Overview
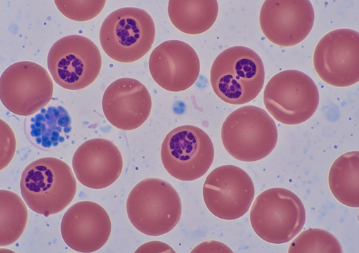
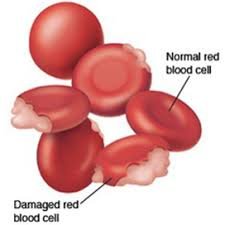
Heinz bodies are abnormal inclusions within red blood cells (RBCs) composed of denatured hemoglobin. They are typically visible only with special staining techniques under a microscope. The presence of Heinz bodies indicates oxidative damage to hemoglobin, which can lead to hemolytic anemia if red blood cells are destroyed prematurely.
Detection of Heinz bodies is clinically important because it can reveal underlying conditions such as glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, thalassemia, or exposure to oxidative drugs and toxins. In South Korea, advanced hematology labs use automated blood analyzers, specialized staining, and molecular diagnostics to accurately identify Heinz bodies and guide treatment.
Key Facts
➲ Heinz bodies are inclusions of denatured hemoglobin in red blood cells.
➲ They are typically detected using supravital stains like crystal violet or new methylene blue.
➲ Their presence indicates oxidative stress or hemoglobin instability.
➲ Common causes include G6PD deficiency, unstable hemoglobin variants, certain medications, and toxins.
➲ Heinz bodies can lead to hemolysis, anemia, jaundice, and fatigue.
➲ Korean hematology centers offer state-of-the-art laboratory testing and targeted therapies for patients with hemolytic disorders.
What are Heinz Bodies?
Heinz bodies are small, round, intracellular inclusions within red blood cells, representing oxidatively damaged hemoglobin.
Key features:
➲ Formed when hemoglobin molecules denature and precipitate inside RBCs.
➲ Typically not visible on routine blood smears; require special supravital staining.
➲ Can cause red blood cells to become rigid and prone to premature destruction in the spleen.
➲ Often associated with bite cells, where portions of RBCs are removed by the spleen.
Heinz bodies are an important diagnostic marker in hematology, helping clinicians detect hemolytic disorders and underlying metabolic or genetic causes.
What Symptoms Are Related to Heinz Bodies?
The presence of Heinz bodies often correlates with symptoms of hemolytic anemia, which arise from the premature destruction of red blood cells:
➲ Fatigue and weakness due to reduced oxygen-carrying capacity.
➲ Pale skin (pallor).
➲ Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) from increased bilirubin.
➲ Dark urine due to hemoglobinuria.
➲ Rapid heart rate (tachycardia).
➲ Splenomegaly (enlarged spleen) in chronic cases.
➲ In severe cases, shortness of breath or dizziness may occur.
Symptoms vary depending on the extent of hemolysis and underlying cause. Mild Heinz body formation may be asymptomatic, whereas severe oxidative stress can lead to acute hemolytic episodes.
What Causes / Possible Causes
Heinz bodies form as a result of oxidative damage to hemoglobin, and several conditions can trigger their formation:
1. Genetic Causes
➲ Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency – a common enzymatic disorder causing RBC vulnerability to oxidative stress.
➲ Unstable hemoglobin variants – inherited hemoglobinopathies that precipitate under stress.
2. Drug-Induced Causes
➲ Certain medications like primaquine, dapsone, sulfonamides, or nitrofurantoin can trigger oxidative stress.
3. Chemical and Toxin Exposure
➲ Exposure to naphthalene, phenylhydrazine, or other oxidizing agents can induce Heinz body formation.
4. Medical Conditions
➲ Chronic liver disease or malignancies can predispose RBCs to oxidative damage.
➲ Severe infections or metabolic disturbances may contribute.
5. Other Triggers
➲ Fava beans in individuals with G6PD deficiency (favism).
➲ Oxidative stress due to infection, fever, or hypoxia.
When Should I See My Doctor?
Medical evaluation is crucial if Heinz bodies are suspected, particularly when associated with hemolytic anemia or related symptoms:
➲ Sudden onset of fatigue, pallor, or jaundice.
➲ Dark or tea-colored urine suggesting hemoglobinuria.
➲ History of G6PD deficiency or hemoglobinopathies.
➲ After exposure to oxidative drugs, chemicals, or certain foods.
➲ Unexplained anemia or recurrent episodes of hemolysis.
Early assessment allows accurate diagnosis, prevention of severe hemolysis, and management of underlying causes.
Care and Treatment
Treatment for Heinz bodies depends on the underlying cause and severity of hemolysis:
1. Avoidance of Triggers
➲ Discontinue oxidative drugs or chemicals.
➲ Avoid fava beans or other known triggers in G6PD-deficient individuals.
2. Supportive Care
➲ Hydration and rest to support kidney function during hemolytic episodes.
➲ Blood transfusions in severe anemia.
➲ Oxygen therapy if needed for hypoxia.
3. Medical Treatment
➲ Folate supplementation to support red blood cell production.
➲ Treatment of underlying infections or metabolic disturbances.
➲ Monitoring and management of chronic hemolytic conditions.
4. Long-Term Management
➲ Genetic counseling for familial hemoglobinopathies or G6PD deficiency.
➲ Regular hematology follow-ups to monitor RBC health and hemolysis markers.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers advanced hematology and laboratory services to diagnose and manage conditions associated with Heinz bodies:
Diagnosis in Korea
➲ Blood smears with supravital staining to detect Heinz bodies.
➲ Complete blood count (CBC), reticulocyte count, and bilirubin tests.
➲ Enzyme assays for G6PD deficiency.
➲ Genetic testing for hemoglobinopathies and enzyme deficiencies.
Medical Treatments in Korea
➲ Individualized supportive care and medication management.
➲ Transfusion services for severe hemolytic anemia.
➲ Nutritional guidance and preventive strategies for G6PD-deficient patients.
Rehabilitation and Support
➲ Patient education on avoiding triggers and managing oxidative stress.
➲ Long-term monitoring in hematology clinics.
➲ Multidisciplinary care combining hematologists, geneticists, and dietitians.
Quick Highlights Box
➲ Heinz bodies are denatured hemoglobin inclusions within red blood cells, visible on special stains.
➲ Indicate oxidative damage to RBCs, often leading to hemolytic anemia.
➲ Causes include G6PD deficiency, unstable hemoglobin variants, oxidative drugs, toxins, and metabolic disorders.
➲ Symptoms may include fatigue, pallor, jaundice, dark urine, and shortness of breath.
➲ Korea provides state-of-the-art hematology labs, genetic testing, supportive care, and preventive guidance.
➲ Early detection and management prevent severe hemolysis and complications.