Overview
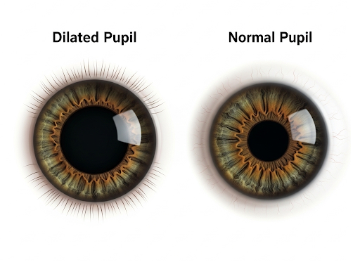
Dilated pupils (mydriasis) occur when the black part of the eye (pupil) becomes larger than normal, often due to changes in light, emotional state, medications, or underlying medical conditions. While pupil dilation is a normal reaction in the dark, persistent or unequal dilation may indicate a serious health problem such as neurological disorders, eye injuries, or drug effects.
In Korea, advanced ophthalmology and neurology clinics provide comprehensive evaluation and treatment for mydriasis, using modern diagnostic tools and specialized care.
Key Facts
Highlights:
➡️ Mydriasis = abnormally enlarged pupils.
➡️ Can be temporary (light changes, emotions, medications).
➡️ May signal eye trauma, brain injury, or nerve damage.
➡️ Certain drugs (e.g., stimulants, antidepressants, eye drops) cause dilation.
➡️ In Korea, specialized eye and neurological clinics offer advanced care.
What is Dilated Pupils (Mydriasis)?
Mydriasis refers to the persistent enlargement of the pupils beyond normal size, unrelated to light changes. Normally, pupils dilate in the dark and constrict in bright light, but abnormal dilation may point to serious neurological or ocular issues.
Key Features:
- Pupils appear larger than normal
- May affect one eye (unilateral) or both (bilateral)
- Can be constant or occur suddenly
What Symptoms are Related to Dilated Pupils?
People with mydriasis may also experience:
- Blurred or double vision
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Headache or eye pain
- Difficulty focusing
- Unequal pupils (anisocoria)
- Confusion or dizziness (if neurological cause)
Highlights:
➡️ Mydriasis is sometimes a medical emergency.
➡️ Can be linked to eye injury, stroke, or drug overdose.
What Causes / Possible Causes?
Highlights:
➡️ Normal causes: low light, emotional arousal, excitement.
➡️ Medications: antidepressants, decongestants, stimulants, antihistamines, anesthetics, or eye drops.
➡️ Drug use: cocaine, amphetamines, LSD, or ecstasy.
➡️ Neurological conditions: brain injury, stroke, intracranial bleeding, tumors.
➡️ Eye trauma or surgery affecting the iris or optic nerve.
➡️ Nerve damage (oculomotor nerve palsy).
When Should I See My Doctor?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
➡️ Sudden or persistent dilation not related to light changes.
➡️ Dilated pupils with headache, confusion, or dizziness.
➡️ Unequal pupil size (anisocoria).
➡️ After head injury or eye trauma.
➡️ Sudden vision changes (blurred or double vision).
Care and Treatment
Treatment depends on the underlying cause.
Highlights:
➡️ Emergency care for trauma, stroke, or drug overdose.
➡️ Medication review (adjusting or discontinuing drugs causing dilation).
➡️ Neurological evaluation for nerve or brain conditions.
➡️ Protective eyewear for light sensitivity.
➡️ Surgical or therapeutic interventions if related to structural eye damage.
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea offers advanced diagnostic and treatment options for mydriasis through specialized hospitals.
Highlights:
➡️ Ophthalmology clinics with modern imaging (OCT, fundus exams).
➡️ Neurology and neurosurgery centers for brain-related causes.
➡️ Emergency care units for trauma or stroke-related dilation.
➡️ Advanced drug toxicity management in specialized hospitals.
➡️ Integrated care with eye doctors, neurologists, and rehabilitation specialists.
➡️ International medical centers assist foreign patients with urgent and chronic eye/neurological conditions.