Overview
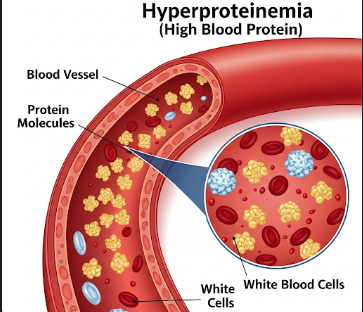
High blood protein, medically called hyperproteinemia, is a condition in which the total protein level in the blood exceeds normal ranges. Blood proteins, primarily albumin and globulin, play vital roles in maintaining fluid balance, immune function, and transporting nutrients and hormones.
While mild increases may be temporary or benign, significant hyperproteinemia can indicate underlying conditions such as chronic inflammation, infections, liver or kidney disease, or blood disorders.
In South Korea, advanced clinical laboratories and healthcare facilities offer accurate diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment plans to address both the underlying cause and any associated complications.
Key Facts
🟢 ➤ Hyperproteinemia refers to abnormally high levels of total protein in the blood.
🟢 ➤ The main blood proteins involved are albumin and globulins.
🟢 ➤ Causes range from dehydration and infections to chronic inflammation or blood disorders.
🟢 ➤ Often detected during routine blood tests.
🟢 ➤ Treatment focuses on managing the underlying cause and maintaining protein balance.
🟢 ➤ Korea offers advanced diagnostic and treatment services, including hematology and nephrology care.
What is High Blood Protein (Hyperproteinemia)?
Hyperproteinemia is the condition of having elevated total protein in the bloodstream, which may result from an increase in globulins, albumin, or both.
Key points:
➤ Albumin – Produced by the liver, helps maintain osmotic pressure and fluid balance.
➤ Globulins – Include antibodies (immunoglobulins) crucial for immune defense.
➤ Elevated proteins may be benign or indicative of serious medical conditions such as chronic infections, liver disease, or blood disorders like multiple myeloma.
➤ Detection typically occurs through blood chemistry panels measuring total protein, albumin, and globulin levels.
Symptoms Related to Hyperproteinemia
Hyperproteinemia itself may not always produce symptoms, but underlying causes can result in noticeable effects:
🟢 ➤ Fatigue or weakness due to chronic illness.
🟢 ➤ Swelling or edema if associated with kidney or liver disorders.
🟢 ➤ Recurrent infections if immune system imbalance is present.
🟢 ➤ Unexplained weight loss or fever in chronic inflammatory conditions.
🟢 ➤ Bone pain or fractures in cases of multiple myeloma.
🟢 ➤ Nausea or digestive issues in liver or kidney involvement.
Causes / Possible Causes
Hyperproteinemia can arise from various physiological or pathological conditions:
Dehydration
➤ Reduced plasma volume concentrates proteins in the blood.
Chronic Infections
➤ Tuberculosis, hepatitis, or HIV can raise globulin levels.
Inflammatory Conditions
➤ Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus increase immunoglobulin production.
Blood Disorders
➤ Multiple myeloma or Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia cause abnormal proliferation of plasma cells, elevating protein levels.
Liver Disease
➤ Impaired albumin regulation or excessive globulin production may lead to increased total protein.
Other Causes
➤ Certain medications or endocrine disorders can indirectly affect protein levels.
When Should I See a Doctor?
Medical evaluation is essential if routine blood tests indicate high total protein or if you experience related symptoms:
🟢 ➤ Unexplained fatigue, weakness, or recurrent infections.
🟢 ➤ Swelling in legs, abdomen, or other areas.
🟢 ➤ Persistent fever or signs of chronic infection.
🟢 ➤ Bone pain, fractures, or other musculoskeletal symptoms.
🟢 ➤ Family history of blood disorders or multiple myeloma.
Early consultation ensures accurate diagnosis, identification of underlying causes, and prevention of complications.
Care and Treatment
Management focuses on treating the underlying cause and maintaining healthy protein levels:
Addressing Dehydration
➤ Adequate fluid intake and intravenous hydration if needed.
Treating Infections or Inflammation
➤ Antibiotics, antivirals, or anti-inflammatory medications depending on cause.
Managing Blood Disorders
➤ Hematology care for conditions like multiple myeloma, including chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or bone marrow transplantation if indicated.
Liver and Kidney Care
➤ Medications or lifestyle adjustments to support liver or kidney function.
➤ Monitoring protein intake and overall nutrition.
Advanced Care in Korea
➤ Korean hospitals provide comprehensive blood analysis, immunology testing, and personalized treatment plans.
➤ Integration of hematology, nephrology, and internal medicine ensures multidisciplinary care for hyperproteinemia patients.
Highlights (Clean Green Arrow Version)
🟢 ➤ Hyperproteinemia is elevated total protein in the blood, including albumin and globulins.
🟢 ➤ Causes: dehydration, infections, chronic inflammation, blood disorders, liver disease.
🟢 ➤ Symptoms: fatigue, swelling, recurrent infections, bone pain, digestive issues.
🟢 ➤ Diagnosis through blood tests measuring total protein, albumin, and globulin levels.
🟢 ➤ Treatment focuses on underlying cause, hydration, medication, and organ support.
🟢 ➤ South Korea provides advanced diagnostic services and multidisciplinary treatment plans.