Overview
Changes in bowel habits refer to alterations in the frequency, consistency, or appearance of stools, which may signal digestive disorders, infections, or systemic illnesses. While occasional changes can be benign, persistent or significant alterations require medical evaluation to identify underlying causes.
In South Korea, gastroenterology clinics provide comprehensive diagnostic services, including stool tests, endoscopy, colonoscopy, and imaging, to evaluate abnormal bowel patterns and guide effective treatment.
Key Facts
Highlights:
➡️ Bowel habit changes can involve constipation, diarrhea, alternating patterns, or unusual stool appearance.
➡️ Persistent alterations over several weeks should prompt medical evaluation.
➡️ Common causes include dietary changes, infections, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and colorectal cancer.
➡️ Red flags include blood in stool, unintentional weight loss, abdominal pain, and fatigue.
➡️ South Korea offers advanced gastroenterology diagnostics, including colonoscopy, imaging, and lab testing for early detection and management.
What are Changes in Bowel Habits?
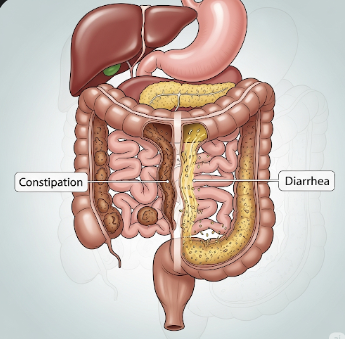
Changes in bowel habits are any persistent alterations in stool frequency, consistency, color, or ease of passage.
Key characteristics:
- Constipation: Infrequent, hard, or difficult-to-pass stools
- Diarrhea: Loose or watery stools, sometimes urgent or frequent
- Alternating patterns: Switching between constipation and diarrhea
- Blood or mucus in stool: May indicate inflammation, infection, or malignancy
- Abnormal stool color: Black, red, or pale stools can indicate gastrointestinal bleeding or liver/bile disorders
These changes can be acute (short-term) or chronic (lasting several weeks or more), with chronic changes warranting careful evaluation.
What Symptoms are Related to Changes in Bowel Habits?
Symptoms often accompanying bowel habit changes include:
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Bloating or distension
- Urgency or incomplete evacuation
- Nausea or vomiting in some cases
- Fatigue or weakness due to blood loss or malabsorption
- Weight changes (loss or gain depending on underlying cause)
Highlights:
➡️ Persistent changes in bowel habits may signal serious underlying conditions like colorectal cancer or inflammatory bowel disease.
➡️ Accompanying symptoms such as blood, mucus, or pain increase the urgency of evaluation.
➡️ Even subtle changes should not be ignored if they persist over time.
What Causes / Possible Causes of Changes in Bowel Habits?
Highlights:
➡️ Dietary Changes: Sudden increases or decreases in fiber, fluids, or processed foods.
➡️ Infections: Bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections can cause diarrhea or altered stool patterns.
➡️ Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Chronic functional disorder causing alternating diarrhea and constipation, abdominal pain, and bloating.
➡️ Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, characterized by chronic inflammation and stool changes.
➡️ Medications: Antibiotics, laxatives, or certain pain medications can affect bowel habits.
➡️ Endocrine or Metabolic Disorders: Diabetes, thyroid disease, or malabsorption syndromes.
➡️ Colorectal Cancer or Polyps: Persistent changes, especially with blood in stool or unexplained weight loss.
➡️ Mechanism: Altered bowel habits result from changes in motility, absorption, secretion, or inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
When Should I See My Doctor?
Highlights:
➡️ Persistent changes in bowel habits lasting more than two to three weeks.
➡️ Presence of blood, mucus, or black stools.
➡️ Unexplained abdominal pain, bloating, or weight loss.
➡️ Family history of colorectal cancer or inflammatory bowel disease.
➡️ Chronic diarrhea or constipation affecting quality of life.
➡️ Early evaluation allows for diagnosis through stool tests, imaging, colonoscopy, or lab tests, ensuring timely treatment.
Care and Treatment
Management depends on the underlying cause of bowel habit changes:
Highlights:
➡️ Dietary and Lifestyle Modifications:
- High-fiber diet for constipation
- Adequate hydration
- Avoidance of irritants like excessive caffeine or alcohol
➡️ Medications:
- Laxatives or stool softeners for constipation
- Anti-diarrheal medications for acute episodes
- Antibiotics or antiparasitic treatment for infections
- Anti-inflammatory drugs or immunosuppressants for IBD
➡️ Behavioral Interventions:
- Regular bowel routines
- Stress management for IBS-related symptoms
➡️ Surgical Interventions: Required in cases of colorectal cancer, severe IBD complications, or structural bowel abnormalities.
➡️ Monitoring and Follow-Up: Regular evaluation ensures resolution of symptoms, prevention of complications, and early detection of serious conditions.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides comprehensive care for patients with changes in bowel habits:
Highlights:
➡️ Gastroenterology Clinics: Detailed assessment, stool testing, colonoscopy, and endoscopic treatment.
➡️ Advanced Imaging: CT colonography, MRI, and ultrasound for structural evaluation.
➡️ Specialized IBD Centers: Chronic disease management for Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
➡️ Nutritional Counseling: Diet modification and guidance for IBS, constipation, and malabsorption syndromes.
➡️ Multidisciplinary Approach: Collaboration among gastroenterologists, dietitians, surgeons, and psychologists for holistic management.
➡️ Medical Tourism Support: Multilingual consultations, diagnostic evaluation, and treatment for international patients.