Overview
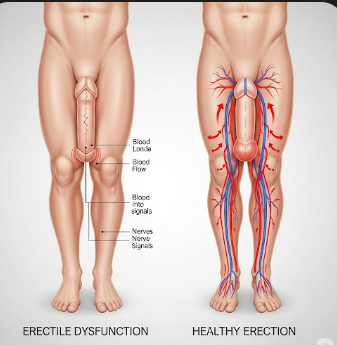
Erectile dysfunction (ED), commonly referred to as impotence, is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. ED is a prevalent condition among men, particularly those over 40, and can significantly impact sexual satisfaction, self-esteem, and relationships. Causes of ED are often multifactorial, including vascular, neurological, hormonal, psychological, or lifestyle factors. In Korea, urology and sexual health clinics offer comprehensive assessment, advanced diagnostics, and individualized treatment plans to restore sexual function and overall quality of life.
Highlights:
➤ Inability to achieve or maintain an erection – Primary feature of ED
➤ Affects sexual health, self-esteem, and relationships
➤ Often treatable with medical, psychological, or lifestyle interventions
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Approximately 40% of men experience ED by age 40, rising to over 70% in men over 70
➤ Age affected: Can occur at any age; incidence increases with age and comorbid conditions
➤ Gender: Male-specific condition
➤ Impact: Can lead to emotional distress, relationship difficulties, and reduced quality of life
➤ Prognosis: Most cases respond well to early evaluation and appropriate treatment
What is Erectile Dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction is the persistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection adequate for sexual intercourse. ED can be classified as:
- Primary ED: Lifelong difficulty achieving erections
- Secondary ED: Acquired after a period of normal erectile function
- Situational ED: Occurs only under certain circumstances, often psychologically mediated
ED may result from vascular insufficiency, nerve damage, hormonal imbalance, or psychological stress. Early identification of the underlying cause is essential for effective treatment.
Highlights:
➤ Multifactorial etiology involving physical and psychological components
➤ Can be temporary or chronic
➤ Diagnosis involves history-taking, physical examination, and laboratory evaluation
What Symptoms Are Related to Erectile Dysfunction?
➤ Difficulty achieving an erection – Primary symptom
➤ Difficulty maintaining an erection during sexual activity
➤ Reduced sexual desire or libido – May accompany ED
➤ Premature or delayed ejaculation – Can coexist with ED
➤ Emotional or psychological effects: Anxiety, stress, low self-esteem, and depression
➤ Relationship strain – Sexual dissatisfaction may affect partner dynamics
Highlights:
➣ Symptoms vary depending on cause and severity
➣ Psychological symptoms often exacerbate physical manifestations
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Vascular causes: Atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes, or peripheral artery disease reducing blood flow to the penis
➤ Neurological causes: Spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, or neuropathy
➤ Hormonal causes: Low testosterone, thyroid dysfunction, or hyperprolactinemia
➤ Psychological causes: Stress, anxiety, depression, performance anxiety, or relationship issues
➤ Lifestyle factors: Smoking, alcohol abuse, sedentary lifestyle, obesity
➤ Medications: Antidepressants, antihypertensives, or other drugs affecting sexual function
➤ Surgical or trauma-related causes: Prostate surgery, pelvic trauma, or pelvic radiation
Highlights:
➣ ED often results from combined physical and psychological factors
➣ Identifying and addressing root causes is critical for effective management
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Persistent difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection – Over weeks or months
➤ Associated loss of sexual desire or psychological distress
➤ History of cardiovascular risk factors or diabetes
➤ Medication-related erectile difficulties – Suspected side effects
➤ Fertility concerns – In men attempting conception
Highlights:
➣ Early consultation with a Korean urologist or sexual health specialist ensures accurate diagnosis
➣ Timely intervention prevents long-term sexual, psychological, and relational consequences
Care and Treatment
➤ Lifestyle modifications: Regular exercise, balanced diet, smoking cessation, alcohol moderation
➤ Psychological therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), counseling, or couples therapy
➤ Medications:
- Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5i): Sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil
- Testosterone replacement therapy: For confirmed low testosterone
➤ Mechanical devices: Vacuum erection devices or penile constriction rings
➤ Surgical interventions: Penile implants or vascular surgery in refractory cases
➤ Monitoring: Ongoing assessment of erectile function, psychological well-being, and medication side effects
Highlights:
➣ Most ED responds well to combined lifestyle, medical, and psychological therapies
➣ Personalized care ensures optimal treatment outcomes
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Urology clinics: Comprehensive evaluation including hormone testing, cardiovascular assessment, and laboratory analysis
➤ Prescription medications: PDE5 inhibitors or hormonal therapy based on etiology
➤ Lifestyle counseling: Exercise, diet modification, stress management, and smoking cessation
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Penile implants: Inflatable or semi-rigid devices for severe or refractory ED
➤ Vascular surgery: For select patients with anatomical vascular defects
➤ Rehabilitative therapy: Pelvic floor exercises and sexual counseling
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Education on sexual techniques, partner communication, and lifestyle optimization
➤ Regular follow-up to monitor treatment response and adjust therapies
➤ Multidisciplinary support for patients with psychological or systemic contributors
Highlights:
➣ Korean clinics provide comprehensive diagnostics, individualized treatment plans, and long-term follow-up
➣ Early intervention ensures restored sexual function, improved confidence, and better relationships