Overview
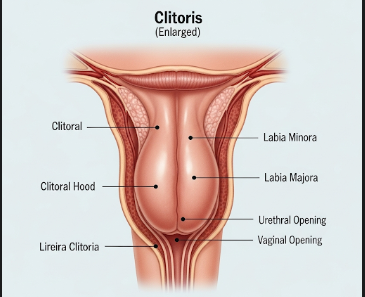
Enlarged clitoris, medically known as clitoromegaly, refers to the abnormal enlargement of the clitoral tissue. This condition can occur congenitally, hormonally, or due to medical conditions. It may be associated with hormonal imbalances, genetic syndromes, or exposure to excess androgens. While clitoromegaly is not always harmful, it can cause physical discomfort, psychological stress, and sexual health concerns. In Korea, gynecology and endocrinology clinics offer specialized evaluation, hormonal assessment, and treatment options for individuals experiencing clitoral enlargement.
Highlights:
➤ Abnormal enlargement of clitoral tissue – Can be congenital or acquired
➤ May cause physical or psychological concerns – Pain, discomfort, or body image issues
➤ Requires careful evaluation – To determine hormonal or structural causes
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Clitoromegaly is rare but can be observed in cases of congenital adrenal hyperplasia or hormonal disorders.
➤ Age affected: Can present at birth (congenital) or develop during puberty or adulthood (acquired).
➤ Gender: Occurs exclusively in individuals assigned female at birth.
➤ Impact: May affect sexual function, body image, and self-esteem, and in some cases, indicate an underlying endocrine disorder.
What is Enlarged Clitoris?
Enlarged clitoris refers to clitoral tissue that exceeds the normal size range, potentially causing visible enlargement, sensitivity, or discomfort. Causes may include:
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH): Excess androgen production before birth
- Hormonal exposure: High levels of androgens during puberty or adulthood
- Tumors: Rare adrenal or ovarian tumors producing excess hormones
- Endocrine disorders: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or other hormonal imbalances
Highlights:
➤ Not always indicative of disease – Requires evaluation to rule out hormonal or genetic conditions
➤ May be congenital or acquired – Timing and cause vary among individuals
➤ Can affect sexual function and comfort
What Symptoms Are Related to Enlarged Clitoris?
➤ Visible enlargement – Clitoris appears larger than typical anatomical range
➤ Increased sensitivity – May cause discomfort or pain during touch or sexual activity
➤ Hirsutism or hair growth – Excess androgen effect may cause facial or body hair
➤ Menstrual irregularities – In cases of hormonal imbalance
➤ Acne or oily skin – Signs of excess androgen activity
➤ Psychological impact – Anxiety, embarrassment, or distress about appearance
Highlights:
➣ Symptoms can be physical, hormonal, or psychological
➣ Early evaluation helps identify treatable causes
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH): Genetic disorder affecting adrenal hormone production
➤ Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): Hormonal imbalance causing elevated androgens
➤ Adrenal or ovarian tumors: Rare hormone-secreting tumors
➤ Exogenous androgen exposure: Medications or supplements containing androgens
➤ Endocrine disorders: Other hormonal imbalances affecting sex steroid production
Highlights:
➣ Causes may be genetic, hormonal, or tumor-related
➣ Proper diagnosis is crucial for targeted therapy and symptom management
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Visible clitoral enlargement – Especially if noticed during puberty or adulthood
➤ Associated hormonal symptoms: Irregular menstruation, hirsutism, acne
➤ Discomfort or pain during sexual activity
➤ Rapid changes in size or appearance – Could indicate a tumor or hormonal surge
➤ Psychological distress – Body image or emotional impact
Highlights:
➣ Early consultation with a Korean gynecologist or endocrinologist ensures accurate diagnosis
➣ Timely evaluation prevents unnecessary anxiety and guides effective treatment
Care and Treatment
➤ Medical evaluation: Hormonal assessment, blood tests for androgens, imaging of adrenal and ovarian glands
➤ Hormonal therapy: In cases of excess androgen, medications may help normalize hormone levels
➤ Surgical intervention: Clitoral reduction surgery may be considered for significant discomfort or psychosocial impact
➤ Psychological support: Counseling or therapy to address body image and emotional well-being
➤ Monitoring: Regular follow-up to track hormonal levels and overall health
Highlights:
➣ Treatment depends on underlying cause, severity, and patient preference
➣ Multidisciplinary care combines endocrinology, gynecology, and psychological support
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Gynecology and endocrinology clinics: Comprehensive hormonal evaluation and monitoring
➤ Pharmacological therapy: Medications for androgen regulation in cases of PCOS or CAH
➤ Lifestyle modifications: Supportive measures for hormone balance, weight management, and overall health
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Clitoral reduction surgery: Minimally invasive procedures preserving sensitivity
➤ Imaging-guided evaluation: MRI or ultrasound to assess adrenal or ovarian glands
➤ Follow-up hormonal monitoring: Ensures normalization of androgen levels and prevents recurrence
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Counseling and therapy to support emotional and psychological well-being
➤ Regular hormonal assessments to maintain long-term health
➤ Patient education on self-monitoring and early symptom recognition
Highlights:
➣ Korean clinics offer state-of-the-art diagnostic tools, individualized treatment plans, and surgical expertise
➣ Early and personalized intervention improves physical comfort, hormonal balance, and psychological health