Overview
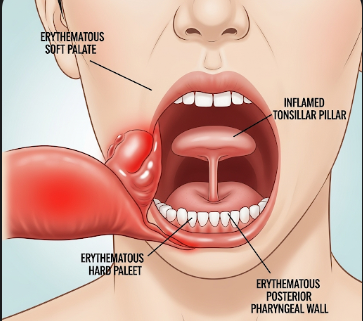
Erythematous mucosa refers to reddening of the mucous membranes, which can occur in the oral cavity, nasal passages, gastrointestinal tract, or other mucosal surfaces. This condition usually indicates inflammation, irritation, or infection of the affected area. Erythema may be localized or diffuse and can result from infections, allergic reactions, autoimmune disorders, or trauma. In Korea, gastroenterology, ENT, and dental clinics provide evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment for erythematous mucosa to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Highlights:
➤ Reddened mucous membranes – Visible sign of inflammation or irritation
➤ May indicate infection, allergy, or systemic disease – Requires evaluation
➤ Occurs in multiple areas – Oral, nasal, gastrointestinal, or other mucosal surfaces
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Erythematous mucosa is commonly observed in patients with infections, allergic reactions, or inflammatory conditions.
➤ Age affected: Can occur at any age depending on underlying cause.
➤ Gender: Affects both males and females equally.
➤ Impact: May cause pain, discomfort, difficulty eating, swallowing, or speaking, and can be a sign of underlying systemic illness.
What is Erythematous Mucosa?
Erythematous mucosa is characterized by reddening of mucosal surfaces due to increased blood flow in response to irritation or inflammation. Common presentations include:
- Oral erythema: Red patches in the mouth or tongue
- Gastrointestinal erythema: Red inflamed mucosa in the stomach or intestines observed via endoscopy
- Nasal erythema: Red mucosal lining in rhinitis or sinusitis
- Urogenital erythema: Redness in vaginal or urethral mucosa due to infection or irritation
Highlights:
➤ Sign of underlying inflammation or irritation – Not a standalone diagnosis
➤ May be symptomatic or asymptomatic – Depends on location and severity
➤ Requires further evaluation to identify cause
What Symptoms Are Related to Erythematous Mucosa?
➤ Redness of the affected mucosa – Visible upon examination
➤ Pain or tenderness – Especially in oral or gastrointestinal mucosa
➤ Swelling or edema – Accompanies inflammation
➤ Ulceration or sores – May develop in severe cases
➤ Bleeding or easy bruising – In cases of trauma or severe inflammation
➤ Difficulty eating, swallowing, or speaking – If oral or pharyngeal involvement
➤ Itching or irritation – Common in nasal or urogenital mucosa
Highlights:
➣ Symptoms can range from mild discomfort to significant functional impairment
➣ Severity often correlates with underlying cause and duration
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Infections: Viral, bacterial, or fungal infections causing mucosal inflammation
➤ Allergic reactions: Food allergies, medications, or environmental allergens
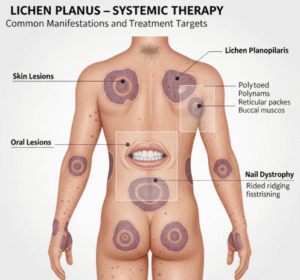
➤ Autoimmune disorders: Conditions like lichen planus, pemphigus vulgaris, or lupus
➤ Trauma or irritation: Mechanical trauma, chemical irritants, or burns
➤ Nutritional deficiencies: Iron, vitamin B12, or folate deficiencies
➤ Systemic diseases: Gastrointestinal disorders, liver disease, or hematologic conditions
Highlights:
➣ Causes may be localized or systemic, requiring comprehensive evaluation
➣ Accurate identification of cause is critical for effective treatment
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Persistent redness or inflammation – Not resolving within a few days
➤ Associated pain, bleeding, or ulceration – Indicates more severe underlying issues
➤ Difficulty eating, swallowing, or breathing – Needs urgent evaluation
➤ Recurrent or widespread erythema – May suggest systemic disease
➤ Accompanying systemic symptoms: Fever, fatigue, or weight loss
Highlights:
➣ Early assessment at a Korean ENT, dental, or gastroenterology clinic is essential
➣ Prompt evaluation prevents complications and allows targeted therapy
Care and Treatment
➤ Identify underlying cause: Laboratory tests, cultures, or biopsies if needed
➤ Medications: Antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, or anti-inflammatory drugs depending on cause
➤ Topical therapy: Corticosteroid gels, antiseptic rinses, or soothing ointments
➤ Lifestyle and dietary modifications: Avoid irritants, spicy foods, or allergens
➤ Symptomatic relief: Pain management, hydration, and mucosal care
➤ Monitoring: Follow-up to assess resolution and prevent recurrence
Highlights:
➣ Treatment depends on location, severity, and underlying cause
➣ Comprehensive care improves symptoms, healing, and mucosal health
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ ENT and dental clinics: Diagnosis and management of oral and nasal erythema
➤ Gastroenterology clinics: Endoscopic evaluation for gastrointestinal mucosal redness
➤ Pharmacological therapy: Targeted medications for infection, inflammation, or allergy
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Endoscopic evaluation: For precise identification of gastrointestinal mucosal inflammation
➤ Biopsy: To rule out autoimmune or neoplastic causes
➤ Laser or topical therapy: For refractory oral or dermatologic mucosal lesions
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Regular monitoring and reassessment of mucosal health
➤ Patient education on oral hygiene, allergen avoidance, and dietary care
➤ Integration of ENT, gastroenterology, dental, and dermatology specialists for multidisciplinary management
Highlights:
➣ Korean clinics offer advanced diagnostics, targeted treatment, and holistic follow-up care
➣ Early and tailored intervention ensures optimal recovery, symptom relief, and prevention of recurrence