Overview
Groin pain in males refers to discomfort, soreness, or aching in the area between the lower abdomen and upper thigh. This region contains muscles, tendons, ligaments, lymph nodes, blood vessels, nerves, and male reproductive organs, making it prone to a variety of pain-inducing conditions.
Groin pain can be acute (sudden onset due to injury or trauma) or chronic (developing over weeks or months due to repetitive stress, hernias, or medical conditions). While some cases are minor and resolve with rest, others may indicate serious conditions such as inguinal hernia, testicular torsion, infections, or tumors, requiring immediate medical attention.
In South Korea, advanced urology, orthopedics, and general surgery centers provide high-quality diagnostics and treatment options, including minimally invasive surgeries and rehabilitation programs.
Key Facts
➲ Male groin pain can arise from musculoskeletal, urological, reproductive, or vascular causes.
➲ Acute pain may indicate testicular torsion, hernia, or trauma, requiring urgent evaluation.
➲ Chronic or recurring pain often involves muscle strain, tendonitis, or sports hernia.
➲ Pain may be localized (testicles, spermatic cord) or radiating (to thigh, lower abdomen, or back).
➲ Korea offers state-of-the-art imaging, minimally invasive surgery, and multidisciplinary care.
What is Groin Pain (Male)?
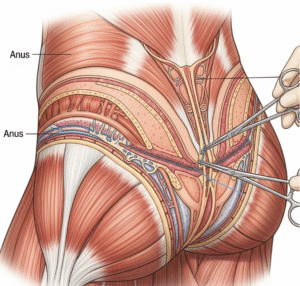
Groin pain in males refers to discomfort or aching in the crease between the abdomen and thigh. It may be sharp, dull, or throbbing, and can be associated with swelling, tenderness, or visible lumps.
Commonly affected structures include:
➲ Muscles and tendons – adductors, hip flexors, and abdominal muscles.
➲ Reproductive organs – testicles, epididymis, and spermatic cord.
➲ Lymph nodes – which can swell due to infection or inflammation.
➲ Vascular structures – femoral vessels or hernias affecting circulation.
Groin pain may interfere with walking, running, lifting, or sexual activity, affecting quality of life.
What Symptoms Are Related to Male Groin Pain?
Symptoms vary depending on the cause and severity:
➲ Pain that worsens with movement or physical activity.
➲ Visible swelling, lumps, or bulges in the groin area.
➲ Tenderness to touch, warmth, or redness.
➲ Testicular pain or heaviness.
➲ Nausea or vomiting in cases of torsion or acute hernia.
➲ Difficulty walking or hip movement limitations.
➲ Fever or malaise if infection is present.
➲ Pain radiating to the lower abdomen, thigh, or back.
What Causes / Possible Causes
Male groin pain can arise from multiple systems and conditions:
1. Musculoskeletal Causes
➲ Muscle strain – commonly adductor muscles in athletes.
➲ Tendonitis or ligament injury from sports or heavy lifting.
➲ Hip joint problems – labral tears or arthritis causing referred pain.
2. Hernias
➲ Inguinal hernia – intestine or tissue protrudes through the abdominal wall.
➲ Femoral hernia – less common in men but may cause swelling and discomfort.
3. Reproductive System Causes
➲ Testicular torsion – twisting of the spermatic cord, urgent condition.
➲ Epididymitis or orchitis – infections of testicles or epididymis.
➲ Varicocele or hydrocele – fluid accumulation or enlarged veins.
4. Urinary Causes
➲ Kidney stones producing referred pain to the groin.
➲ Urinary tract infections (UTIs) causing lower abdominal and groin discomfort.
5. Infection and Lymphatic Causes
➲ Swollen lymph nodes from infections or sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
➲ Abscess formation or cellulitis.
6. Trauma or Other Causes
➲ Direct injury to the groin or testicles.
➲ Post-surgical pain or chronic irritation.
➲ Rare tumors in testicles or surrounding tissues.
When Should I See My Doctor?
Immediate medical evaluation is necessary if:
➲ Sudden, severe groin pain, especially with nausea or vomiting (possible testicular torsion).
➲ Visible swelling, redness, or bulge in the groin.
➲ Persistent or worsening pain lasting more than a few days.
➲ Fever or signs of infection.
➲ Difficulty walking or limited mobility.
➲ Blood in urine or abnormal discharge.
Prompt evaluation prevents permanent testicular damage, hernia complications, or infection spread.
Care and Treatment
Treatment depends on the underlying cause:
1. Home and Supportive Care
➲ Rest and avoid activities aggravating the pain.
➲ Ice packs for acute injury to reduce swelling.
➲ Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises for mild muscle strain.
2. Medications
➲ NSAIDs for pain and inflammation.
➲ Antibiotics for infections (e.g., epididymitis, orchitis, or UTI).
➲ Pain management for chronic or post-surgical conditions.
3. Surgical and Procedural Treatments
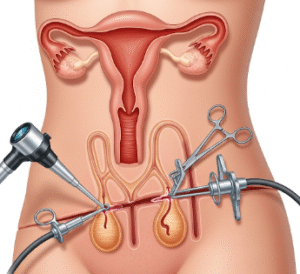
➲ Hernia repair (open or laparoscopic).
➲ Testicular torsion surgery to restore blood flow.
➲ Drainage of abscesses or cyst removal.
➲ Orthopedic procedures for hip or musculoskeletal-related pain.
4. Rehabilitation and Follow-Up
➲ Physical therapy to restore strength and flexibility.
➲ Gradual return to sports or daily activity.
➲ Long-term monitoring for recurring hernias or chronic conditions.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea is internationally recognized for advanced urology, surgery, and sports medicine care for male groin pain.
Diagnosis in Korea
➲ Ultrasound for testicular, spermatic cord, and lymph node evaluation.
➲ MRI or CT scans for detailed soft tissue and organ assessment.
➲ Blood and urine tests for infections or systemic causes.
➲ Orthopedic and sports medicine assessment for musculoskeletal pain.
Medical Treatments in Korea
➲ Targeted antibiotics for infections.
➲ NSAIDs and physical therapy for musculoskeletal causes.
➲ Nutritional guidance and lifestyle counseling for chronic conditions.
Surgical and Advanced Therapies
➲ Laparoscopic or robotic-assisted hernia repair.
➲ Testicular or epididymal surgery for torsion or infections.
➲ Orthopedic or arthroscopic interventions for sports-related groin injuries.
Rehabilitation and Support
➲ Multidisciplinary rehabilitation programs.
➲ Post-surgical recovery with guided physical therapy.
➲ Follow-up monitoring for recurrence and long-term outcomes.
Quick Highlights Box
➲ Male groin pain can arise from muscle strain, hernia, reproductive or urinary causes, or infections.
➲ Sudden severe pain may indicate testicular torsion or hernia, requiring urgent care.
➲ Symptoms include pain, swelling, tenderness, lumps, and limited mobility.
➲ Korea provides advanced imaging, minimally invasive surgery, and multidisciplinary care.
➲ Early evaluation prevents permanent tissue damage, infection, or hernia complications.
➲ Treatment includes rest, medications, surgery, and rehabilitation programs.