Overview
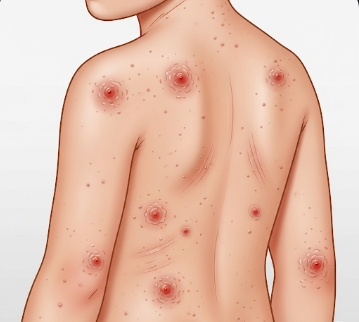
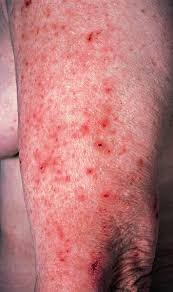
Hives in children, medically known as urticaria, are raised, itchy, red or skin-colored welts that appear suddenly on the skin. These welts can vary in size and shape, often merging to form larger patches. Hives are a common allergic skin reaction in children and can occur due to food, medication, infections, or environmental triggers.
While most cases are mild and self-limiting, severe or chronic hives may require medical attention. In South Korea, pediatric dermatology and allergy centers provide diagnosis, treatment, and management strategies for children with hives.
Key Facts
🟢 ➤ Hives are raised, itchy welts that can appear anywhere on the child’s body.
🟢 ➤ Common triggers include foods (nuts, eggs, milk), medications, insect bites, infections, and environmental allergens.
🟢 ➤ Hives may appear suddenly (acute) or persist for more than six weeks (chronic).
🟢 ➤ Symptoms can be accompanied by swelling of lips, eyelids, or other body parts (angioedema).
🟢 ➤ Most hives are mild and resolve on their own, but severe cases require prompt medical care.
🟢 ➤ Korean pediatric clinics provide allergy testing, medications, and education for prevention and management.
What is Hives in Children?
Hives (urticaria) are a skin reaction caused by the release of histamine and other chemicals from mast cells, leading to:
➤ Swelling of the skin (wheals) that can appear suddenly.
➤ Itchiness or burning sensation, which may worsen at night or with heat.
➤ Rapid appearance and disappearance – individual hives may last a few hours, but new ones can appear continuously.
➤ Acute vs chronic hives – Acute hives appear suddenly and resolve within days, whereas chronic hives persist for more than six weeks.
Symptoms Related to Hives in Children
Symptoms can vary in intensity and frequency:
🟢 ➤ Raised, red or skin-colored welts (wheals) that itch intensely.
🟢 ➤ Swelling of lips, eyelids, hands, feet, or genitals (angioedema).
🟢 ➤ Pain or burning sensation in some cases.
🟢 ➤ Hives that change location or size within hours.
🟢 ➤ Possible low-grade fever or irritability if associated with infection.
🟢 ➤ Rarely, severe allergic reactions may include difficulty breathing, vomiting, or swelling of the tongue and throat (anaphylaxis).
Causes / Possible Causes
Hives in children can result from various triggers and underlying conditions:
Allergic Reactions
➤ Foods: nuts, eggs, milk, shellfish, and soy.
➤ Medications: antibiotics, aspirin, or other drugs.
➤ Insect stings or bites.
Infections
➤ Viral infections are a common trigger in children.
➤ Bacterial infections may also lead to urticaria.
Environmental Factors
➤ Pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or chemicals in soaps and detergents.
Physical Triggers
➤ Cold, heat, pressure, or sunlight can induce hives in sensitive children.
Chronic or Idiopathic Causes
➤ In some children, no clear cause is identified, leading to chronic idiopathic urticaria.
When Should I See a Doctor?
Medical evaluation is essential if:
🟢 ➤ Hives are severe, persistent, or spreading rapidly.
🟢 ➤ Swelling affects the lips, eyelids, tongue, or throat.
🟢 ➤ The child experiences difficulty breathing, wheezing, or vomiting (possible anaphylaxis).
🟢 ➤ Hives are accompanied by fever, lethargy, or signs of infection.
🟢 ➤ Hives persist for more than six weeks or recur frequently.
Prompt assessment ensures appropriate treatment, prevents complications, and identifies potential allergens.
Care and Treatment
Treatment for hives focuses on relieving symptoms and managing triggers:
Home Care and Comfort
➤ Cool compresses or lukewarm baths to reduce itching.
➤ Loose, soft clothing to avoid skin irritation.
➤ Avoid scratching to prevent infection.
Medications
➤ Antihistamines – reduce itching and swelling; often the first line of treatment.
➤ Corticosteroids – prescribed in severe or persistent cases.
➤ Epinephrine – used in emergency cases of anaphylaxis.
Identifying Triggers
➤ Keep a food and symptom diary to identify possible allergens.
➤ Avoid known triggers such as specific foods, medications, or environmental irritants.
Advanced Care in Korea
➤ Pediatric dermatology and allergy clinics provide allergy testing (skin or blood tests), immunotherapy, and personalized care plans.
➤ Education on prevention strategies, emergency management, and safe medication use is part of comprehensive care.
Highlights (Clean Green Arrow Version)
🟢 ➤ Hives are raised, itchy welts that appear on the skin, common in children.
🟢 ➤ Causes: foods, medications, infections, insect bites, environmental allergens, or physical triggers.
🟢 ➤ Symptoms: itching, swelling (angioedema), redness, burning sensation, and rarely anaphylaxis.
🟢 ➤ Most cases are mild and self-limiting, but severe or chronic hives require medical attention.
🟢 ➤ Treatment includes antihistamines, corticosteroids, identifying triggers, and home care measures.
🟢 ➤ South Korea offers pediatric allergy testing, treatment, and educational support for prevention and management.