Overview
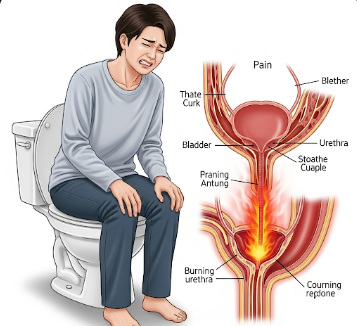
Dysuria is the medical term for painful or uncomfortable urination, which can present as burning, stinging, or sharp sensations during urination. It is a common symptom associated with urinary tract infections (UTIs), sexually transmitted infections (STIs), bladder inflammation, or kidney issues. Dysuria can significantly impact daily life, work productivity, and overall well-being. In Korea, urology and nephrology clinics offer advanced diagnostics and treatments for patients experiencing dysuria.
Highlights:
➤ Urinary symptom – Pain or discomfort during urination
➤ Acute or chronic – Can appear suddenly or persist over time
➤ Indicator of underlying conditions – Often signals infection, inflammation, or obstruction
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Dysuria is common, particularly among women due to short urethra anatomy, but also affects men and children.
➤ Age affected: Can occur at any age, with higher prevalence in sexually active adults and older adults.
➤ Gender: More common in women but may be more complicated in men due to prostate involvement.
➤ Impact: Untreated dysuria can lead to urinary tract infections, kidney infections, or chronic bladder problems.
What is Dysuria?
Dysuria refers to any pain, burning, or discomfort during urination, caused by irritation, infection, inflammation, or obstruction in the urinary tract. The severity can range from mild discomfort to severe pain that limits daily activities.
Highlights:
➤ Burning sensation: Often felt in the urethra or bladder
➤ Pain during urination: May be continuous or only at the start or end of urination
➤ Associated urinary changes: Frequent urges, urgency, or incomplete emptying
What Symptoms Are Related to Dysuria?
➤ Burning or stinging during urination – Most common symptom
➤ Frequent urination (polyuria) – Increased urge to urinate
➤ Urgency: Sudden, compelling need to urinate
➤ Cloudy or strong-smelling urine – Indicative of infection
➤ Blood in urine (hematuria) – May appear pink, red, or brown
➤ Lower abdominal or pelvic discomfort – Pain or pressure in bladder area
➤ Fever or malaise: In case of infection spreading to kidneys
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Urinary tract infections (UTIs): Most common cause in women and children
➤ Sexually transmitted infections (STIs): Chlamydia, gonorrhea, or herpes
➤ Prostatitis: Inflammation of the prostate in men
➤ Bladder inflammation (cystitis): Infection-related or interstitial
➤ Kidney stones or obstruction: Blocks urine flow, causing pain
➤ Medications or irritants: Certain drugs, hygiene products, or chemicals may irritate urinary tract
➤ Underlying medical conditions: Diabetes, immunosuppression, or structural abnormalities
Highlights:
➣ Dysuria is a symptom, not a disease itself
➣ Accurate identification of the underlying cause is essential for effective treatment
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Persistent pain during urination: Symptoms lasting more than 2–3 days
➤ Blood in urine or severe discomfort
➤ Fever, chills, or flank pain: Could indicate kidney involvement
➤ Recurring dysuria: Suggests chronic infection or structural issue
➤ In men: Painful urination may indicate prostate problems or STI
Highlights:
➣ Early evaluation by a urologist in Korea prevents complications
➣ Diagnostic tests may include urine analysis, urine culture, ultrasound, or cystoscopy
Care and Treatment
➤ Antibiotics: For bacterial infections such as UTIs or STIs
➤ Pain relief: NSAIDs or urinary analgesics for symptom relief
➤ Hydration: Increased water intake to flush bacteria and reduce irritation
➤ Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding irritants such as caffeine, alcohol, and harsh hygiene products
➤ Bladder care: Frequent urination and emptying completely to prevent stagnation
➤ Adjunct therapies: Cranberry extracts, probiotics, or topical treatments for chronic or recurrent cases
Highlights:
➣ Proper treatment depends on cause identification
➣ Untreated dysuria can lead to kidney infection, chronic inflammation, or systemic infection
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Urology clinics: Comprehensive evaluation and treatment for infections, stones, or prostate-related dysuria
➤ Pharmacological therapy: Targeted antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, or antivirals depending on cause
➤ STI management: Specialized testing and treatment for sexually transmitted infections
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Cystoscopy: Visual examination of the bladder for structural issues
➤ Stone removal: Lithotripsy or surgical intervention for kidney or ureteral stones
➤ Prostate therapies: For chronic prostatitis or enlarged prostate causing dysuria
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Regular follow-up ensures infection clearance and prevents recurrence
➤ Education on urinary hygiene, hydration, and safe sexual practices
➤ Holistic care in Korea integrates urology, nephrology, and lifestyle counseling
Highlights:
➣ Korean clinics provide advanced diagnostics and personalized treatment plans
➣ Early intervention reduces recurrence and prevents complications such as kidney infections