Overview
Facial swelling, also known as facial edema, refers to abnormal puffiness or enlargement of facial tissues. It can occur suddenly or gradually and may involve one or both sides of the face. Facial swelling can range from mild cosmetic concern to a medical emergency, depending on the underlying cause. Common triggers include infections, allergies, trauma, dental problems, systemic illnesses, or hormonal imbalances. In Korea, dermatology, ENT, dental, and internal medicine clinics offer specialized evaluation, imaging, and treatment options to address facial swelling and its root causes effectively.
Highlights:
➤ Visible puffiness or enlargement of facial tissues
➤ Can affect one side or the entire face
➤ May indicate minor issues or serious medical conditions
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Facial swelling is a common symptom; exact prevalence varies by cause
➤ Age affected: Can occur at any age; certain conditions are age-specific (e.g., angioedema more common in adults)
➤ Gender: Affects both males and females
➤ Impact: May cause pain, discomfort, impaired vision, or social anxiety
➤ Prognosis: Dependent on the underlying cause; many cases resolve with treatment
What is Facial Swelling?
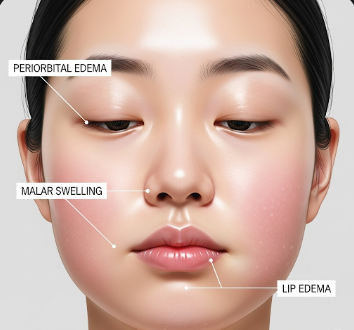
Facial swelling occurs when fluid accumulates in the tissues of the face, leading to puffiness or edema. It may affect eyelids, cheeks, lips, jawline, or the entire face. Types include:
- Localized swelling: Confined to a specific area due to trauma, insect bite, or dental infection
- Generalized swelling: Involves the entire face; may result from systemic conditions such as kidney disease or heart failure
- Sudden vs. gradual onset: Rapid swelling may indicate allergic reactions or infection, while slow swelling may signal chronic conditions
Highlights:
➤ Facial swelling is a visible symptom that may signal underlying medical issues
➤ Pattern, onset, and associated symptoms help determine cause
➤ Early evaluation is essential for serious conditions
What Symptoms Are Related to Facial Swelling?
➤ Puffiness or enlargement of cheeks, eyelids, or lips
➤ Redness or warmth – Often seen in infections or inflammation
➤ Pain or tenderness – Associated with trauma, dental infection, or sinusitis
➤ Difficulty opening eyes, speaking, or eating – In severe swelling
➤ Itching or rash – May indicate allergic reaction
➤ Fever or malaise – Suggests infection
➤ Other systemic signs: Shortness of breath, dizziness, or swelling in other parts of the body
Highlights:
➣ Symptoms vary depending on cause and severity
➣ Accompanying signs like fever, rash, or difficulty breathing may indicate urgent conditions
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Allergic reactions (angioedema): Triggered by foods, medications, insect bites, or environmental allergens
➤ Infections: Sinusitis, dental abscess, cellulitis, or viral infections such as mumps
➤ Trauma or injury: Bruising, fractures, or surgical procedures
➤ Dental problems: Tooth abscess, impacted teeth, or gum infections
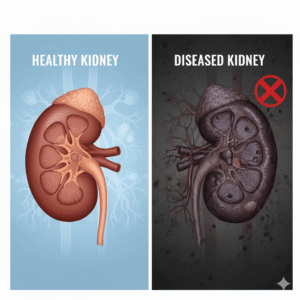
➤ Systemic conditions: Kidney disease, heart failure, liver disease, or hypothyroidism
➤ Medications: Certain antihypertensives, steroids, or NSAIDs
➤ Hormonal changes: Pregnancy or hormonal imbalances
➤ Idiopathic causes: Sometimes swelling occurs without identifiable reason
Highlights:
➣ Facial swelling can result from local, systemic, allergic, infectious, or traumatic causes
➣ Determining the exact cause is crucial for proper management
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Sudden onset facial swelling – Especially with difficulty breathing or swallowing
➤ Pain, redness, or warmth – Suggests infection requiring urgent care
➤ Associated fever or malaise – May indicate systemic infection
➤ Persistent or progressive swelling – Could be a sign of chronic illness
➤ Visual changes or eye involvement – Requires immediate evaluation
Highlights:
➣ Urgent consultation at a Korean ENT, dermatology, or emergency clinic is critical for severe cases
➣ Early diagnosis prevents complications and permanent tissue damage
Care and Treatment
➤ Lifestyle modifications: Avoid allergens, maintain hydration, and reduce salt intake in systemic edema
➤ Medications:
- Antihistamines: For allergic reactions
- Steroids: Reduce inflammation in severe allergy or autoimmune cases
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections like cellulitis or dental abscess
➤ Cold or warm compresses: Reduce localized swelling and discomfort
➤ Dental care: Root canal, extraction, or treatment of dental abscesses
➤ Management of systemic conditions: Treat kidney, heart, or liver-related edema
➤ Monitoring: Track swelling, pain, and any new associated symptoms
Highlights:
➣ Treatment depends on underlying cause and severity
➣ Early and appropriate care prevents complications and accelerates recovery
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Dermatology and ENT clinics: Evaluation, imaging, and prescription therapy
➤ Dental clinics: Comprehensive oral examination and treatment for dental infections
➤ Internal medicine clinics: Management of systemic causes like kidney, liver, or heart disease
➤ Allergy centers: Testing and treatment for angioedema and other allergic reactions
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Surgical drainage: For severe abscesses or cellulitis
➤ Immunotherapy or biologics: For chronic allergic or autoimmune causes
➤ Emergency interventions: Epinephrine for severe angioedema causing airway compromise
➤ Follow-up care: Regular monitoring to prevent recurrence and manage complications
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Education on allergen avoidance, oral hygiene, and systemic disease management
➤ Continuous monitoring of swelling, underlying condition, and response to therapy
➤ Multidisciplinary support for functional, cosmetic, and psychological concerns
Highlights:
➣ Korean clinics provide comprehensive diagnostics, individualized treatment, and long-term follow-up
➣ Early intervention ensures reduced swelling, minimized complications, and improved quality of life