Overview
Peeling skin, medically known as desquamation, is a condition where the outer layer of the skin, the epidermis, begins to shed or flake off. While occasional skin peeling is normal due to natural skin regeneration, excessive or persistent peeling may signal an underlying health problem. This condition can affect any part of the body but is commonly seen on the hands, feet, face, or areas exposed to sun or friction.
➤ Peeling skin can be both cosmetic and medical concern, depending on its cause and severity.
➤ It may accompany itching, redness, or inflammation, causing discomfort.
➤ Identifying the underlying reason is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
In Korea, dermatology clinics are well-equipped to diagnose and treat peeling skin, offering advanced therapies for conditions ranging from eczema to post-sunburn recovery.
Key Facts
➤ Peeling skin occurs due to damage or shedding of the outer epidermal layer.
➤ Can be localized or widespread, depending on the cause.
➤ Often associated with dry skin, sunburn, infections, or inflammatory skin conditions.
➤ Chronic peeling may indicate nutritional deficiencies, autoimmune disorders, or systemic illnesses.
➤ Proper care can restore skin health, improve appearance, and prevent secondary infections.
What is Peeling Skin?
Peeling skin refers to the shedding or flaking of the outermost skin layer. The epidermis naturally regenerates approximately every 28–40 days, but certain conditions accelerate this process or damage the skin, leading to visible peeling.
➤ Medical perspective: Desquamation occurs when the skin barrier is compromised due to injury, infection, or inflammation.
➤ Types of peeling skin:
➤ Acute peeling – often follows sunburn, burns, or allergic reactions.
➤ Chronic peeling – may result from eczema, psoriasis, or genetic disorders.
➤ Appearance: Skin may look dry, cracked, reddish, or scaly.
While peeling skin is sometimes a cosmetic concern, it can also indicate serious health issues, particularly if accompanied by pain, blisters, or systemic symptoms.
What Symptoms Are Related To
Peeling skin rarely occurs in isolation; it is often accompanied by other skin or systemic symptoms:
➤ Redness and inflammation: Skin may appear pink or red before peeling.
➤ Itching or burning sensation: Common in eczema or allergic reactions.
➤ Dryness or flakiness: Indicates dehydration or environmental stress on the skin.
➤ Blisters or sores: Seen in infections like impetigo or viral conditions.
➤ Pain or tenderness: May occur if peeling is severe or linked to burns.
➤ Discoloration: Skin may appear lighter or darker after peeling.
Recognizing these associated symptoms helps differentiate between minor skin irritation and serious dermatological conditions.
What Causes / Possible Causes
Peeling skin can result from external factors, internal health conditions, or both. Common causes include:
➤ Sunburn: UV damage destroys skin cells, leading to shedding.
➤ Dry skin (xerosis): Low humidity, cold weather, or excessive washing can strip natural oils.
➤ Allergic reactions: Contact dermatitis from soaps, cosmetics, or chemicals.
➤ Infections: Bacterial, fungal, or viral infections like athlete’s foot or measles.
➤ Skin conditions:
➤ Eczema – chronic inflammation and dryness.
➤ Psoriasis – accelerated skin turnover and scaling.
➤ Medications: Certain antibiotics or chemotherapy drugs can trigger peeling.
➤ Nutritional deficiencies: Lack of vitamin A, zinc, or essential fatty acids.
➤ Systemic diseases: Thyroid disorders, diabetes, or autoimmune diseases may affect skin integrity.
Environmental triggers and lifestyle factors, such as prolonged water exposure or harsh chemicals, can exacerbate peeling in vulnerable individuals.
When Should I See My Doctor
While mild skin peeling often resolves with self-care, medical evaluation is necessary if:
➤ Peeling is widespread or persistent, not improving with moisturizers.
➤ Accompanied by pain, bleeding, blisters, or signs of infection.
➤ Associated with systemic symptoms like fever, fatigue, or swelling.
➤ Recurring peeling despite protective measures, indicating an underlying condition.
➤ Interfering with daily activities or sleep due to discomfort or itching.
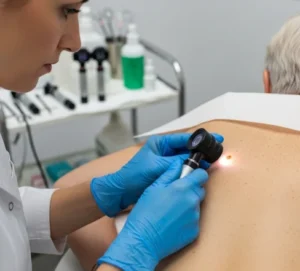
Early consultation with a dermatologist in Korea ensures accurate diagnosis, prevention of complications, and personalized treatment plans.
Care and Treatment
Treatment of peeling skin focuses on restoring the skin barrier, preventing further damage, and addressing underlying causes:
➤ Moisturization:
➤ Use emollients with ingredients like glycerin, hyaluronic acid, or ceramides.
➤ Apply immediately after bathing to lock in moisture.
➤ Sun protection:
➤ Avoid excessive sun exposure.
➤ Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen to prevent UV-induced peeling.
➤ Gentle skin care:
➤ Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers.
➤ Avoid hot water or harsh scrubs.
➤ Treat underlying causes:
➤ Topical steroids or anti-inflammatory creams for eczema or dermatitis.
➤ Antifungal or antibiotic treatments for infections.
➤ Nutritional supplementation if deficiencies are identified.
➤ Lifestyle adjustments:
➤ Hydrate adequately.
➤ Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals.
➤ Wear breathable, soft clothing to reduce irritation.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean dermatology clinics offer state-of-the-art treatments for peeling skin:
➤ Advanced topical therapies: Prescription creams with optimized absorption and minimal side effects.
➤ Laser and light therapies: For severe skin conditions like psoriasis or chronic eczema.
➤ Clinical-grade moisturizers and barrier repair treatments designed for sensitive skin.
➤ Integrated dermatology programs combining medication, diet, and lifestyle guidance.
➤ Expert assessment of underlying systemic conditions, ensuring holistic care.
➤ Follow-up and monitoring using modern digital tools to track improvement and prevent recurrence