Overview
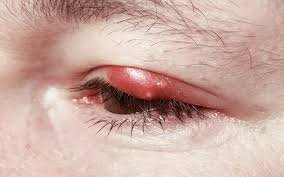
Ear pain, also called otalgia or earache, is a common symptom affecting the outer, middle, or inner ear. It can range from mild discomfort to severe pain that interferes with daily activities. Ear pain can be primary, originating from the ear itself, or referred, caused by conditions affecting nearby structures such as the throat, jaw, or teeth. In Korea, ENT clinics and pain management centers provide advanced diagnosis and treatment for ear pain, addressing both acute and chronic causes.
Highlights:
➤ Common symptom – Affects people of all ages
➤ Primary or referred – Pain may originate from the ear or nearby structures
➤ Impact on daily life – Can interfere with sleep, work, and hearing
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Ear pain is one of the most frequent reasons for ENT visits worldwide.
➤ Age affected: Can affect children, adults, and the elderly; children often experience ear infections causing pain.
➤ Gender: Both men and women are equally affected.
➤ Impact: Untreated ear pain can lead to hearing loss, chronic infections, or secondary complications.
What is Ear Pain?
Ear pain refers to any discomfort, aching, or sharp sensation in or around the ear. Causes are diverse, ranging from ear infections, trauma, wax impaction, and inflammation, to referred pain from the teeth, jaw, or throat. It is generally classified as:
- Primary otalgia: Directly arising from the ear structures
- Secondary (referred) otalgia: Pain felt in the ear but originating elsewhere
Highlights:
➤ Pain types vary – Sharp, dull, throbbing, or burning
➤ Can affect one or both ears
➤ Associated symptoms: Fever, discharge, hearing loss, or dizziness
What Symptoms Are Related to Ear Pain?
➤ Sharp or throbbing pain – May worsen at night or when chewing
➤ Fullness or pressure in the ear – Common in middle ear infections
➤ Hearing changes: Muffled hearing or partial loss
➤ Ear discharge: Pus or blood if infection or trauma is present
➤ Tinnitus: Ringing or buzzing in the ear
➤ Fever or malaise: Often accompanies infections
➤ Dizziness or vertigo: When inner ear structures are affected
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Ear infections: Otitis externa (outer ear), otitis media (middle ear), mastoiditis
➤ Earwax impaction: Blockage causing pressure and discomfort
➤ Injury or trauma: Foreign bodies, blows to the ear, or barotrauma
➤ Dental or jaw problems: TMJ disorders, tooth infections causing referred pain
➤ Throat or sinus infections: Pharyngitis, tonsillitis, or sinusitis
➤ Neurological causes: Neuralgia of the facial or glossopharyngeal nerve
➤ Tumors or growths: Rare but serious causes
Highlights:
➣ Ear pain can result from local ear conditions or referred sources
➣ Identification of the underlying cause is essential for effective treatment
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Severe or sudden ear pain – May indicate infection, trauma, or other acute conditions
➤ Persistent pain lasting more than 2–3 days
➤ Accompanied by fever, hearing loss, or discharge
➤ Recurrent pain – Suggests chronic infection or structural problem
➤ After trauma or foreign object insertion
Highlights:
➣ Early evaluation at an ENT clinic in Korea prevents complications
➣ Prompt diagnosis can prevent hearing loss, chronic infections, and structural damage
Care and Treatment
➤ Pain management: Analgesics such as NSAIDs or acetaminophen for symptom relief
➤ Infection treatment: Antibiotics for bacterial infections, antifungals for fungal infections
➤ Ear cleaning: Removal of impacted wax or foreign objects by professionals
➤ Hydration and rest: Supports recovery from infections
➤ Lifestyle adjustments: Avoid inserting objects into the ear and reduce exposure to irritants
➤ Dental or jaw treatment: For TMJ or dental-related referred ear pain
Highlights:
➣ Treatment depends on cause, severity, and duration of pain
➣ Multidisciplinary care may include ENT, dentistry, and pain management specialists
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ ENT clinics: Comprehensive evaluation including otoscopy, audiometry, and imaging
➤ Pharmacological therapy: Antibiotics, antifungals, or analgesics tailored to the underlying cause
➤ Specialized therapies: For TMJ disorders, neuralgias, or referred pain
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Ear microsurgery: For chronic infections, structural issues, or tumors
➤ Myringotomy or ear tube placement: For recurrent middle ear infections
➤ Removal of foreign bodies: Endoscopic or minimally invasive techniques
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Regular follow-up to ensure resolution of infection and pain
➤ Education on ear hygiene, prevention of trauma, and management of chronic conditions
➤ Holistic care in Korea integrates ENT, audiology, dental, and pain management services
Highlights:
➣ Korean clinics provide advanced diagnostics and multidisciplinary treatment plans
➣ Early intervention prevents chronic pain, hearing loss, and repeated infections