Overview
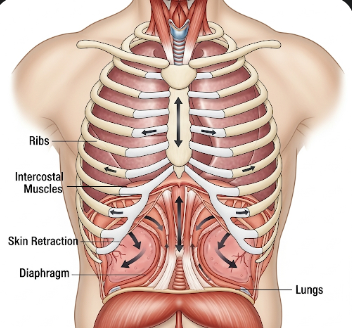
Intercostal retractions refer to a visible pulling in of the skin between the ribs during breathing. This occurs when a person has difficulty breathing and the chest muscles are working harder than normal to draw air into the lungs. Intercostal retractions are often a sign of respiratory distress and may indicate an underlying condition affecting the lungs or airways.
In Korea, intercostal retractions are recognized in both pediatric and adult patients, and hospitals with advanced respiratory care are equipped to diagnose and manage the underlying causes efficiently. Prompt evaluation is essential because these retractions can signal serious conditions such as pneumonia, asthma attacks, or bronchiolitis.
Key Facts
- ➔ Intercostal retractions occur when the skin and muscles between the ribs pull inward during inhalation.
- ➔ They are more noticeable in infants and young children due to their softer chest walls.
- ➔ Often associated with labored breathing, rapid respiratory rate, or wheezing.
- ➔ Can indicate conditions ranging from mild airway obstruction to severe respiratory compromise.
- ➔ Immediate medical evaluation is recommended if accompanied by cyanosis (blue lips), lethargy, or nasal flaring.
What is Intercostal Retractions?
Intercostal retractions are a physical sign rather than a disease. They indicate that the respiratory muscles are working harder than usual to maintain adequate airflow into the lungs. Normally, breathing involves gentle expansion of the chest, but when airflow is obstructed or lung compliance is reduced, the negative pressure inside the chest pulls the skin inward between the ribs.
- ➔ Mild retractions: Only visible on deep breaths or when the person is exerting themselves.
- ➔ Moderate retractions: Visible even at rest, often accompanied by flaring nostrils.
- ➔ Severe retractions: Significant pulling at the chest and neck, indicating urgent respiratory compromise.
In children, intercostal retractions are particularly important to monitor because their airways are smaller, and even minor obstruction can lead to serious breathing difficulties.
What Symptoms Are Related To
Intercostal retractions rarely occur in isolation. They are often seen with other signs of respiratory distress, including:
- ➔ Rapid breathing (tachypnea)
- ➔ Nasal flaring
- ➔ Cyanosis (bluish skin or lips)
- ➔ Wheezing or noisy breathing
- ➔ Use of accessory muscles (neck and shoulder muscles) during inhalation
- ➔ Fatigue or lethargy due to increased effort in breathing
Recognizing these related symptoms can help caregivers and medical professionals determine the urgency and possible underlying cause.
What Causes / Possible Causes
Intercostal retractions are caused by conditions that impair normal airflow or lung expansion. Common causes include:
- ➔ Respiratory infections: Pneumonia, bronchiolitis, or severe influenza can restrict airflow.
- ➔ Asthma attacks: Constriction of the airways increases the effort needed to inhale.
- ➔ Obstructive airway conditions: Foreign body aspiration, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in adults.
- ➔ Congenital conditions: Infants with laryngeal malformations or underdeveloped lungs may show retractions.
- ➔ Heart-related causes: Severe heart failure may lead to pulmonary edema, causing labored breathing and retractions.
In pediatric populations, viral bronchiolitis caused by RSV (respiratory syncytial virus) is one of the most frequent causes of intercostal retractions.
When Should I See My Doctor
Intercostal retractions are a warning sign, not a disease itself. Immediate evaluation is necessary in the following scenarios:
- ➔ Persistent or worsening retractions at rest
- ➔ Blue lips or fingers (cyanosis)
- ➔ Difficulty speaking or feeding in children
- ➔ Severe lethargy or unresponsiveness
- ➔ Fever or other signs of infection
- ➔ Wheezing that does not improve with prescribed inhalers
Prompt assessment can prevent respiratory failure and identify the underlying condition early.
Care and Treatment
Management of intercostal retractions depends on the underlying cause. General care measures include:
- ➔ Ensuring the patient is in an upright position to maximize lung expansion
- ➔ Providing supplemental oxygen if oxygen saturation is low
- ➔ Keeping the airway clear, especially in infants
- ➔ Administering bronchodilators for asthma or airway obstruction
- ➔ Hydration and supportive care for respiratory infections
- ➔ Close monitoring of breathing patterns and vital signs
It is crucial that parents and caregivers avoid delaying medical attention, as retractions can escalate quickly in children or vulnerable adults.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korean hospitals and clinics offer advanced care for patients showing intercostal retractions:
- ➔ Pediatric Respiratory Units: Specialized units for infants and children with severe respiratory distress.
- ➔ Advanced Diagnostics: Chest X-rays, CT scans, and blood tests to identify infections or structural abnormalities.
- ➔ Bronchodilator Therapy: Nebulized medications for asthma, bronchiolitis, and other airway constrictions.
- ➔ Oxygen Therapy: High-flow oxygen support or CPAP for severe cases.
- ➔ Critical Care: ICU management for respiratory failure caused by infections, congenital issues, or heart-lung complications.
- ➔ Follow-up and Rehabilitation: Long-term monitoring for children with recurrent respiratory issues or chronic conditions.
In Korea, hospitals like Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, and Samsung Medical Center are well-equipped to manage severe respiratory distress with a combination of pediatric, adult, and ICU expertise.
In Summary: Intercostal retractions are an important clinical sign of respiratory distress. While they are not a disease themselves, they reflect the body’s increased effort to breathe. Recognizing the early signs, understanding related symptoms, and seeking timely medical care—especially in children—is critical. Korean hospitals provide state-of-the-art treatment and monitoring to ensure patients with intercostal retractions receive rapid and effective care.
- ➔ Key Takeaway: Always treat intercostal retractions as a potential emergency, particularly in children and infants.
- ➔ Action Point: Seek medical assessment immediately if retractions are severe, persistent, or accompanied by other warning signs.