Overview
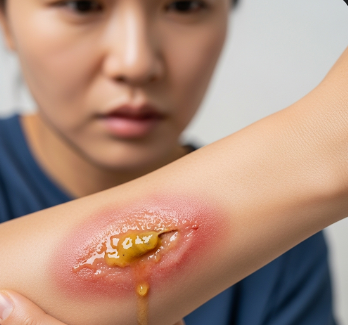
Purulent drainage refers to thick, cloudy, yellow, green, or brown fluid that oozes from a wound, surgical site, abscess, or infection site. It is a sign of infection or ongoing inflammation, often containing dead white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris.
Purulent drainage is not a disease by itself but a symptom of underlying infection or tissue damage. Early recognition is crucial because untreated infections can lead to sepsis, delayed healing, or systemic complications.
In Korea, hospitals offer state-of-the-art wound care, infection control, and surgical interventions, making it a leading destination for managing conditions associated with purulent drainage.
➤ Thick, cloudy or colored fluid from wounds or infections
➤ Indicates bacterial infection or tissue inflammation
➤ Requires prompt medical evaluation to prevent complications
Key Facts
➤ Purulent drainage is commonly associated with bacterial infections, abscesses, or post-surgical wounds.
➤ Color may vary: yellow, green, brown, or gray, often indicating the type of infection.
➤ It may be accompanied by foul odor, swelling, redness, or warmth.
➤ Persistent drainage may signal chronic infection or poor wound healing.
➤ Korean hospitals provide specialized infection management and advanced wound care technologies.
What is Purulent Drainage?
Purulent drainage is exudate produced by the body in response to infection. When white blood cells fight invading bacteria, they die and mix with tissue fluid, forming pus.
Key points about purulent drainage:
➤ Can appear from skin wounds, surgical incisions, abscesses, or internal infections.
➤ May be accompanied by systemic symptoms such as fever, fatigue, or malaise.
➤ Volume and color can indicate the severity and stage of infection.
What Symptoms Are Related To
Purulent drainage often occurs alongside other infection-related symptoms:
➤ Thick, cloudy, yellow, green, or brown fluid.
➤ Foul-smelling discharge.
➤ Redness and swelling around the affected area.
➤ Pain or tenderness at the site of drainage.
➤ Fever or chills (systemic infection).
➤ Delayed wound healing or wound reopening.
➤ Warmth at the site, indicating inflammation.
What Causes / Possible Causes
Purulent drainage arises due to infection or tissue necrosis. Common causes include:
➤ Bacterial Infections
➤ Staphylococcus aureus (common in skin infections and abscesses).
➤ Streptococcus species.
➤ Pseudomonas aeruginosa (frequent in burns or chronic wounds).
➤ Surgical or Wound-Related Infections
➤ Postoperative infections.
➤ Improper wound care or delayed dressing changes.
➤ Chronic Medical Conditions
➤ Diabetes mellitus – delayed healing and increased infection risk.
➤ Peripheral vascular disease – poor blood flow leading to ulcers.
➤ Internal Abscesses
➤ Appendicitis, diverticulitis, or intra-abdominal infections.
➤ Foreign Bodies or Trauma
➤ Splinters, surgical implants, or deep puncture wounds may cause localized purulent drainage.
When Should I See My Doctor
Purulent drainage is a red flag for infection. Seek medical care if you notice:
➤ Thick, cloudy, or colored fluid from a wound or incision.
➤ Foul odor coming from the drainage site.
➤ Increasing pain, redness, or swelling.
➤ Fever, chills, or malaise alongside drainage.
➤ Wound not healing or reopening after closure.
➤ Rapidly spreading redness or streaks (possible cellulitis).
Immediate care is critical to prevent sepsis or systemic infection, especially in immunocompromised patients.
Care and Treatment
Treatment focuses on eliminating infection, promoting wound healing, and addressing underlying causes.
➤ Wound Care
➤ Regular cleaning with antiseptic solutions.
➤ Proper dressing changes to keep the wound moist and protected.
➤ Surgical drainage if abscesses or pockets of pus are present.
➤ Antibiotic Therapy
➤ Topical or systemic antibiotics depending on severity and culture results.
➤ Targeted therapy based on bacterial identification and sensitivity tests.
➤ Pain Management
➤ Analgesics or anti-inflammatory medications to reduce discomfort.
➤ Supportive Measures
➤ Adequate hydration and nutrition to promote healing.
➤ Blood sugar control in diabetic patients to reduce infection risk.
➤ Advanced Care for Severe Cases
➤ Hospitalization for intravenous antibiotics.
➤ Surgical debridement in necrotic or chronic wounds.
➤ Monitoring for signs of sepsis or systemic infection.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea provides highly advanced wound care and infection management, combining modern medicine with supportive therapies.
➤ Top Hospitals for Purulent Drainage & Infections
➤ Asan Medical Center (Seoul): Advanced wound care units and infectious disease management.
➤ Samsung Medical Center: Surgical debridement, IV antibiotics, and postoperative care.
➤ Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH): Comprehensive infection and immunocompromised patient care.
➤ Yonsei Severance Hospital: Expertise in chronic wounds, diabetic foot ulcers, and abscess management.
➤ Advanced Interventions Available
➤ Wound vacuum-assisted closure (VAC therapy).
➤ Culture-guided intravenous antibiotics.
➤ Minimally invasive abscess drainage techniques.
➤ Integration with traditional Korean medicine for improved healing, including herbal therapy and acupuncture.
➤ Patient Education & Follow-Up
➤ Education on proper wound hygiene.
➤ Regular follow-up for chronic wounds or post-surgical recovery.
➤ Multidisciplinary approach: infectious disease, surgery, dermatology, and rehabilitation teams.