Overview
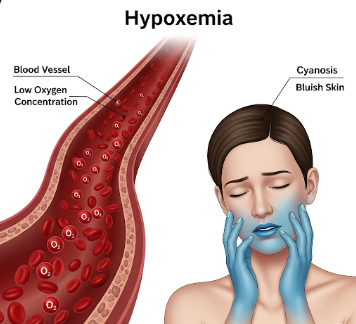
Hypoxemia is a medical condition characterized by low levels of oxygen in the blood, particularly in the arteries. Oxygen is vital for cellular metabolism and organ function, and insufficient oxygen can affect the brain, heart, and other vital organs, leading to serious health complications if not addressed promptly.
In South Korea, hospitals and specialized clinics provide advanced diagnostics and treatments for hypoxemia, including oxygen therapy, ventilatory support, and management of underlying respiratory or cardiovascular conditions.
Key Facts
🟢 ➤ Hypoxemia is defined as arterial oxygen levels (PaO₂) below 80 mmHg in adults.
🟢 ➤ Common causes include lung diseases, heart conditions, high altitude exposure, and anemia.
🟢 ➤ Symptoms may be mild or severe, ranging from shortness of breath to confusion or cyanosis.
🟢 ➤ Diagnosis involves arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis, pulse oximetry, and imaging studies.
🟢 ➤ Treatment focuses on improving oxygen delivery and addressing the underlying cause.
🟢 ➤ South Korean medical centers offer modern respiratory care, including ICU support and specialized oxygen therapies.
What is Hypoxemia?
Hypoxemia occurs when oxygen levels in the arterial blood are insufficient to meet tissue demands.
Key points:
➤ It can be acute (sudden onset) or chronic (long-term low oxygen levels).
➤ Oxygen is transported in the blood bound to hemoglobin, and hypoxemia can result from low oxygen in the lungs, impaired gas exchange, or low hemoglobin levels.
➤ Prolonged hypoxemia can cause organ dysfunction, particularly affecting the brain, heart, and kidneys.
➤ Differentiation is important: hypoxemia (low blood oxygen) vs. hypoxia (low tissue oxygen).
Symptoms Related to Hypoxemia
Symptoms vary based on severity, duration, and underlying cause:
🟢 ➤ Shortness of breath, especially during exertion.
🟢 ➤ Rapid breathing (tachypnea) and increased heart rate (tachycardia).
🟢 ➤ Cyanosis (bluish lips, fingers, or toes).
🟢 ➤ Fatigue, weakness, or reduced exercise tolerance.
🟢 ➤ Confusion, dizziness, or headache in moderate to severe cases.
🟢 ➤ Severe hypoxemia may lead to loss of consciousness or organ failure.
Causes / Possible Causes
Hypoxemia can result from respiratory, cardiovascular, blood-related, or environmental factors:
Respiratory Causes
➤ Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, pneumonia, or pulmonary edema.
➤ Pulmonary embolism obstructing blood flow to the lungs.
➤ High altitude exposure reducing available oxygen.
Cardiovascular Causes
➤ Congenital or acquired heart defects causing mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
➤ Heart failure reducing effective circulation and oxygen delivery.
Blood-Related Causes
➤ Anemia lowering hemoglobin levels and oxygen-carrying capacity.
➤ Carbon monoxide poisoning preventing oxygen binding to hemoglobin.
Other Causes
➤ Hypoventilation due to sedatives, neurological disorders, or respiratory muscle weakness.
➤ Severe infections like sepsis causing impaired oxygen delivery.
When Should I See a Doctor?
Immediate medical attention is required if:
🟢 ➤ Shortness of breath occurs suddenly or worsens rapidly.
🟢 ➤ Cyanosis (bluish lips or fingertips) appears.
🟢 ➤ Chest pain, palpitations, or confusion accompany low oxygen levels.
🟢 ➤ Oxygen saturation is persistently below 90% on pulse oximetry.
🟢 ➤ There is a history of chronic lung or heart disease with new or worsening symptoms.
Early evaluation ensures timely intervention, prevention of organ damage, and management of underlying causes.
Care and Treatment
Management depends on cause, severity, and patient health status:
Oxygen Therapy
➤ Supplemental oxygen via nasal cannula, face mask, or high-flow devices.
➤ Continuous monitoring of oxygen saturation and arterial blood gases.
Treatment of Underlying Causes
➤ Bronchodilators, corticosteroids, or antibiotics for lung diseases.
➤ Anticoagulation for pulmonary embolism.
➤ Medications or interventions for heart failure or congenital heart defects.
➤ Blood transfusions or iron therapy for anemia.
Advanced or Critical Care
➤ Mechanical ventilation or non-invasive positive pressure ventilation in severe hypoxemia.
➤ ICU support for multi-organ involvement or respiratory failure.
➤ Pulmonary rehabilitation for chronic lung disease patients.
Advanced Care in Korea
➤ South Korean hospitals provide modern respiratory ICUs, advanced oxygen delivery systems, and specialized care for both acute and chronic hypoxemia.
➤ Multidisciplinary teams ensure rapid diagnosis, stabilization, and long-term management.
➤ Patient education emphasizes recognizing early warning signs, adherence to therapy, and lifestyle modifications to optimize oxygenation.
Highlights (Clean Green Arrow Version)
🟢 ➤ Hypoxemia is low oxygen levels in the blood, affecting tissue and organ function.
🟢 ➤ Symptoms: shortness of breath, rapid breathing, cyanosis, fatigue, confusion, and in severe cases, organ failure.
🟢 ➤ Causes: lung disease, heart defects, anemia, high altitude, hypoventilation, or poisoning.
🟢 ➤ Seek urgent medical care if oxygen saturation drops below 90%, or if severe shortness of breath, cyanosis, or confusion occur.
🟢 ➤ Treatments include oxygen therapy, medications for underlying conditions, ventilation support, and critical care if necessary.
🟢 ➤ South Korea offers advanced ICUs, pulmonary care, and multidisciplinary management for hypoxemia with continuous monitoring and rehabilitation programs.