Overview
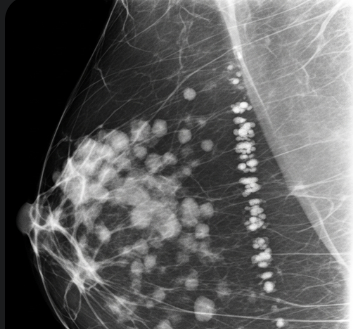
Breast calcifications are tiny deposits of calcium in the breast tissue that appear as white spots or flecks on a mammogram. They are common in women over 40 and are usually benign, though certain patterns can indicate early breast cancer or precancerous changes.
In South Korea, breast imaging centers and specialized oncology clinics provide detailed evaluation, monitoring, and management of breast calcifications, ensuring early detection and peace of mind for patients.
Key Facts
Highlights:
➡️ Breast calcifications are often discovered incidentally during routine mammography.
➡️ They can be benign or suspicious, depending on size, shape, and distribution.
➡️ Most breast calcifications are harmless, but some require biopsy to rule out malignancy.
➡️ Patterns that are clustered, irregular, or linear may suggest the need for further investigation.
➡️ South Korea provides advanced mammography, ultrasound, and biopsy services for accurate diagnosis and management.
What are Breast Calcifications?
Breast calcifications are small calcium deposits within the breast tissue that show up as white spots on imaging tests.
Characteristics include:
- Size: Typically 0.1–1 mm in diameter
- Shape: Round, oval, linear, or irregular
- Distribution: Scattered, clustered, or segmental patterns
- Detection: Usually found during mammograms, sometimes with ultrasound or MRI for further evaluation
- Clinical Significance: Most are benign, but certain suspicious patterns may indicate ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) or early-stage breast cancer
What Symptoms are Related to Breast Calcifications?
Most breast calcifications do not cause symptoms and are discovered incidentally. However, associated symptoms may include:
- None in most cases
- Rarely, palpable lumps if associated with a mass
- Breast pain or tenderness is uncommon and usually unrelated
- Changes in breast skin or nipple may indicate a more serious underlying problem requiring evaluation
Highlights:
➡️ Breast calcifications are mostly asymptomatic.
➡️ Any palpable lump, nipple discharge, or skin changes warrant immediate medical assessment.
What Causes / Possible Causes of Breast Calcifications?
Highlights:
➡️ Benign Causes:
- Age-related changes
- Fibrocystic breast changes
- Past injuries or trauma
- Infections or inflammation
➡️ Hormonal Influence: Calcifications can appear due to changes during menopause or hormone therapy.
➡️ Cancerous Causes: Certain patterns, such as fine, linear, or branching calcifications, may indicate ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) or early breast cancer.
➡️ Other Causes:
- Previous radiation therapy
- Surgical scars or biopsies
➡️ Mechanism: Calcium deposits form as a result of tissue damage, cell turnover, or abnormal growth, appearing as bright spots on mammography.
When Should I See My Doctor?
Highlights:
➡️ If mammography shows suspicious calcification patterns, further evaluation is required.
➡️ If you notice new breast lumps, nipple discharge, or skin changes.
➡️ For routine follow-up if prior imaging indicated calcifications.
➡️ Early consultation ensures accurate diagnosis, ruling out malignancy and guiding appropriate monitoring or treatment.
➡️ Prompt evaluation reduces anxiety and enables timely intervention if cancer is present.
Care and Treatment
Management of breast calcifications focuses on monitoring and addressing suspicious findings:
Highlights:
➡️ Regular Mammography: Follow-up imaging every 6–12 months for benign calcifications.
➡️ Ultrasound or MRI: Used for further evaluation if mammography results are inconclusive.
➡️ Biopsy: Core needle or stereotactic biopsy for suspicious calcifications to rule out cancer.
➡️ Lifestyle and Monitoring: Maintaining breast health through regular self-exams and reporting changes promptly.
➡️ Patient Education: Understanding benign versus suspicious calcifications, imaging intervals, and signs that require immediate attention.
➡️ Reassurance: Most calcifications are non-cancerous and do not require treatment beyond monitoring.
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea provides advanced diagnostic and management options for breast calcifications:
Highlights:
➡️ Breast Imaging Centers: High-resolution digital mammography and tomosynthesis for early detection.
➡️ Ultrasound and MRI Services: Detailed assessment of calcification patterns.
➡️ Biopsy Services: Stereotactic or ultrasound-guided biopsies for suspicious findings.
➡️ Multidisciplinary Care: Collaboration among radiologists, oncologists, and breast surgeons for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
➡️ Patient Counseling: Guidance on monitoring, follow-up imaging schedules, and lifestyle modifications.
➡️ Advanced Screening Programs: Early detection programs for high-risk patients.
➡️ Medical Tourism Support: Multilingual consultations, diagnostic services, and follow-up care for international patients.