Overview
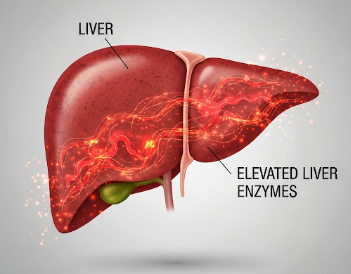
Elevated liver enzymes refer to higher-than-normal levels of certain enzymes in the blood, indicating liver stress, inflammation, or damage. The key enzymes usually monitored include alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT). Elevated levels do not always indicate serious liver disease but require evaluation to determine the underlying cause. In Korea, hepatology and gastroenterology clinics provide specialized testing and treatment for patients with elevated liver enzymes to prevent liver damage and complications.
Highlights:
➤ Indicates liver stress or injury – Not a disease but a marker
➤ Monitored through blood tests – ALT, AST, ALP, GGT
➤ Can signal mild to serious liver conditions – Early evaluation is key
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Elevated liver enzymes are commonly detected during routine health checkups in adults.
➤ Age affected: Can affect all age groups, though risk increases with alcohol use, obesity, or chronic diseases.
➤ Gender: Both men and women are affected; men may have slightly higher incidence due to lifestyle factors.
➤ Impact: Persistent elevation may indicate hepatitis, fatty liver, drug-induced injury, or bile duct obstruction.
What is Elevated Liver Enzymes?
Elevated liver enzymes occur when liver cells release enzymes into the bloodstream due to stress, injury, or inflammation. The most commonly tested enzymes are:
- ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase): High levels indicate liver cell injury
- AST (Aspartate Aminotransferase): Elevated in liver and muscle injury
- ALP (Alkaline Phosphatase): Increased with bile duct obstruction or bone disorders
- GGT (Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase): High in liver disease and alcohol use
Highlights:
➤ Marker of liver cell damage – Helps identify underlying liver conditions
➤ Not a diagnosis alone – Requires further testing for cause
➤ May be mild, moderate, or severe – Correlates with degree of liver injury
What Symptoms Are Related to Elevated Liver Enzymes?
➤ Fatigue or weakness – Common in liver stress or inflammation
➤ Abdominal discomfort – Particularly in the right upper quadrant
➤ Nausea or vomiting – Digestive symptoms may accompany liver dysfunction
➤ Jaundice: Yellowing of skin or eyes in severe liver impairment
➤ Dark urine or pale stools – Signs of bile flow obstruction
➤ Swelling or fluid retention – In advanced liver disease
➤ Itching or skin rashes – Cholestatic or autoimmune liver conditions
➤ No symptoms: Many people with mild elevation are asymptomatic
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Fat accumulation in liver cells
➤ Alcohol-related liver disease: Chronic alcohol consumption damages liver cells
➤ Viral hepatitis: Hepatitis A, B, C, D, or E infections
➤ Medications or toxins: Acetaminophen overdose, statins, or herbal supplements
➤ Autoimmune liver disease: Autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cholangitis
➤ Bile duct obstruction: Gallstones or tumors
➤ Metabolic disorders: Hemochromatosis, Wilson’s disease
➤ Heart failure or other systemic illness: Can indirectly elevate liver enzymes
Highlights:
➣ Elevated enzymes can result from liver-specific or systemic conditions
➣ Accurate evaluation is crucial to prevent further liver damage
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Persistent elevation – Detected on routine blood tests
➤ Associated symptoms: Fatigue, jaundice, abdominal pain, nausea
➤ History of liver disease or risk factors: Alcohol use, obesity, diabetes, viral hepatitis exposure
➤ Medication use: Potential hepatotoxic drugs
➤ Rapid increase in enzymes or abnormal liver function tests
Highlights:
➣ Early consultation with a Korean hepatologist or gastroenterologist is essential
➣ Timely assessment prevents progression to cirrhosis or liver failure
Care and Treatment
➤ Identify underlying cause: Blood tests, imaging (ultrasound, CT), and sometimes liver biopsy
➤ Lifestyle modification: Reduce alcohol intake, maintain healthy weight, manage diabetes
➤ Medications: Treat underlying viral hepatitis, autoimmune conditions, or bile duct issues
➤ Avoid hepatotoxic substances: Certain medications or supplements may need discontinuation
➤ Regular monitoring: Repeat liver enzyme tests to track improvement or progression
➤ Nutritional support: Balanced diet rich in antioxidants and low in saturated fats
Highlights:
➣ Treatment targets the underlying cause rather than the enzyme elevation itself
➣ Multidisciplinary care improves liver function and overall health
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Hepatology clinics: Comprehensive evaluation including lab tests, imaging, and liver fibrosis assessment
➤ Gastroenterology departments: Management of viral hepatitis, fatty liver, and autoimmune conditions
➤ Pharmacological therapy: Antivirals, immunosuppressants, or medications for metabolic disorders
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Liver imaging and elastography: Non-invasive assessment of fibrosis or cirrhosis
➤ Endoscopic procedures: For bile duct obstruction or gallstone removal
➤ Liver transplantation: In severe, irreversible liver disease
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Regular monitoring of liver enzymes and liver function tests
➤ Lifestyle counseling and nutritional guidance
➤ Integration of hepatology, gastroenterology, and nutrition specialists
Highlights:
➣ Korean clinics offer state-of-the-art diagnostics, individualized treatment plans, and advanced interventions
➣ Early management improves liver health, prevents complications, and enhances quality of life