Overview
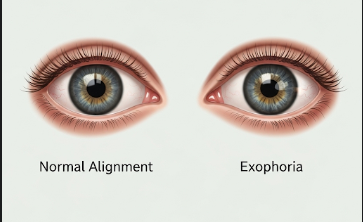
Exophoria is a type of latent eye misalignment (heterophoria) where the eyes tend to drift outward when binocular vision is disrupted. Unlike exotropia, which is a constant outward deviation, exophoria is usually hidden under normal visual conditions and becomes noticeable during specialized testing or eye fatigue. In Korea, ophthalmology and optometry clinics provide accurate assessment and management for exophoria to reduce eye strain, headaches, and intermittent double vision, enhancing visual comfort and function.
Highlights:
➤ Latent outward deviation of the eyes – Becomes apparent when fusion is disrupted
➤ Often asymptomatic – Symptoms appear mainly with eye fatigue or prolonged visual tasks
➤ Can affect reading, vision comfort, and eye coordination
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Exophoria is relatively common and may occur in children and adults.
➤ Age affected: Can develop in childhood or adulthood; often associated with near-vision tasks or stress.
➤ Gender: Affects both males and females.
➤ Impact: May lead to eye strain, blurred vision, headaches, intermittent double vision, and difficulty focusing on near tasks.
What is Exophoria?
Exophoria is a latent outward deviation of the eyes that is normally compensated by the brain’s fusional mechanisms, allowing single binocular vision. Key characteristics include:
- Outward drift tendency: Eyes naturally move away from the nose when fusion is broken
- Controlled by fusion reflexes: The brain aligns the eyes to maintain normal vision
- Latent condition: Detected during specialized tests such as cover-uncover or Maddox rod testing
Highlights:
➤ Hidden under normal circumstances – Detected only under specific conditions
➤ Can cause visual discomfort if fusional control is strained
➤ Not always a sign of serious pathology but may affect quality of vision
What Symptoms Are Related to Exophoria?
➤ Eye strain or fatigue – Especially after reading or prolonged near work
➤ Intermittent double vision (diplopia) – Occurs when fusional control is weakened
➤ Headaches – Resulting from prolonged eye muscle effort
➤ Blurred vision – Difficulty maintaining clear focus
➤ Difficulty concentrating on visual tasks – Especially in academic or occupational settings
➤ Occasional eye closing or squinting – To relieve strain or reduce double vision
Highlights:
➣ Symptoms are situational and worsen with fatigue or prolonged near tasks
➣ Early detection prevents chronic eye strain and associated complications
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Muscle imbalance: Minor variations in extraocular muscle tone
➤ Refractive errors: Uncorrected myopia, hyperopia, or astigmatism can exacerbate exophoria
➤ Eye fatigue: Prolonged near work or digital screen use
➤ Stress or illness: Physical or emotional stress can weaken fusional control
➤ Neurological changes: Rarely, post-surgical or neurological conditions can influence eye alignment
Highlights:
➣ Exophoria usually arises from subtle muscular or visual system imbalances
➣ Identifying contributing factors helps optimize treatment and reduce symptoms
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Persistent eye strain or headaches – Particularly during reading or computer work
➤ Intermittent double vision – Indicates compromised binocular vision
➤ Difficulty focusing on near tasks – Affecting academic or occupational performance
➤ Sudden changes in vision or eye alignment – Requires urgent evaluation
➤ Family history of eye misalignment – Increases likelihood of latent or manifest deviations
Highlights:
➣ Early consultation with a Korean ophthalmologist or optometrist ensures accurate diagnosis
➣ Timely management prevents long-term visual discomfort and fatigue
Care and Treatment
➤ Vision therapy: Exercises to improve binocular coordination, eye tracking, and fusional capacity
➤ Corrective lenses: Prescription glasses or prism lenses to reduce strain and double vision
➤ Visual hygiene and posture: Frequent breaks during near work and ergonomic adjustments
➤ Surgical intervention: Rarely required, usually only in severe or symptomatic cases
➤ Monitoring: Regular follow-up to track symptoms and adjust therapy
Highlights:
➣ Treatment focuses on strengthening binocular vision and reducing visual fatigue
➣ Individualized care improves visual comfort, academic performance, and occupational efficiency
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Ophthalmology clinics: Comprehensive eye exams, binocular vision testing, and prescription lenses
➤ Vision therapy centers: Structured programs for eye muscle coordination and fusional strengthening
➤ Prism correction: Special lenses to correct latent outward deviation
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Orthoptic evaluation: Tailored exercises for fusional control and eye coordination
➤ Surgical options: Reserved for persistent, symptomatic cases resistant to therapy
➤ Follow-up care: Adjustments of lenses and therapy to maintain optimal eye function
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Routine monitoring of eye alignment and binocular vision
➤ Patient education on visual ergonomics, eye exercises, and lifestyle modifications
➤ Multidisciplinary care if combined with neurology or pediatric management
Highlights:
➣ Korean clinics provide state-of-the-art vision therapy, diagnostic tools, and personalized treatment plans
➣ Early and consistent management ensures symptom reduction and improved visual performance