Overview
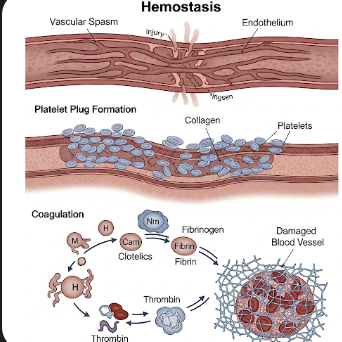
Hemostasis is the natural process that stops bleeding when blood vessels are injured. It is a crucial physiological mechanism that prevents excessive blood loss while maintaining normal blood flow. The process involves a complex interaction between blood vessels, platelets, and clotting factors, resulting in the formation of a stable blood clot.
Hemostasis occurs in three stages: vascular spasm, platelet plug formation, and coagulation. Disruption in any of these stages can lead to bleeding disorders or excessive clotting, making hemostasis a key focus in medical care worldwide, including in South Korea, where advanced hematology and clotting disorder management are available.
Key Facts
🟢 ➤ Hemostasis is the body’s mechanism to stop bleeding after blood vessel injury.
🟢 ➤ It involves blood vessels, platelets, and clotting factors.
🟢 ➤ The three stages are vascular spasm, platelet plug formation, and coagulation.
🟢 ➤ Disorders in hemostasis can lead to excessive bleeding or clotting.
🟢 ➤ Proper hemostasis is essential for surgical procedures, trauma care, and chronic disease management.
🟢 ➤ South Korea provides advanced hematology services and clotting disorder treatments.
What is Hemostasis?
Hemostasis is a physiological process that maintains the balance between bleeding and clotting. Its primary goal is to prevent blood loss while preserving blood flow through the circulatory system.
The process includes:
➤ Vascular Spasm – Immediate constriction of blood vessels to reduce blood flow.
➤ Platelet Plug Formation – Platelets adhere to the damaged vessel wall and release chemicals to attract more platelets.
➤ Coagulation (Blood Clotting) – Clotting factors activate a cascade that converts fibrinogen to fibrin, forming a stable clot that seals the injury.
Effective hemostasis is critical for injury repair, surgical procedures, and trauma response.
Symptoms Related to Hemostasis Disorders
Problems with hemostasis can manifest as either excessive bleeding or abnormal clotting:
🟢 ➤ Easy bruising or petechiae (small red spots on the skin).
🟢 ➤ Prolonged bleeding from minor cuts or injuries.
🟢 ➤ Nosebleeds, gum bleeding, or heavy menstrual bleeding.
🟢 ➤ Hematomas or swelling due to internal bleeding.
🟢 ➤ Excessive clotting may cause deep vein thrombosis, stroke, or pulmonary embolism.
🟢 ➤ Fatigue or weakness related to chronic blood loss or anemia.
Causes / Possible Causes
Disorders of hemostasis can result from problems in blood vessels, platelets, or clotting factors:
Platelet Disorders
➤ Low platelet count (thrombocytopenia) or platelet dysfunction can impair clot formation.
Clotting Factor Deficiencies
➤ Hemophilia A and B are genetic disorders causing deficient clotting factors VIII and IX.
Vitamin K Deficiency
➤ Essential for synthesizing clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X.
Liver Disease
➤ Impaired liver function can reduce production of clotting factors.
Medications
➤ Anticoagulants, aspirin, or other blood-thinning drugs may affect hemostasis.
Vascular Disorders
➤ Fragile or abnormal blood vessels may increase bleeding risk.
When Should I See a Doctor?
Medical evaluation is important if there are signs of abnormal bleeding or clotting:
🟢 ➤ Frequent or unexplained bruising or bleeding.
🟢 ➤ Prolonged bleeding from minor cuts or nosebleeds.
🟢 ➤ Heavy or irregular menstrual bleeding.
🟢 ➤ Swelling or pain in limbs suggestive of clot formation.
🟢 ➤ Family history of bleeding disorders or clotting disorders.
Early diagnosis allows proper treatment, prevention of complications, and management of underlying causes.
Care and Treatment
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of the hemostasis disorder:
Medications
➤ Clotting factor concentrates for hemophilia.
➤ Vitamin K supplementation for deficiencies.
➤ Anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs for preventing abnormal clotting.
Lifestyle and Dietary Measures
➤ Balanced diet rich in vitamins K and C to support healthy blood vessels and clotting.
➤ Avoidance of medications or supplements that may worsen bleeding unless prescribed.
Medical Procedures
➤ In severe cases, platelet transfusions, plasma transfusions, or surgical interventions may be required.
Advanced Care in Korea
➤ Hematology centers provide diagnostic testing, genetic counseling, and personalized treatment plans for bleeding or clotting disorders.
➤ Cutting-edge treatments include targeted therapies, recombinant clotting factors, and minimally invasive interventions.
Highlights (Clean Green Arrow Version)
🟢 ➤ Hemostasis is the body’s process to stop bleeding and maintain blood flow.
🟢 ➤ Involves vascular spasm, platelet plug formation, and coagulation.
🟢 ➤ Disorders can cause excessive bleeding or abnormal clotting.
🟢 ➤ Common causes: platelet disorders, clotting factor deficiencies, vitamin K deficiency, liver disease, medications.
🟢 ➤ Treatment includes medications, dietary support, medical procedures, and monitoring.
🟢 ➤ Korea provides advanced hematology services, genetic counseling, and personalized care for hemostasis disorders.