Overview
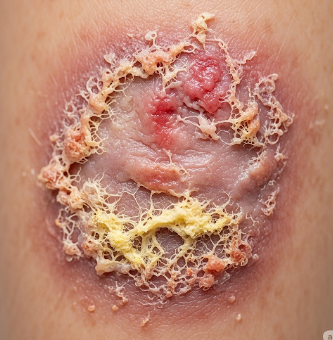
Chronic wounds are injuries to the skin or underlying tissues that fail to heal within a normal timeframe, typically persisting for more than 4–6 weeks. These wounds can result from vascular insufficiency, diabetes, infections, or pressure injuries, and pose a significant risk of complications such as infection, tissue damage, and reduced mobility. In Korea, advanced medical facilities and wound care centers provide state-of-the-art diagnostics, specialized dressings, surgical interventions, and rehabilitation programs to manage chronic wounds effectively, promoting faster healing and preventing recurrence.
Key Facts
▶ Prevalence: Common among older adults, diabetic patients, and individuals with poor circulation.
▶ Causes: Diabetes, venous or arterial insufficiency, pressure injuries, trauma, or infections.
▶ Associated Symptoms: Non-healing sores, redness, swelling, discharge, and pain.
▶ Treatment Options in Korea: Advanced wound care, surgical management, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, and infection control.
▶ Complications: Infection, cellulitis, gangrene, delayed healing, or amputation in severe cases.
What is a Chronic Wound?
A chronic wound is defined as a wound that does not progress through the normal healing stages—hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling—within a standard healing period.
▶ Diabetic Ulcers: Commonly affect the feet due to neuropathy and poor circulation.
▶ Venous Leg Ulcers: Occur due to poor venous return, often on the lower legs.
▶ Arterial Ulcers: Result from reduced blood flow due to peripheral artery disease.
▶ Pressure Injuries (Bedsores): Develop over bony prominences due to prolonged pressure, immobility, or friction.
▶ Infected Wounds: Chronic infection can delay healing and increase tissue damage.
Note: Chronic wounds require specialized management to prevent severe complications and restore skin integrity.
What Symptoms Are Related to Chronic Wounds?
▶ Non-Healing Skin Lesion: Persistent open sore or ulcer lasting weeks or months.
▶ Pain or Discomfort: Varies from mild tenderness to severe pain depending on depth and infection.
▶ Redness or Swelling: Indicates inflammation or potential infection.
▶ Discharge or Pus: May have foul odor, especially in infected wounds.
▶ Itching or Burning: Often accompanies healing attempts or infection.
▶ Skin Discoloration: Surrounding skin may appear darkened or unhealthy.
▶ Delayed Healing: No significant improvement over weeks despite care.
▶ Mobility Issues: Painful or large wounds may limit movement or daily activities.
What Causes / Possible Causes
Chronic wounds develop due to impaired healing mechanisms, poor circulation, or repeated trauma:
▶ Diabetes Mellitus: High blood sugar impairs nerve function and wound healing.
▶ Venous Insufficiency: Poor venous return leads to edema and skin breakdown.
▶ Arterial Insufficiency: Reduced blood flow causes tissue ischemia and necrosis.
▶ Pressure Injuries: Prolonged pressure on bony areas in immobile patients.
▶ Infections: Bacterial, fungal, or mixed infections delaying wound closure.
▶ Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of protein, vitamins, or minerals affecting tissue repair.
▶ Chronic Inflammation: Autoimmune conditions or persistent inflammation impair healing.
▶ Repeated Trauma: Continuous friction or injury preventing wound closure.
Note: Timely identification of underlying causes is essential for effective management and prevention of recurrence.
When Should I See a Doctor?
▶ Non-Healing Wound: Lasting more than 4 weeks without improvement.
▶ Severe Pain or Discomfort: Uncontrolled pain affecting mobility or sleep.
▶ Signs of Infection: Redness, swelling, warmth, pus, or foul odor.
▶ Fever or Malaise: Suggests systemic infection.
▶ Underlying Conditions: Diabetes, vascular disease, or immune disorders complicating healing.
▶ Delayed Healing Despite Care: Home treatments failing to improve wound.
▶ Rapidly Worsening Wound: Enlargement, tissue necrosis, or spreading infection.
▶ Mobility Impairment: Wound restricting movement or daily activities.
Tip: In Korea, specialized wound care centers provide rapid evaluation and tailored treatment plans to prevent severe complications.
Care and Treatment
Effective management focuses on promoting healing, controlling infection, and addressing underlying causes:
▶ Wound Cleaning: Regular debridement and antiseptic care to remove dead tissue and bacteria.
▶ Advanced Dressings: Hydrocolloid, foam, alginate, or antimicrobial dressings to maintain a moist healing environment.
▶ Pain Management: Analgesics or local treatments to reduce discomfort.
▶ Infection Control: Topical or systemic antibiotics for infected wounds.
▶ Offloading Pressure: Special cushions, mattresses, or footwear to prevent further tissue damage.
▶ Nutritional Support: Adequate protein, vitamins, and minerals to support tissue repair.
▶ Lifestyle Modifications: Smoking cessation, glycemic control, and mobility exercises.
▶ Monitoring: Regular wound assessment to track healing and adjust treatment.
Treatment Options in Korea
Medical Evaluation:
▶ Specialized Wound Clinics: Multidisciplinary assessment including dermatology, vascular medicine, and endocrinology.
▶ Laboratory Tests: Blood sugar, infection markers, and nutritional assessment.
▶ Imaging: Doppler, X-ray, or MRI to evaluate blood flow and tissue involvement.
▶ Microbial Testing: Culture and sensitivity testing for targeted antibiotic therapy.
Advanced Therapies:
▶ Surgical Intervention: Debridement, skin grafting, or flap surgery for large or non-healing wounds.
▶ Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Enhances oxygen supply to tissues, promoting healing.
▶ Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT): Uses vacuum-assisted closure to improve healing.
▶ Laser or Ultrasound Therapy: Stimulates tissue repair and reduces infection risk.
Rehabilitation & Support:
▶ Patient Education: Guidance on wound care, nutrition, and preventive strategies.
▶ Follow-Up Care: Regular monitoring for healing progress and prevention of recurrence.
▶ Integrated Care: Korean hospitals offer coordinated care combining dermatology, surgery, endocrinology, and rehabilitation services.
Outcome: With timely evaluation and advanced treatment in Korea, chronic wounds can heal effectively, pain is reduced, and long-term complications such as infection, tissue loss, or amputation are minimized.