Overview
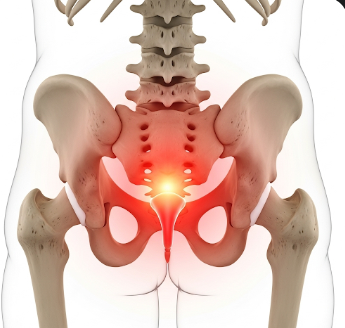
Coccyx pain, also known as coccydynia, is discomfort or pain in the tailbone area (coccyx) at the bottom of the spine. It can range from mild irritation to severe, chronic pain that affects sitting, standing, and daily activities.
In South Korea, orthopedic clinics and pain management centers offer comprehensive evaluation and treatment for coccyx pain, combining diagnostic imaging, physical therapy, medications, and minimally invasive procedures to improve quality of life.
Key Facts
Highlights:
➡️ Coccyx pain is more common in women due to anatomical differences in the pelvis.
➡️ Pain is usually worsened by sitting for prolonged periods, sudden movements, or pressure on the tailbone.
➡️ Causes include trauma, repetitive strain, degenerative changes, or idiopathic (unknown) origins.
➡️ Chronic coccyx pain can significantly impact daily life, work, and mobility.
➡️ South Korea provides state-of-the-art orthopedic and pain management care to relieve symptoms and treat underlying causes.
What is Coccyx Pain?
Coccyx pain is localized discomfort in the tailbone region, often described as aching, sharp, or throbbing.
Key characteristics:
- Location: At the bottom of the spine, above the anus
- Type of Pain: Can be sharp, stabbing, or dull ache
- Duration: Acute (short-term) or chronic (lasting months or years)
- Triggers: Sitting on hard surfaces, leaning back, childbirth, or trauma
Coccydynia may be mechanical, post-traumatic, or related to underlying spinal or pelvic conditions.
What Symptoms are Related to Coccyx Pain?
Symptoms commonly accompanying coccyx pain include:
- Pain while sitting or rising from a chair
- Tenderness when pressing the tailbone
- Pain during bowel movements in severe cases
- Radiating discomfort to the lower back, hips, or pelvis
- Swelling or bruising if caused by trauma
Highlights:
➡️ Pain may increase with prolonged sitting or physical activity.
➡️ Chronic cases may lead to sleep disturbances or difficulty performing daily tasks.
➡️ Early intervention helps prevent worsening and reduces the risk of chronic pain development.
What Causes / Possible Causes of Coccyx Pain?
Highlights:
➡️ Trauma: Falls, accidents, or direct blows to the tailbone.
➡️ Childbirth: Pressure on the coccyx during vaginal delivery may cause bruising or dislocation.
➡️ Repetitive Strain: Long periods of cycling, rowing, or sitting on hard surfaces.
➡️ Degenerative Changes: Arthritis or disc degeneration affecting the coccyx or sacrococcygeal joint.
➡️ Infections or Tumors: Rare causes including pilonidal cysts or tumors near the tailbone.
➡️ Idiopathic: Some cases have no identifiable cause, yet still cause chronic discomfort.
➡️ Mechanism: Pain arises from inflammation, ligament or muscle strain, or abnormal movement of the coccyx.
When Should I See My Doctor?
Highlights:
➡️ If pain persists for more than a few weeks despite home remedies.
➡️ If accompanied by swelling, redness, or discharge, which may indicate infection.
➡️ After trauma or falls to rule out fractures or dislocations.
➡️ If severe pain interferes with sitting, walking, or daily activities, medical evaluation is necessary.
➡️ Early consultation ensures accurate diagnosis, targeted treatment, and prevention of chronic pain.
Care and Treatment
Treatment focuses on pain relief, improving mobility, and addressing underlying causes:
Highlights:
➡️ Lifestyle and Ergonomic Measures:
- Use of cushions or donut pillows to relieve pressure
- Avoid prolonged sitting on hard surfaces
- Adjust posture and seating ergonomics
➡️ Medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain and inflammation
- Muscle relaxants if muscle spasm contributes to pain
- Local anesthetic injections for severe cases
➡️ Physical Therapy:
- Stretching and strengthening exercises for pelvic floor and lower back muscles
- Manual therapy or massage to relieve muscle tension
➡️ Minimally Invasive Procedures:
- Corticosteroid injections at the coccyx for persistent inflammation
- Nerve blocks for chronic pain
➡️ Surgery: Rarely, coccygectomy (removal of the coccyx) is considered for severe, refractory cases.
➡️ Monitoring: Follow-up ensures symptom improvement and prevention of recurrence.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides advanced care for coccyx pain, including:
Highlights:
➡️ Orthopedic Clinics: Comprehensive evaluation using X-rays, MRI, and CT scans.
➡️ Pain Management Centers: Specialized injections, nerve blocks, and multidisciplinary care.
➡️ Physical Therapy: Tailored exercise programs to relieve coccyx and pelvic floor tension.
➡️ Minimally Invasive Interventions: Image-guided injections and localized therapies for chronic pain.
➡️ Multidisciplinary Approach: Collaboration among orthopedists, physiotherapists, and pain specialists.
➡️ Medical Tourism Support: Multilingual consultations, diagnostics, and personalized treatment plans for international patients.