Overview
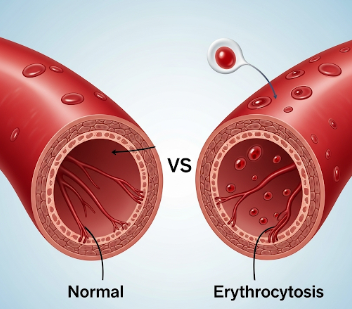
Erythrocytosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormally high number of red blood cells (RBCs) in the bloodstream. This increase can thicken the blood, potentially leading to complications such as blood clots, strokes, or heart attacks. The condition may be primary, arising from intrinsic bone marrow disorders like polycythemia vera, or secondary, resulting from factors such as chronic hypoxia, smoking, or tumors producing erythropoietin. In Korea, hematology and internal medicine clinics provide thorough diagnosis and management options, including advanced blood tests, imaging, and therapeutic procedures to reduce risks associated with elevated red blood cell counts.
Highlights:
➤ Elevated red blood cell count – Can affect oxygen delivery and blood flow
➤ Primary or secondary causes – Including genetic, environmental, and disease-related factors
➤ Potentially serious complications – Risk of clot formation, stroke, or heart attack
Key Facts
➤ Normal RBC count: Typically 4.5–5.9 million/µL in men and 4.1–5.1 million/µL in women
➤ Prevalence: Erythrocytosis is less common than anemia but occurs in specific populations, particularly older adults or those with chronic hypoxic conditions
➤ Age affected: Can develop at any age depending on underlying cause
➤ Gender: Slight male predominance, especially in primary erythrocytosis
➤ Impact: May lead to fatigue, dizziness, headaches, hypertension, and increased cardiovascular risk
What is Erythrocytosis?
Erythrocytosis refers to an increase in red blood cell mass, often detected via blood tests showing elevated hemoglobin, hematocrit, and RBC count. The condition can be classified as:
- Primary erythrocytosis: Caused by bone marrow disorders like polycythemia vera, often due to JAK2 gene mutations
- Secondary erythrocytosis: Triggered by hypoxia (low oxygen levels), chronic lung disease, smoking, or tumors producing erythropoietin
- Relative erythrocytosis: Resulting from dehydration or plasma volume contraction, without actual increase in red blood cell mass
Key characteristics include:
- High hemoglobin and hematocrit levels
- Increased blood viscosity – Risk factor for clotting
- Possible splenomegaly – Enlargement of the spleen in primary erythrocytosis
Highlights:
➤ Can be a primary disorder or secondary to other conditions
➤ Diagnosis relies on blood tests and clinical evaluation
➤ Early detection prevents serious cardiovascular complications
What Symptoms Are Related to Erythrocytosis?
➤ Fatigue and weakness – Due to impaired blood flow and oxygen delivery
➤ Headaches and dizziness – Often caused by hyperviscosity
➤ Red or flushed skin – Especially on the face and hands
➤ Visual disturbances – Blurred vision or transient visual loss
➤ High blood pressure – Due to increased blood volume and viscosity
➤ Itching (pruritus) – Particularly after warm showers, common in polycythemia vera
➤ Abdominal discomfort or fullness – If spleen is enlarged
➤ Shortness of breath – Especially in secondary erythrocytosis due to hypoxia
Highlights:
➣ Symptoms may vary depending on the type and severity
➣ Early recognition can reduce risk of complications
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Primary erythrocytosis: Bone marrow disorders such as polycythemia vera, often associated with JAK2 mutations
➤ Secondary erythrocytosis:
- Chronic hypoxia from lung disease or high-altitude living
- Smoking-induced hypoxia
- Tumors producing excess erythropoietin (renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma)
- Heart disease causing reduced oxygenation
➤ Relative erythrocytosis: Due to dehydration or plasma volume contraction
➤ Medications: Certain anabolic steroids or erythropoiesis-stimulating agents
Highlights:
➣ Causes are diverse and can be intrinsic, environmental, or secondary to other diseases
➣ Identifying the underlying cause is critical for targeted treatment
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Persistent fatigue, dizziness, or headaches – Could indicate elevated RBCs
➤ High blood pressure or visual disturbances – Requires evaluation
➤ Red, flushed skin or pruritus – May suggest polycythemia vera
➤ History of smoking or chronic lung disease – Risk factor for secondary erythrocytosis
➤ Family history of blood disorders – May indicate genetic predisposition
Highlights:
➣ Early consultation with a Korean hematologist or internal medicine specialist ensures accurate diagnosis
➣ Timely intervention reduces risk of blood clots, stroke, and cardiovascular complications
Care and Treatment
➤ Phlebotomy: Regular removal of blood to reduce hematocrit in primary erythrocytosis
➤ Medications:
- Hydroxyurea to suppress bone marrow production in polycythemia vera
- Low-dose aspirin to reduce risk of blood clots
➤ Addressing underlying causes: Oxygen therapy for hypoxia, smoking cessation, or treatment of tumors
➤ Lifestyle adjustments: Staying hydrated, avoiding excessive iron supplementation, managing cardiovascular risk factors
➤ Monitoring: Regular blood tests to track hemoglobin, hematocrit, and RBC counts
Highlights:
➣ Treatment is cause-specific and aimed at reducing complications
➣ Ongoing monitoring ensures long-term safety and symptom control
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Hematology clinics: Comprehensive blood tests, bone marrow evaluation, and genetic testing
➤ Phlebotomy therapy: Standard treatment for polycythemia vera or severe erythrocytosis
➤ Prescription medications: Hydroxyurea, aspirin, or targeted therapies
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Oxygen therapy or ventilatory support: For hypoxia-related secondary erythrocytosis
➤ Tumor management: Surgical or oncologic treatment for erythropoietin-producing tumors
➤ Follow-up care: Regular monitoring of blood counts and cardiovascular health
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Education on lifestyle modifications, hydration, and cardiovascular risk reduction
➤ Regular check-ups to prevent thrombotic events
➤ Multidisciplinary care for patients with complex systemic causes
Highlights:
➣ Korean clinics provide advanced diagnostics, targeted treatment, and long-term monitoring
➣ Early intervention ensures symptom relief, prevention of complications, and improved quality of life