Overview
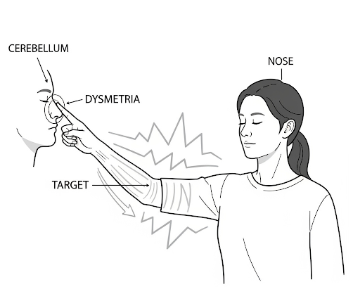
Dysmetria is a neurological condition characterized by the inability to properly control the distance, power, or speed of voluntary movements. It is commonly associated with cerebellar dysfunction, meaning that the part of the brain responsible for coordination is affected. Individuals with dysmetria often overshoot or undershoot targets when reaching for objects or walking, which can significantly impact daily activities. In Korea, specialized neurology and rehabilitation clinics provide comprehensive assessment and management for this condition.
Highlights:
➤ Neurological disorder – Usually involves cerebellar dysfunction
➤ Coordination issue – Affects voluntary movements and balance
➤ Impact on daily life – Can impair self-care, mobility, and fine motor skills
Key Facts
➤ Prevalence: Dysmetria is most commonly observed in people with cerebellar injuries, stroke, multiple sclerosis, or other neurological disorders.
➤ Age affected: Adults are more frequently diagnosed, but children with developmental cerebellar issues can also experience it.
➤ Gender: Both males and females are equally affected.
➤ Impact: Can lead to difficulties in walking, writing, eating, and other precision tasks, affecting independence and confidence.
What is Dysmetria?
Dysmetria refers to a lack of coordination in voluntary movements, where the brain cannot accurately judge the force, speed, or distance required to perform a task. It is a hallmark symptom of cerebellar disorders, where fine motor control is disrupted.
Highlights:
➤ Overshooting (hypermetria): Reaching beyond the intended target
➤ Undershooting (hypometria): Failing to reach the intended target
➤ Difficulty with repetitive movements: Movements may become increasingly inaccurate
What Symptoms Are Related to Dysmetria?
➤ Unsteady gait: Difficulty walking in a straight line
➤ Poor hand-eye coordination: Trouble writing, picking up objects, or buttoning clothes
➤ Tremors during movement: Intention tremors that appear when reaching for objects
➤ Difficulty with rapid alternating movements: Known as dysdiadochokinesia
➤ Frequent mistakes in reaching or grasping objects: Causing spills or dropped items
➤ Balance issues: Increased risk of falls due to misjudged steps
What Causes / Possible Causes
➤ Cerebellar injury: Stroke, trauma, or tumors affecting the cerebellum
➤ Neurodegenerative diseases: Multiple sclerosis, spinocerebellar ataxia
➤ Vitamin deficiencies: Severe vitamin B12 deficiency can impair coordination
➤ Toxins or medications: Alcohol, certain chemotherapeutic agents, or anti-seizure drugs may contribute
➤ Genetic disorders: Some hereditary ataxias result in dysmetria
➤ Peripheral neuropathy: Rarely, peripheral nerve damage can exacerbate coordination issues
Highlights:
➣ Dysmetria is almost always a sign of underlying neurological dysfunction
➣ Identifying the cause is critical for effective management and rehabilitation
When Should I See My Doctor?
➤ Persistent coordination problems: Difficulty performing daily tasks over time
➤ Sudden onset: Could indicate stroke or acute cerebellar injury
➤ Progressive worsening: Suggests a neurodegenerative disorder
➤ Associated symptoms: Tremors, slurred speech, or balance problems
➤ Impact on independence: Interference with daily life activities
Highlights:
➣ Early consultation with a neurologist is essential for diagnosis and treatment planning
➣ In Korea, advanced neurological assessments, including MRI and movement analysis, are available
Care and Treatment
➤ Physical therapy: Exercises to improve balance, coordination, and strength
➤ Occupational therapy: Focus on fine motor skills, adaptive techniques, and daily living activities
➤ Medications: Address underlying conditions such as multiple sclerosis or vitamin deficiencies
➤ Assistive devices: Canes, walkers, or special utensils to improve safety and independence
➤ Home adjustments: Reducing fall hazards and creating supportive environments
➤ Lifestyle modifications: Avoid alcohol or neurotoxic substances, maintain proper nutrition
Highlights:
➣ Rehabilitation is highly individualized and requires consistent effort
➣ Combining physical and occupational therapy often produces the best outcomes
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Treatments:
➤ Neurology clinics: Provide detailed assessment, imaging, and cause-specific therapy
➤ Medication management: To treat underlying neurological conditions or deficiencies
➤ Pain and spasticity management: For associated muscle issues
Advanced Procedures:
➤ Robot-assisted therapy or virtual reality rehabilitation: Enhance motor learning and coordination
➤ Cerebellar stimulation or neuromodulation: Experimental therapies in specialized centers
➤ Integrated rehabilitation programs: Multidisciplinary approach including physiotherapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy if needed
Rehabilitation & Follow-Up Care:
➤ Regular follow-ups ensure progress monitoring and therapy adjustments
➤ Patient education on safety, home exercises, and adaptive strategies reduces fall risk
➤ Korean clinics provide holistic care, combining neurology, rehabilitation, and counseling
Highlights:
➣ Advanced Korean clinics specialize in personalized, technology-assisted rehabilitation
➣ Early and consistent intervention improves coordination and quality of life