Overview
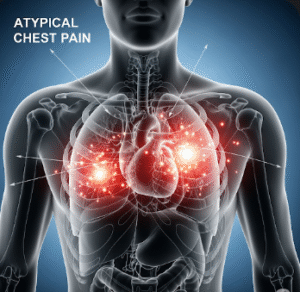
Left-side chest pain refers to discomfort or pain located on the left side of the chest, which may range from a dull ache to a sharp, stabbing sensation. While sometimes caused by muscle strain or anxiety, it can also signal serious medical emergencies such as heart attack, angina, or lung conditions.
In Korea, hospitals and cardiology centers provide rapid assessment, diagnostic testing, and treatment for patients experiencing left-side chest pain. Early detection is critical to prevent life-threatening complications and ensure optimal recovery.
Key Facts
- ➔ Chest pain on the left side can arise from cardiac, pulmonary, gastrointestinal, musculoskeletal, or psychological causes.
- ➔ Heart-related conditions are the most urgent causes and require immediate attention.
- ➔ Pain may be sharp, pressure-like, burning, or tight, sometimes radiating to the arm, neck, jaw, or back.
- ➔ Other accompanying symptoms like shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, or dizziness may indicate a cardiac emergency.
- ➔ Accurate evaluation is essential to differentiate between benign and life-threatening causes.
What is Left-Side Chest Pain?
Left-side chest pain is the perception of discomfort originating from structures in or near the left chest area.
- ➔ Cardiac causes: Heart attack, angina, or pericarditis.
- ➔ Pulmonary causes: Pulmonary embolism, pleuritis, or pneumonia.
- ➔ Gastrointestinal causes: Acid reflux, hiatal hernia, or esophageal spasms.
- ➔ Musculoskeletal causes: Rib fractures, muscle strain, or costochondritis.
- ➔ Neurological causes: Nerve compression or shingles.
Understanding the origin and nature of the pain is critical for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What Symptoms Are Related To
Left-side chest pain may be accompanied by additional symptoms depending on its cause:
- ➔ Pain radiating to the left arm, neck, jaw, or back (cardiac origin)
- ➔ Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- ➔ Sweating, palpitations, or feeling faint
- ➔ Nausea or vomiting
- ➔ Cough, fever, or hemoptysis (pulmonary causes)
- ➔ Heartburn, regurgitation, or difficulty swallowing (gastrointestinal causes)
- ➔ Tenderness or bruising over the chest wall (musculoskeletal causes)
Recognizing these associated symptoms helps clinicians prioritize emergency evaluation versus routine care.
What Causes / Possible Causes
Several conditions can lead to left-side chest pain:
- ➔ Myocardial infarction (heart attack): Blockage of blood flow to the heart muscle.
- ➔ Angina pectoris: Reduced blood supply to the heart causing temporary chest pain.
- ➔ Pericarditis: Inflammation of the lining around the heart.
- ➔ Pulmonary embolism: Blood clot in the lungs causing sudden pain and shortness of breath.
- ➔ Pneumothorax or pneumonia: Lung collapse or infection can produce sharp pain.
- ➔ Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): Acid reflux irritating the esophagus.
- ➔ Costochondritis: Inflammation of rib cartilage causing localized tenderness.
- ➔ Anxiety or panic attacks: Often accompanied by palpitations, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
Prompt identification of the underlying cause is crucial, as some conditions require immediate emergency intervention.
When Should I See My Doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if left-side chest pain is accompanied by:
- ➔ Severe, crushing, or persistent pain
- ➔ Pain radiating to the left arm, jaw, or back
- ➔ Shortness of breath, sweating, dizziness, or fainting
- ➔ Nausea or vomiting
- ➔ History of heart disease, high blood pressure, or diabetes
- ➔ Sudden onset after trauma, exertion, or stress
Early evaluation can prevent heart attacks, pulmonary embolism, or other critical events.
Care and Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause of chest pain:
- ➔ Heart attack or angina: Emergency care including medications, angioplasty, stents, or surgery.
- ➔ Pericarditis: Anti-inflammatory medications and rest.
- ➔ Pulmonary conditions: Oxygen therapy, anticoagulants, antibiotics, or surgery depending on the condition.
- ➔ Gastrointestinal causes: Acid-suppressing medications, dietary modifications, or endoscopic procedures.
- ➔ Musculoskeletal pain: Rest, physiotherapy, pain relievers, or anti-inflammatory medications.
- ➔ Anxiety or panic-related pain: Counseling, stress management, or medications for anxiety.
Proper diagnosis ensures targeted treatment and prevention of complications.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean hospitals provide state-of-the-art care for left-side chest pain:
- ➔ Cardiology evaluation: ECG, echocardiography, and cardiac biomarkers for heart-related causes.
- ➔ Pulmonology assessment: Chest X-ray, CT scan, and blood tests for lung conditions.
- ➔ Gastroenterology consultation: Endoscopy and pH monitoring for acid reflux or esophageal disorders.
- ➔ Emergency care: Rapid intervention for heart attacks, pulmonary embolism, or severe trauma.
- ➔ Rehabilitation and follow-up: Cardiac rehab, physiotherapy, and lifestyle counseling for long-term recovery.
- ➔ Multidisciplinary approach: Coordination between cardiologists, pulmonologists, gastroenterologists, and pain specialists.
Leading hospitals such as Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, and Samsung Medical Center provide comprehensive diagnostic and treatment plans, ensuring both acute care and long-term prevention.
In Summary: Left-side chest pain can range from benign musculoskeletal discomfort to life-threatening emergencies like heart attack or pulmonary embolism. Early recognition, rapid evaluation, and advanced treatment in Korea can relieve symptoms, treat underlying causes, and prevent serious complications.
- ➔ Key Takeaway: Any sudden or severe chest pain should be treated as a potential emergency.
- ➔ Action Point: Seek immediate medical care and consult specialists for accurate diagnosis and treatment.