Overview
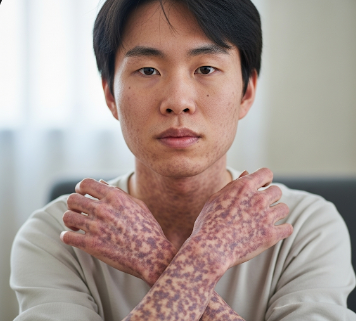
Mottled skin refers to a patchy or blotchy appearance of the skin, often showing irregular areas of red, purple, or pale discoloration. This pattern can occur due to circulatory changes, temperature fluctuations, or underlying medical conditions. While occasional mottling may be harmless, persistent or severe cases may indicate circulatory, cardiac, or systemic health issues.
In Korea, dermatology and internal medicine clinics provide diagnostic evaluation and treatment for mottled skin, including management of underlying causes such as vascular disorders, autoimmune conditions, or systemic illnesses.
Key Facts
➤ Mottled skin appears as patchy, irregular discoloration of the skin.
➤ Often linked to circulatory changes, cold exposure, or underlying medical conditions.
➤ Can be temporary or chronic, depending on the cause.
➤ May occur anywhere on the body, commonly on hands, feet, and limbs.
➤ In Korea, medical evaluation can determine if mottling is benign or a sign of systemic illness.
What is Mottled Skin?
Mottled skin is characterized by an irregular mixture of colors, typically reddish, purplish, or pale areas, resulting from uneven blood flow in the superficial blood vessels. It may be influenced by temperature, circulation, or vascular integrity. In some cases, mottled skin can be an early sign of serious conditions like shock, sepsis, or cardiac insufficiency.
Symptoms Related to Mottled Skin
The main features and associated symptoms include:
➔ Patchy discoloration that may be reddish, purplish, or pale.
➔ Cold extremities in some cases, especially hands and feet.
➔ Skin that feels cool or clammy to touch.
➔ Possible associated pain, tingling, or numbness in underlying conditions.
➔ In chronic cases, dryness or ulceration may occur in affected areas.
Causes / Possible Causes
Mottled skin can result from a variety of physiological or pathological factors:
Physiological Causes
➤ Cold exposure – temporary vasoconstriction leads to patchy skin appearance.
➤ Stress or anxiety – can cause transient changes in blood flow.
➤ Age-related vascular changes – slower circulation in elderly individuals.
Pathological Causes
➤ Shock or hypotension – uneven perfusion can produce mottling.
➤ Sepsis or systemic infection – early sign of poor circulation.
➤ Peripheral vascular disease – impaired blood flow in limbs.
➤ Autoimmune or connective tissue disorders – such as lupus or vasculitis.
➤ Heart or lung conditions – reducing oxygen delivery to the skin.
Other Contributing Factors
➤ Prolonged immobility or bed rest.
➤ Certain medications affecting circulation.
➤ Smoking or diabetes causing vascular compromise.
Risk Factors
➤ Advanced age due to slower circulation.
➤ Chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, or autoimmune disorders.
➤ Exposure to extreme cold or fluctuating temperatures.
➤ Immobility or bedridden status.
➤ Use of vasoconstrictive medications.
Complications
While temporary mottled skin is usually harmless, persistent mottling may lead to:
➤ Tissue damage due to inadequate blood supply.
➤ Skin ulceration or necrosis in severe vascular compromise.
➤ Increased risk of infection if skin integrity is broken.
➤ Early warning sign of serious systemic illness, including shock or sepsis.
When Should I See My Doctor?
Seek medical attention if:
➤ Mottled skin appears suddenly or worsens rapidly.
➤ Accompanied by pain, swelling, or numbness.
➤ Linked with cold, clammy skin, dizziness, or shortness of breath.
➤ Occurs in individuals with heart, lung, or vascular diseases.
➤ Persistent or chronic mottling does not resolve with warming or rest.
Care and Treatment
Treatment depends on the underlying cause:
Home Care for Mild Cases
➤ Keep affected areas warm and dry.
➤ Gentle massage or movement to improve circulation.
➤ Avoid smoking and maintain healthy lifestyle habits.
➤ Hydration to support vascular health.
Medical Treatments
➤ Medications to improve blood flow or treat underlying vascular disorders.
➤ Management of systemic conditions (heart failure, sepsis, autoimmune disorders).
➤ Physical therapy for circulatory improvement in chronic cases.
➤ In severe cases, surgical intervention for peripheral arterial disease.
Monitoring & Follow-Up
➤ Regular evaluation of circulation, oxygenation, and skin integrity.
➤ Blood tests to detect infections or systemic inflammation.
➤ Cardiovascular assessment for underlying heart or vascular conditions.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean hospitals provide comprehensive care for mottled skin through dermatology, internal medicine, and vascular clinics:
Diagnostic Services
➤ Blood tests for inflammation, infection, and metabolic disorders.
➤ Doppler ultrasound for peripheral circulation assessment.
➤ Cardiac evaluation including echocardiography or stress tests.
➤ Skin biopsy in chronic or unexplained cases.
Medical and Supportive Care
➤ Treatment of underlying systemic illness (e.g., sepsis, vascular disease).
➤ Medication to improve blood flow and skin perfusion.
➤ Lifestyle programs for circulation, nutrition, and vascular health.
➤ Follow-up monitoring to prevent skin complications.