Overview
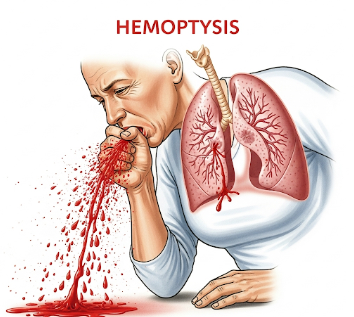
Haemoptysis refers to the coughing up of blood from the lower respiratory tract, including the lungs and bronchi. The blood may appear bright red, frothy, or mixed with sputum. Haemoptysis is a serious symptom that can indicate a wide range of underlying conditions, from infections and inflammatory lung diseases to tumors or cardiovascular problems.
In South Korea, pulmonology and thoracic centers provide advanced diagnostics, imaging, and treatment options for haemoptysis, ensuring rapid evaluation and management to prevent complications.
Key Facts
🟢 ➤ Haemoptysis is the expectoration of blood originating from the respiratory tract.
🟢 ➤ Can range from small streaks of blood to massive, life-threatening bleeding.
🟢 ➤ Common causes include respiratory infections, chronic lung diseases, tumors, and cardiovascular issues.
🟢 ➤ Immediate medical evaluation is crucial for severe or recurrent cases.
🟢 ➤ Diagnostic tools include chest X-ray, CT scan, bronchoscopy, and laboratory tests.
🟢 ➤ South Korean hospitals offer integrated care with pulmonologists, interventional radiologists, and thoracic surgeons.
What is Haemoptysis?
Haemoptysis occurs when blood from the lungs or airways is expelled through coughing, differing from epistaxis (nosebleed) or blood from the gastrointestinal tract.
Key points:
➤ Small amounts of blood-streaked sputum may be benign, often related to mild infections.
➤ Moderate to massive haemoptysis can indicate serious conditions such as bronchiectasis, tuberculosis, lung cancer, or pulmonary embolism.
➤ Blood is typically frothy and bright red, mixed with sputum, and may have a distinct odor.
➤ Immediate assessment is required if haemoptysis is recurrent, increasing, or accompanied by systemic symptoms.
Symptoms Related to Haemoptysis
Symptoms depend on underlying cause and severity:
🟢 ➤ Coughing up blood, ranging from streaks to large volumes.
🟢 ➤ Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, especially in severe cases.
🟢 ➤ Chest pain or discomfort in associated lung conditions.
🟢 ➤ Fever, night sweats, or weight loss if caused by infection like tuberculosis.
🟢 ➤ Fatigue, palpitations, or dizziness in significant blood loss.
🟢 ➤ Wheezing or noisy breathing in airway inflammation or obstruction.
Causes / Possible Causes
Haemoptysis can result from infectious, inflammatory, structural, or systemic causes:
Infectious Causes
➤ Tuberculosis (TB) – a leading cause worldwide.
➤ Pneumonia or bronchitis.
➤ Fungal infections in immunocompromised individuals.
Chronic Lung Diseases
➤ Bronchiectasis – permanent dilation of bronchi leading to recurrent infections.
➤ Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and emphysema.
Tumors and Malignancies
➤ Lung cancer or metastatic lesions.
➤ Benign tumors of the airway (rare).
Cardiovascular Causes
➤ Pulmonary embolism or infarction.
➤ Left-sided heart failure causing pulmonary congestion.
Other Causes
➤ Trauma to the chest or airways.
➤ Coagulation disorders or anticoagulant therapy.
➤ Foreign body aspiration in children or elderly.
When Should I See a Doctor?
Seek immediate medical attention if:
🟢 ➤ Haemoptysis is sudden, severe, or massive (over 200–600 ml in 24 hours).
🟢 ➤ Accompanied by shortness of breath, chest pain, or palpitations.
🟢 ➤ Blood is bright red, recurrent, or associated with fever, night sweats, or weight loss.
🟢 ➤ There is a history of lung disease, smoking, or anticoagulant use.
Early evaluation is essential to identify the source of bleeding, prevent life-threatening complications, and start appropriate treatment.
Care and Treatment
Management of haemoptysis focuses on stabilizing the patient, identifying the underlying cause, and treating both symptoms and source of bleeding:
Emergency Management
➤ Secure airway and maintain oxygenation in severe cases.
➤ Hospitalization and monitoring for large-volume haemoptysis.
Medical Management
➤ Antibiotics for bacterial infections.
➤ Antitubercular therapy if tuberculosis is diagnosed.
➤ Medications to improve coagulation or treat underlying systemic disorders.
Procedures and Interventions
➤ Bronchoscopy – to locate the bleeding source, remove clots, or perform local interventions.
➤ Endovascular embolization – blocking bleeding vessels using interventional radiology.
➤ Surgery – reserved for uncontrolled bleeding or tumors requiring resection.
Advanced Care in Korea
➤ South Korean pulmonology centers provide CT-guided imaging, bronchoscopy, and interventional radiology.
➤ Multidisciplinary management involves pulmonologists, thoracic surgeons, and interventional radiologists.
➤ Patient education includes recognizing warning signs, follow-up care, and managing underlying conditions.
Highlights (Clean Green Arrow Version)
🟢 ➤ Haemoptysis is the coughing up of blood from the lungs or airways, ranging from mild to life-threatening.
🟢 ➤ Symptoms: blood-streaked or frothy sputum, shortness of breath, chest pain, fever, and fatigue.
🟢 ➤ Causes: infections (TB, pneumonia), chronic lung disease, tumors, cardiovascular issues, trauma, or coagulation disorders.
🟢 ➤ Immediate evaluation is critical for severe, recurrent, or unexplained haemoptysis.
🟢 ➤ Treatment includes medications, bronchoscopy, endovascular embolization, or surgery depending on cause and severity.
🟢 ➤ South Korea offers advanced pulmonology and thoracic care with integrated diagnostics, intervention, and patient education.