections and boils.
➤ Streptococcus species – cellulitis or pharyngitis.
➤ Pseudomonas aeruginosa – burn wounds and chronic ulcers.
➤ Surgical or Wound-Related Infections
➤ Postoperative infections.
➤ Improper wound care or delayed dressing changes.
➤ Internal Infections
➤ Appendicitis, diverticulitis, liver abscess, or empyema.
➤ Infections of the lungs, brain, or kidneys can also produce pus.
➤ Chronic Conditions
➤ Diabetes – delayed wound healing and higher infection risk.
➤ Immunocompromised states – HIV, chemotherapy, or long-term steroids.
➤ Foreign Bodies or Trauma
➤ Splinters, surgical implants, or deep puncture wounds may create localized pus.
When Should I See My Doctor
Pus is a clear signal of infection, and prompt evaluation is critical. Seek medical attention if:
➤ You notice thick, colored discharge from any wound or body site.
➤ Pus is accompanied by redness, swelling, or increasing pain.
➤ Fever, chills, or malaise appear alongside the pus.
➤ Wound or abscess does not heal or reopens.
➤ Rapidly spreading redness or streaks are present (possible cellulitis or lymphangitis).
Immediate care is crucial to prevent systemic infection, sepsis, or organ involvement.
Care and Treatment
Treatment of pus depends on the site, severity, and underlying cause of infection.
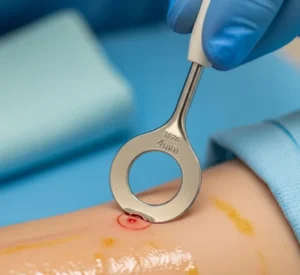
➤ Wound Care
➤ Clean with antiseptic solutions and keep covered.
➤ Proper dressing changes to prevent further contamination.
➤ Surgical drainage for abscesses or deep collections.
➤ Antibiotic Therapy
➤ Topical or systemic antibiotics based on bacterial culture and sensitivity.
➤ Early administration prevents spread and systemic infection.
➤ Pain and Inflammation Management
➤ Analgesics and anti-inflammatory medications.
➤ Elevation and rest of the affected area.
➤ Supportive Measures
➤ Adequate hydration and nutrition.
➤ Blood sugar control in diabetic patients to reduce infection risk.
➤ Advanced Care for Severe Cases
➤ Hospitalization for intravenous antibiotics.
➤ Surgical debridement in chronic or necrotic infections.
➤ Monitoring for sepsis or systemic complications.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers advanced care for infections producing pus, combining surgical, medical, and supportive approaches.
➤ Top Hospitals for Pus & Infection Management
➤ Asan Medical Center (Seoul): Specialized in abscess drainage and infection control.
➤ Samsung Medical Center: Advanced post-surgical infection management and IV antibiotics.
➤ Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH): Multidisciplinary care for internal and external infections.
➤ Yonsei Severance Hospital: Chronic wound and diabetic ulcer management.
➤ Advanced Interventions Available
➤ Wound vacuum-assisted closure (VAC therapy).
➤ Culture-guided intravenous antibiotics.
➤ Minimally invasive abscess drainage techniques.
➤ Integration with traditional Korean medicine for enhanced healing, including herbal therapy and acupuncture.
➤ Follow-Up and Education
➤ Proper wound hygiene instructions.
➤ Regular monitoring for chronic infections.
➤ Multidisciplinary approach: infectious disease, surgery, dermatology, and rehabilitation teams.