Overview
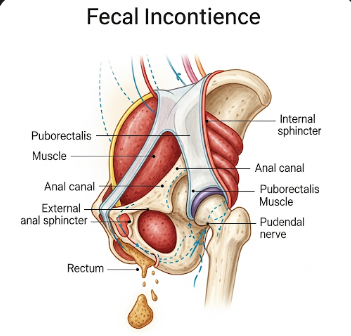
Faecal incontinence is the involuntary loss of stool or inability to control bowel movements, leading to accidental leakage. It can range from occasional minor leaks to complete loss of bowel control, significantly affecting quality of life, social interactions, and emotional well-being. In Korea, specialized gastroenterology and colorectal clinics provide advanced diagnostic tests, medical management, and surgical treatments to manage faecal incontinence effectively.
Key Facts
▶ Prevalence: Can affect people of all ages, particularly older adults and individuals with a history of childbirth, surgery, or neurological disorders.
▶ Causes: Muscle damage, nerve injury, chronic constipation, diarrhea, or systemic illnesses.
▶ Associated Symptoms: Urgency, leakage, discomfort, abdominal pain, and skin irritation.
▶ Treatment Options in Korea: Pelvic floor therapy, medications, minimally invasive procedures, and surgical interventions.
▶ Urgency: Persistent or worsening incontinence requires prompt evaluation to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
What is Faecal Incontinence?
Faecal incontinence refers to the loss of voluntary bowel control, leading to unintentional passage of stool. Severity varies from occasional minor leakage to complete inability to control bowel movements.
▶ Temporary Incontinence: Often caused by diarrhea, infections, or medications.
▶ Chronic Incontinence: Linked to nerve damage, muscle dysfunction, or structural issues in the rectum and anus.
▶ Functional Incontinence: Difficulty controlling stool due to impaired bowel habits or cognitive dysfunction.
▶ Impact: Emotional distress, social isolation, and skin problems are common consequences.
Note: Early recognition and targeted treatment are essential to restore control and prevent complications.
What Symptoms Are Related to Faecal Incontinence?
▶ Accidental Leakage: Uncontrolled passage of stool, ranging from mild to severe.
▶ Urgency: Sudden, strong need to defecate without time to reach the bathroom.
▶ Incomplete Evacuation: Feeling that stool remains after bowel movement.
▶ Diarrhea or Loose Stools: Exacerbates incontinence.
▶ Constipation: Chronic straining can weaken pelvic floor muscles.
▶ Abdominal Discomfort: Cramping or bloating may occur.
▶ Skin Irritation: Perianal dermatitis or infections from frequent leakage.
▶ Emotional and Social Impact: Anxiety, embarrassment, and avoidance of social activities.
What Causes / Possible Causes
Faecal incontinence can result from muscular, neurological, or systemic factors:
▶ Sphincter Muscle Damage: Injury during childbirth, surgery, or trauma.
▶ Nerve Damage: Diabetes, spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, or neuropathy.
▶ Chronic Constipation: Straining weakens anal sphincter and pelvic floor muscles.
▶ Diarrhea: Loose or watery stools are harder to control.
▶ Rectal Prolapse: Weakening of rectal walls affects bowel control.
▶ Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease may contribute.
▶ Aging: Muscle and nerve function decline with age.
▶ Post-Surgical Changes: Rectal or anal surgery can impair sphincter integrity.
Note: Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective and lasting management.
When Should I See a Doctor?
▶ Persistent Leakage: Any ongoing involuntary stool passage.
▶ Severe Urgency or Frequent Accidents: Interfering with daily activities or work.
▶ Pain or Bleeding: May indicate infection or structural abnormalities.
▶ Associated Diarrhea or Constipation: Complicates control and treatment.
▶ Skin Irritation or Infection: Persistent leakage causing dermatitis.
▶ Emotional Distress: Anxiety, depression, or social withdrawal related to incontinence.
▶ Children or Older Adults: Prompt evaluation for congenital, neurological, or age-related causes.
Tip: Korean colorectal and gastroenterology clinics provide specialized evaluation, diagnostic imaging, and comprehensive treatment plans.
Care and Treatment
Management depends on cause, severity, and patient needs:
▶ Dietary Adjustments: High-fiber diet for regular stools; avoidance of triggers causing diarrhea.
▶ Pelvic Floor Exercises (Kegel Exercises): Strengthen anal sphincter and pelvic muscles.
▶ Biofeedback Therapy: Teaches control of sphincter muscles and coordination during bowel movements.
▶ Medications: Anti-diarrheal agents, stool softeners, or laxatives depending on stool consistency.
▶ Behavioral Interventions: Scheduled toileting and bowel habit training.
▶ Minimally Invasive Procedures: Bulking agents injected into anal canal to improve closure.
▶ Surgical Interventions: Sphincter repair, sacral nerve stimulation, or colostomy in severe cases.
▶ Monitoring: Regular follow-up to assess improvement and prevent complications.
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Evaluation:
▶ Physical Examination: Assessment of anal sphincter function, muscle strength, and reflexes.
▶ Diagnostic Tests: Anorectal manometry, endorectal ultrasound, or colonoscopy to identify structural or functional issues.
▶ Laboratory Tests: Evaluate for infections, inflammatory bowel disease, or metabolic disorders.
▶ Specialist Consultation: Gastroenterologists, colorectal surgeons, and physiotherapists collaborate for care.
Advanced Therapies:
▶ Biofeedback and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation: Offered in specialized clinics to restore control.
▶ Injection Therapies: Bulking agents or botulinum toxin for sphincter dysfunction.
▶ Surgical Repair: Sphincteroplasty, sacral nerve stimulation, or stoma creation for refractory cases.
▶ Multidisciplinary Care: Combines gastroenterology, surgery, and physiotherapy for holistic management.
Rehabilitation & Support:
▶ Patient Education: Proper toileting techniques, dietary guidance, and bowel habit training.
▶ Follow-Up Care: Ensures ongoing improvement, prevention of skin issues, and emotional support.
▶ Specialist Clinics: Korean hospitals provide integrated care combining medical, procedural, and rehabilitative services.
Outcome: With early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment in Korea, faecal incontinence can be effectively managed, restoring bowel control, improving comfort, and enhancing overall quality of life.