Overview
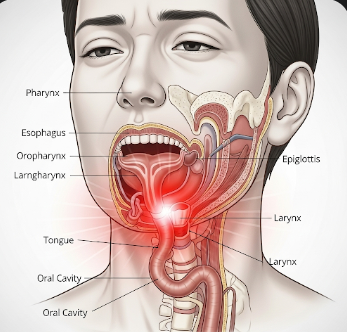
Dysphagia is the medical term for difficulty or discomfort while swallowing, which can involve problems in the mouth, throat, or esophagus. It affects both solids and liquids, and can range from mild discomfort to severe obstruction that impairs nutrition and hydration. Dysphagia can significantly impact daily life, mental health, and overall well-being. In Korea, gastroenterology, ENT, and rehabilitation clinics provide advanced diagnostics and treatments for patients experiencing swallowing difficulties.
Highlights:
➤ Swallowing disorder – Impairs passage of food or liquids from mouth to stomach
➤ Acute or chronic – Can develop suddenly or gradually
➤ Potentially serious – May lead to malnutrition, dehydration, or aspiration
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Dysphagia affects millions worldwide, especially older adults and individuals with neurological disorders.
➤ Age affected: More common in the elderly but can occur at any age depending on underlying causes.
➤ Gender: Both men and women are equally affected.
➤ Impact: Untreated dysphagia can result in malnutrition, dehydration, respiratory infections, and decreased quality of life.
What is Dysphagia?
Dysphagia is defined as difficulty swallowing food, liquids, or saliva, caused by structural obstruction, muscle weakness, or nerve dysfunction. It is generally classified as:
- Oropharyngeal dysphagia: Problems with mouth or throat muscles, difficulty initiating swallowing
- Esophageal dysphagia: Problems with the esophagus, such as narrowing, tumors, or motility disorders
Highlights:
➤ Oropharyngeal type: Trouble starting a swallow or choking on food
➤ Esophageal type: Food sticks in the throat or chest after swallowing
➤ Potential complications: Aspiration, malnutrition, dehydration
What Symptoms Are Related to Dysphagia?
➤ Painful swallowing (odynophagia) – Burning or discomfort in throat or chest
➤ Sensation of food sticking – Feeling like food is stuck in the throat or chest
➤ Choking or coughing – Particularly with liquids
➤ Regurgitation – Food coming back into the mouth
➤ Unexplained weight loss – Difficulty eating sufficient food
➤ Frequent throat clearing – Attempt to move food down
➤ Hoarseness or voice changes – Especially with aspiration
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Neurological disorders: Stroke, Parkinson’s disease, ALS, multiple sclerosis
➤ Muscle disorders: Myasthenia gravis, muscular dystrophies
➤ Obstructions: Tumors, strictures, esophageal webs
➤ Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): Chronic irritation leading to narrowing or motility problems
➤ Infections or inflammation: Severe throat infections, abscesses, or radiation therapy
➤ Aging: Natural decline in swallowing coordination and muscle strength
Highlights:
➣ Dysphagia may result from neurological, structural, or functional dysfunctions
➣ Accurate identification of the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Persistent difficulty swallowing – Symptoms lasting more than a few days
➤ Pain while swallowing – May indicate infection, inflammation, or obstruction
➤ Frequent choking or coughing – Especially with liquids
➤ Unexplained weight loss or malnutrition
➤ Recurrent respiratory infections – Could indicate aspiration
Highlights:
➣ Early evaluation by a gastroenterologist or ENT specialist in Korea is recommended
➣ Diagnostic tests may include barium swallow, endoscopy, or videofluoroscopy
Care and Treatment
➤ Dietary modifications: Soft, pureed, or thickened foods to ease swallowing
➤ Swallowing therapy: Exercises guided by a speech-language pathologist to improve coordination
➤ Posture and positioning techniques: Sitting upright, head tilting strategies to reduce aspiration
➤ Medications: For underlying GERD, infections, or muscle relaxation
➤ Hydration and nutrition monitoring – Ensuring adequate intake
➤ Avoid irritants: Spicy, dry, or rough-textured foods that worsen discomfort
Highlights:
➣ Multidisciplinary care including nutritionists, speech therapists, and physicians improves outcomes
➣ Consistent therapy and diet modifications are essential for safe swallowing
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Gastroenterology and ENT clinics: Advanced diagnostics including imaging and endoscopic evaluation
➤ Pharmacological therapy: Medications for reflux, infection, or esophageal motility disorders
➤ Neurological management: For dysphagia secondary to stroke, Parkinson’s, or ALS
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Endoscopic dilation or surgery: To relieve esophageal narrowing or strictures
➤ Botulinum toxin injection: For achalasia or esophageal muscle spasm
➤ Feeding tube placement: For severe or prolonged swallowing difficulties
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Ongoing speech-language therapy to improve swallowing efficiency
➤ Regular monitoring for nutrition, hydration, and aspiration risk
➤ Holistic care in Korea integrates gastroenterology, neurology, rehabilitation, and nutrition services
Highlights:
➣ Korean clinics offer personalized, technology-assisted swallowing rehabilitation
➣ Early intervention reduces aspiration risk, malnutrition, and improves quality of life