Overview
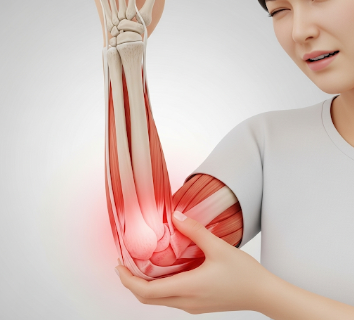
Elbow pain is a common musculoskeletal complaint that can affect anyone from athletes to office workers. It refers to discomfort, aching, or sharp pain around the elbow joint, which may be caused by injury, overuse, inflammation, or underlying medical conditions. The elbow is a complex joint composed of bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and nerves, making it susceptible to multiple pain sources. In Korea, orthopedic clinics and sports medicine centers provide specialized evaluation and treatment for elbow pain, ranging from conservative therapy to surgical interventions.
Highlights:
➤ Pain around the elbow joint – Can be acute or chronic
➤ Caused by injury, overuse, or medical conditions
➤ Affects daily activities – Lifting, typing, or sports performance
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Elbow pain is common in adults engaged in repetitive motions, such as typing, lifting, or playing racquet sports.
➤ Age affected: Can affect all ages; sports injuries are more common in younger individuals, while arthritis is more prevalent in older adults.
➤ Gender: Both men and women are affected, though certain sports or occupational risks may vary by gender.
➤ Impact: Untreated elbow pain can lead to reduced range of motion, chronic discomfort, and functional limitations.
What is Elbow Pain?
Elbow pain is defined as discomfort or aching in the joint or surrounding tissues, which may involve the bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, or nerves. It can be classified as:
- Acute pain: Sudden onset, often from trauma or injury
- Chronic pain: Gradual development, often from overuse, arthritis, or repetitive strain
Highlights:
➤ Variety of causes – From injury to systemic conditions
➤ Pain may be localized or radiating – Can extend to forearm or upper arm
➤ Associated symptoms – Swelling, stiffness, or reduced grip strength
What Symptoms Are Related to Elbow Pain?
➤ Aching or sharp pain – Depending on the cause
➤ Swelling or inflammation – Common in tendonitis or bursitis
➤ Stiffness or limited range of motion – Difficulty bending or straightening the elbow
➤ Weakness or reduced grip strength – May indicate tendon or nerve involvement
➤ Redness or warmth – Sign of infection or inflammatory condition
➤ Numbness or tingling – If nerves such as the ulnar nerve are affected
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis): Overuse of forearm muscles causing pain on the outer elbow
➤ Golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis): Pain on the inner elbow due to repetitive wrist and forearm movements
➤ Bursitis: Inflammation of the olecranon bursa leading to swelling and tenderness
➤ Fractures or dislocations: Trauma or accidents can damage the elbow bones or joint
➤ Arthritis: Osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis causing chronic pain and stiffness
➤ Tendon or ligament injuries: Strains, tears, or sprains from overuse or trauma
➤ Nerve compression: Cubital tunnel syndrome affecting the ulnar nerve
Highlights:
➣ Elbow pain can arise from musculoskeletal, neurological, or systemic causes
➣ Correct diagnosis is crucial to targeted and effective treatment
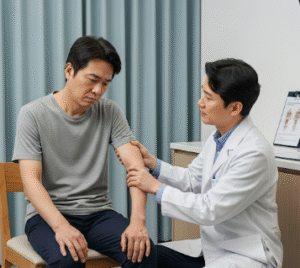
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Severe or sudden pain – Especially after trauma or fall
➤ Persistent pain lasting more than a few weeks – Suggests chronic overuse or tendon injury
➤ Swelling, redness, or warmth – May indicate infection or inflammation
➤ Numbness, tingling, or weakness – Suggests nerve involvement
➤ Limited range of motion affecting daily activities
Highlights:
➣ Early evaluation at a Korean orthopedic or sports medicine clinic can prevent chronic complications
➣ Timely treatment helps restore mobility, reduce pain, and prevent recurrence
Care and Treatment
➤ Rest and activity modification: Avoid activities that exacerbate pain
➤ Ice or heat therapy: Reduces inflammation and alleviates discomfort
➤ Medications: NSAIDs for pain and inflammation
➤ Physical therapy: Stretching, strengthening, and range-of-motion exercises
➤ Bracing or splinting: Supports the elbow and reduces strain on tendons
➤ Corticosteroid injections: For persistent inflammation in conditions like epicondylitis
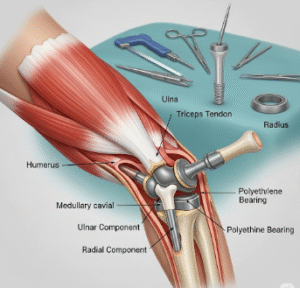
➤ Surgical intervention: Reserved for severe tendon tears, fractures, or chronic cases unresponsive to conservative treatment
Highlights:
➣ Treatment depends on cause, severity, and duration of pain
➣ Multidisciplinary care may involve orthopedists, physiotherapists, and occupational therapists
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Orthopedic clinics: Comprehensive evaluation including X-rays, MRI, and physical examination
➤ Sports medicine centers: Focus on injury prevention and rehabilitation for athletes
➤ Pharmacological therapy: Pain relief, anti-inflammatory medications, and supportive injections
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Minimally invasive surgery: Arthroscopic repair of tendons or ligaments
➤ Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy: Promotes tendon healing in chronic epicondylitis
➤ Ultrasound-guided interventions: Precise targeting for injections or diagnosis
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Ongoing monitoring of pain, mobility, and functional recovery
➤ Structured physiotherapy programs for strength and flexibility
➤ Education on ergonomics and injury prevention
Highlights:
➣ Korean clinics provide advanced diagnostics, minimally invasive procedures, and comprehensive rehabilitation
➣ Early intervention ensures faster recovery, reduced pain, and improved function